Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) – Construction, Working, and Applications
Construction, Working and Applications of BLDC (Brushless DC Motor)
Brushless DC motors (BLDCs) have been a much-focused area for numerous motor manufacturers as these motors are increasingly the preferred choice in many applications, especially in the field of motor control technology. BLDC motors offer several advantages over brushed DC motors, including the ability to operate at high speeds, high efficiency, and better heat dissipation.
They are essential components of modern drive technology, commonly used in actuating drives, machine tools, electric propulsion, robotics, computer peripherals, and even electrical power generation. With the development of sensorless technology and digital control, these electric motors have become highly effective in terms of total system cost, size, and reliability.
- Related Post: Difference Between Brushed and Brushless Motor
What is a Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)?
A brushless DC motor (known as BLDC) is a permanent magnet synchronous electric motor which is driven by direct current (DC) electricity and it accomplishes electronically controlled commutation system (commutation is the process of producing rotational torque in the motor by changing phase currents through it at appropriate times) instead of a mechanically commutation system. BLDC motors are also referred as trapezoidal permanent magnet motors.
Unlike conventional brushed type DC motor, wherein the brushes make the mechanical contact with commutator on the rotor so as to form an electric path between a DC electric source and rotor armature windings, BLDC motor employs electrical commutation with permanent magnet rotor and a stator with a sequence of coils. In this motor, permanent magnet (or field poles) rotates and current carrying conductors are fixed.
The armature coils are switched electronically by transistors or silicon controlled rectifiers at the correct rotor position in such a way that armature field is in space quadrature with the rotor field poles. Hence the force acting on the rotor causes it to rotate. Hall sensors or rotary encoders are most commonly used to sense the position of the rotor and are positioned around the stator. The rotor position feedback from the sensor helps to determine when to switch the armature current.
This electronic commutation arrangement eliminates the commutator arrangement and brushes in a DC motor and hence more reliable and less noisy operation is achieved. Due to the absence of brushes BLDC motors are capable to run at high speeds. The efficiency of BLDC motors is typically 85 to 90 percent, whereas as brushed type DC motors are 75 to 80 percent efficient. There are wide varieties of BLDC motors available ranging from small power range to fractional horsepower, integral horsepower and large power ranges.
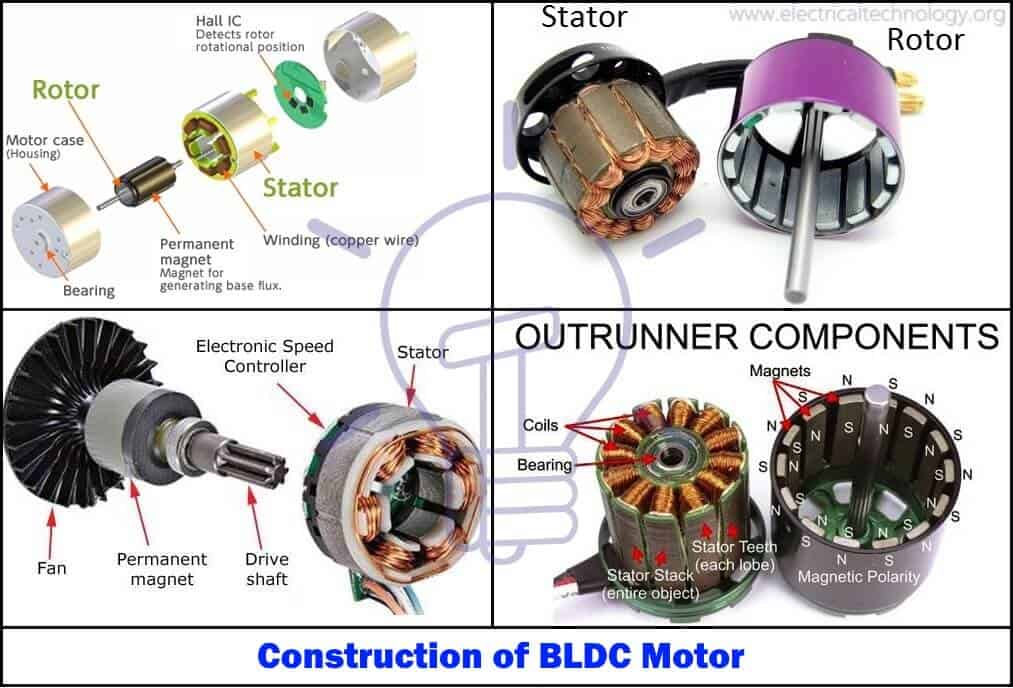
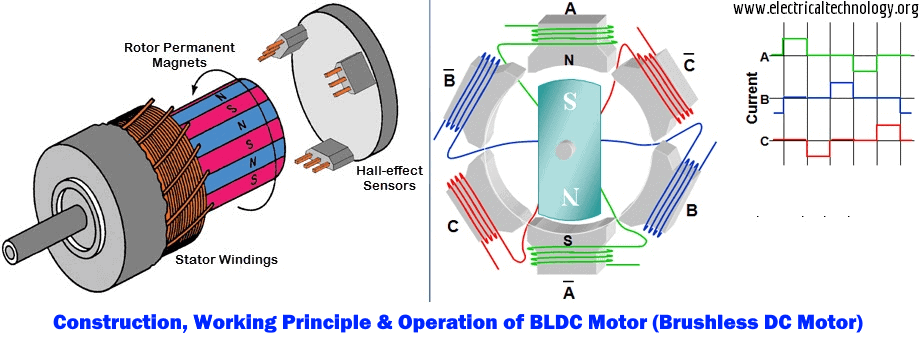
Construction of BLDC Motor
BLDC motors can be constructed in different physical configurations. Depending on the stator windings, these can be configured as single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase motors. However, three-phase BLDC motors with permanent magnet rotor are most commonly used.
The construction of this motor has many similarities of three phase induction motor as well as conventional DC motor. This motor has stator and rotor parts as like all other motors.
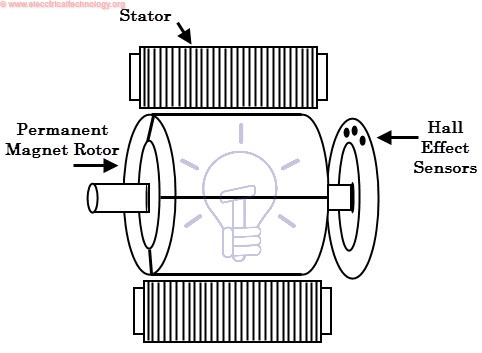
Stator
Stator of a BLDC motor made up of stacked steel laminations to carry the windings. These windings are placed in slots which are axially cut along the inner periphery of the stator. These windings can be arranged in either star or delta. However, most BLDC motors have three phase star connected stator.
Each winding is constructed with numerous interconnected coils, where one or more coils are placed in each slot. In order to form an even number of poles, each of these windings is distributed over the stator periphery.
The stator must be chosen with the correct rating of the voltage depending on the power supply capability. For robotics, automotive and small actuating applications, 48 V or less voltage BLDC motors are preferred. For industrial applications and automation systems, 100 V or higher rating motors are used.
Rotor
BLDC motor incorporates a permanent magnet in the rotor. The number of poles in the rotor can vary from 2 to 8 pole pairs with alternate south and north poles depending on the application requirement. In order to achieve maximum torque in the motor, the flux density of the material should be high. A proper magnetic material for the rotor is needed to produce required magnetic field density.
Ferrite magnets are inexpensive, however they have a low flux density for a given volume. Rare earth alloy magnets are commonly used for new designs. Some of these alloys are Samarium Cobalt (SmCo), Neodymium (Nd), and Ferrite and Boron (NdFeB). The rotor can be constructed with different core configurations such as the circular core with permanent magnet on the periphery, circular core with rectangular magnets, etc.
Hall Sensors
Hall sensor provides the information to synchronize stator armature excitation with rotor position. Since the commutation of BLDC motor is controlled electronically, the stator windings should be energized in sequence in order to rotate the motor. Before energizing a particular stator winding, acknowledgment of rotor position is necessary. So the Hall Effect sensor embedded in stator senses the rotor position.
Most BLDC motors incorporate three Hall sensors which are embedded into the stator. Each sensor generates Low and High signals whenever the rotor poles pass near to it. The exact commutation sequence to the stator winding can be determined based on the combination of these three sensor’s response.
Working of Brushless DC Motor
BLDC motor works on the principle similar to that of a conventional DC motor, i.e., the Lorentz force law which states that whenever a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field it experiences a force. As a consequence of reaction force, the magnet will experience an equal and opposite force. In case BLDC motor, the current carrying conductor is stationary while the permanent magnet moves.
When the stator coils are electrically switched by a supply source, it becomes electromagnet and starts producing the uniform field in the air gap. Though the source of supply is DC, switching makes to generate an AC voltage waveform with trapezoidal shape. Due to the force of interaction between electromagnet stator and permanent magnet rotor, the rotor continues to rotate.
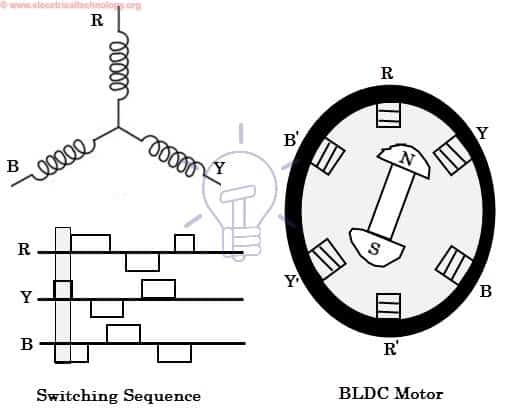
Consider the figure below in which motor stator is excited based on different switching states. With the switching of windings as High and Low signals, corresponding winding energized as North and South poles. The permanent magnet rotor with North and South poles align with stator poles causing motor to rotate.
Observe that motor produces torque because of the development of attraction forces (when North-South or South-North alignment) and repulsion forces (when North-North or South-South alignment). By this way motor moves in a clockwise direction.
Here, one might get a question that how we know which stator coil should be energized and when to do. This is because; the motor continuous rotation depends on the switching sequence around the coils. As discussed above that Hall sensors give shaft position feedback to the electronic controller unit.
Based on this signal from sensor, the controller decides particular coils to energize. Hall-effect sensors generate Low and High level signals whenever rotor poles pass near to it. These signals determine the position of the shaft.
Types of Brushless DC Motors
There are several types of BLDC motors, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements. Here are some common types:
- Inner Rotor BLDC Motors: In this type, the rotor is located at the center, and the stator surrounds it. This design offers good heat dissipation and is commonly used in high-speed applications.
- Outer Rotor BLDC Motors: Here, the rotor is located on the outside, surrounding the stator. This design provides higher torque at lower speeds and is often used in applications requiring high starting torque.
- Surface Mounted BLDC Motors: These motors have magnets mounted on the surface of the rotor, facing the stator. They are compact and offer high efficiency, making them suitable for various applications.
- Interior Permanent Magnet (IPM) BLDC Motors: These motors have magnets embedded within the rotor core, increasing magnetic flux and improving efficiency. They are often used in high-efficiency applications.
- Transverse Flux BLDC Motors: In this type, the magnetic flux flows parallel to the axis of rotation, offering high torque density and efficiency. They are suitable for applications requiring high torque in a compact size.
-
Fractional Horsepower BLDC Motors: These motors are smaller in size and are used in applications requiring lower power output, such as in home appliances and automotive systems.
Brushless DC Motor Drive
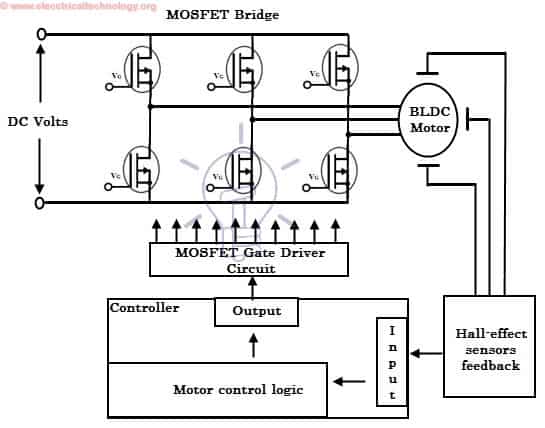
As described above that the electronic controller circuit energizes appropriate motor winding by turning transistor or other solid state switches to rotate the motor continuously. The figure below shows the simple BLDC motor drive circuit which consists of MOSFET bridge (also called as inverter bridge), electronic controller, hall effect sensor and BLDC motor.
Here, Hall-effect sensors are used for position and speed feedback. The electronic controller can be a microcontroller unit or microprocessor or DSP processor or FPGA unit or any other controller. This controller receives these signals, processes them and sends the control signals to the MOSFET driver circuit.
In addition to the switching for a rated speed of the motor, additional electronic circuitry changes the motor speed based on required application. These speed control units are generally implemented with PID controllers to have precise control. It is also possible to produce four-quadrant operation from the motor whilst maintaining good efficiency throughout the speed variations using modern drives.
Related Electrical Drives Articles
Advantages & Disadvantages of BLDC Motor
Advantages
BLDC motor has several advantages over conventional DC motors and some of these are
- It has no mechanical commutator and associated problems
- High efficiency due to the use of permanent magnet rotor
- High speed of operation even in loaded and unloaded conditions due to the absence of brushes that limits the speed
- Smaller motor geometry and lighter in weight than both brushed type DC and induction AC motors
- Long life as no inspection and maintenance is required for commutator system
- Higher dynamic response due to low inertia and carrying windings in the stator
- Less electromagnetic interference
- Quite operation (or low noise) due to absence of brushes
Disadvantages
- These motors are costly
- Electronic controller required control this motor is expensive
- Not much availability of many integrated electronic control solutions, especially for tiny BLDC motors
- Requires complex drive circuitry
- Need of additional sensors
Applications of Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) are used in a wide variety of applications, including varying loads, constant loads, and positioning applications in industrial control, automotive, aviation, automation systems, healthcare equipment, and more. Some specific applications of BLDC motors include:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): BLDC motors are used in electric and hybrid vehicles for propulsion, providing high efficiency and performance compared to traditional internal combustion engines.
- Industrial Automation: BLDC motors are used in robotics, CNC machines, belt driven systems, and other automated systems for precise motion control and high efficiency.
- Consumer Electronics: BLDC motors are used in appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, compressors, fans, pumps, blowers, and dryers for improved efficiency and reliability.
- Aerospace: BLDC motors are used in aircraft systems for actuation, such as in flight control surfaces, landing gear, and fuel pumps, due to their high power-to-weight ratio and reliability.
- Medical Devices: BLDC motors are used in medical equipment like surgical tools, pumps, and ventilators for precise control and reliability.
- Computer Peripherals: BLDC motors are used in hard disk drives (HDDs), optical disk drives (ODDs), and cooling fans for their reliability and efficiency.
- Renewable Energy: BLDC motors are used in wind turbines and solar tracking systems for their efficiency and ability to operate in harsh environments.
- Home Automation: BLDC motors are used in smart home devices like smart locks, curtains, and HVAC systems for their efficiency and quiet operation.
Related Posts
- Linear Induction Motor – Working Principle and Applications
- What is Motor Generator Set and How Does it Work?
- Motor Efficiency and How to improve it?
- Cable Size Calculation for LT & HT Motors
- What is Motor Starter? Types of Motor Starters and Motor Starting Methods
- Direct Online Starter – DOL Starter Wiring Diagram for Motors
- Difference Between Single Phase & Three Phase Induction Motor
- Why Motor rated in kW instead of kVA?
- Electrical Transformer – Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Alternator or Synchronous Generator: Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Induction Generator or Asynchronous Generator: Construction & Working
- Speed Control of DC Motor – Voltage, Rheostatic & Flux Control Methods
- Three Phase Motor Power & Control Wiring Diagrams
- Electric Motors Symbols
- Applications of Electric Motors











you are doing awonderful job promoting application oriented wisdom free of cost.
You’re great thank you
hi I’m mojibul islam from Bangladesh. I’ m interested in learning about RAC.pelase send me a electrical circuit diagram of 3 phase dc motor drive and explain type of rectifire is use in the drive.
I’m very thank full to you….
Thank you for a great article. It helped me a lot.
People like you inspire us to do great thing in electronics.
simple complete drive circuit for bldc motor
Yr information on bldc was very good thanks
Very good explanation indeed!