Power Distribution in Industries – All You Need to Know
Power Distribution in Industries – Everything You Need to Know
Today we are intended to take you to the industrial environment by giving the picture of how an electric power distributed in industries. In industries, electrical panels play a major role in distributing the power that houses various equipments such as bus bars, circuit breakers, meters, etc.
These panels are distributed over various sections of an industry in order to supply the power to individual installed systems and are connected through cable ducts. Let’s look on this concept in brief.
Structure of Power Distribution in Industries
In an industrial electric power system, electric power is supplied from either private utilities or public utilities, or both. The supplied voltage is in the range of 11KV, 33KV, 66KV or 132KV. These high voltages are stepped down to a low voltage using step-down transformers.
The voltages in the range of 440 volts or below are called as low tension systems. This stepped voltage is further supplied to various panels and equipments through a switchgear arrangement that consisting of electrical switches, circuit breakers, fuses, protection equipment, metering boards, etc.
The figure below shows a schematic diagram of the power distribution. This model scheme is mostly employed for large and medium scale industries. In some cases, sub-LT panels are not found; instead power is supplied directly from LT panels to SDBs depending upon the size of distribution area where the number of units (or sections) to be supplied is the major consideration.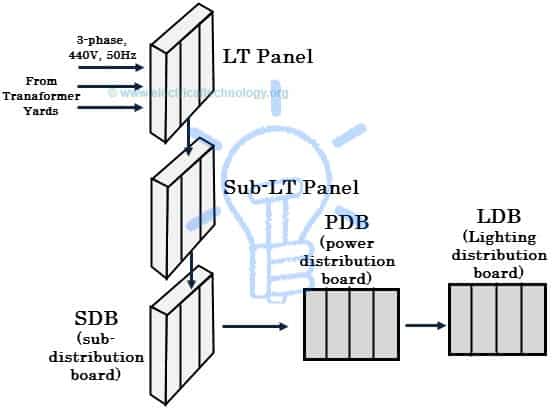
Various transformers supply is given to the LT panels, which acts as a main switching system for entire power distribution scheme and carries the total load demand. We will discuss the elements inside of the LT panels in brief later in this article. The output feeders of the LT panel are connected to sub-LT panels which are placed for a group of loads over a given section to supply the demand.
The sub-LT panel incomer is applied at SDB which are placed for supplying the power to loads that consists of a group of machineries such as electrical furnaces, hoists, etc. (that are connected to various PDBs).
PDBs acts like an actual power connection of load to source where individual machinery is connected directly to the supply. And part of the power from PDB is supplied to LDBs where it supplies the power to lighting equipment such as street lights (See simple Street light project here), lighting in the working area, plug boards etc.
All the panels in the distribution system are ground with a proper grounding & earthing to protect the appliances as well as operating personnel.
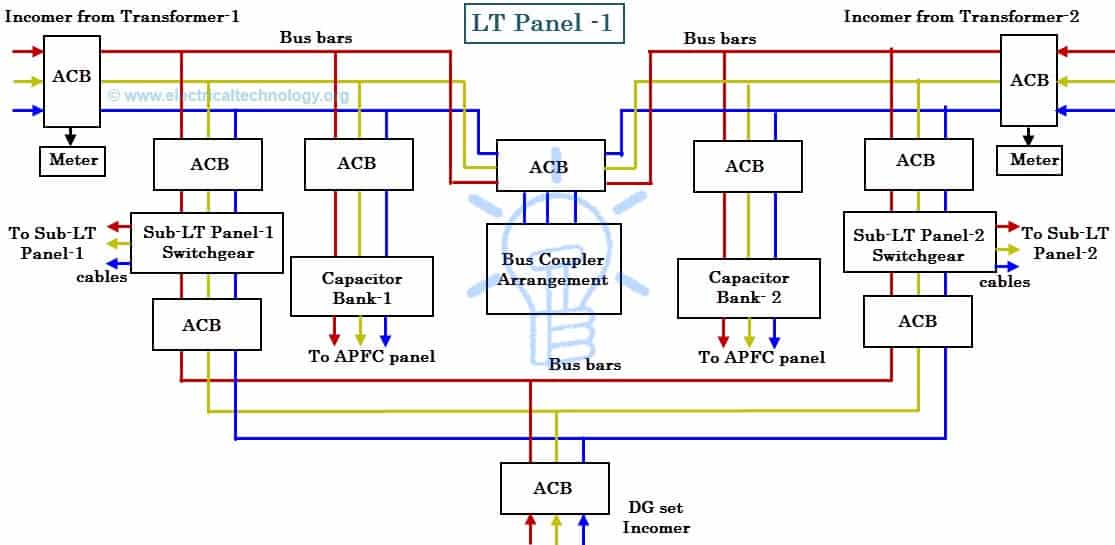
Low Tension (LT) Panel
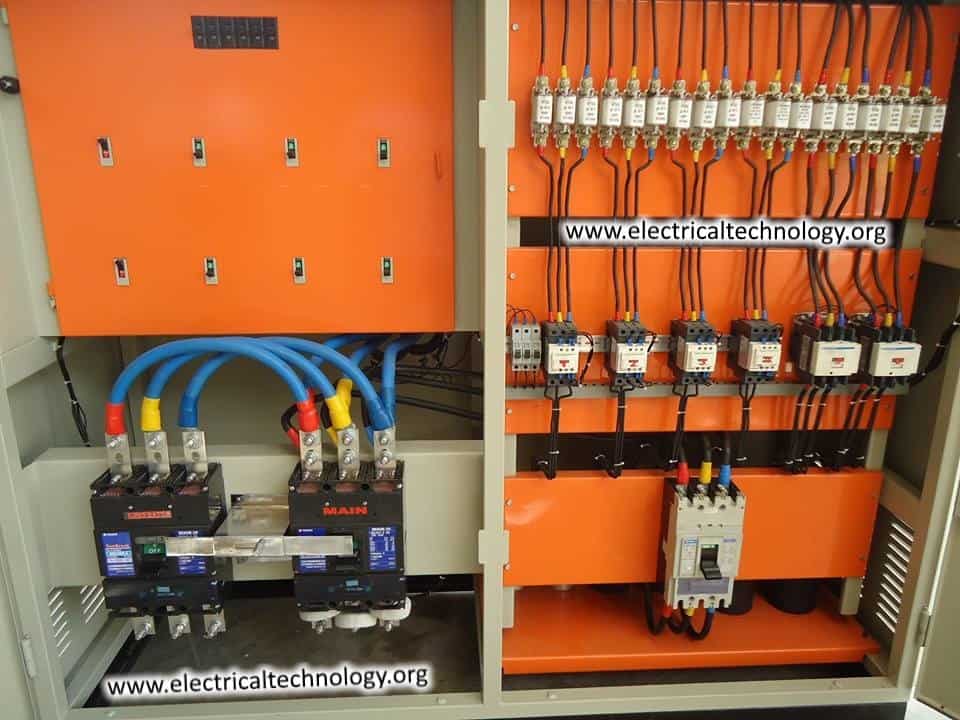

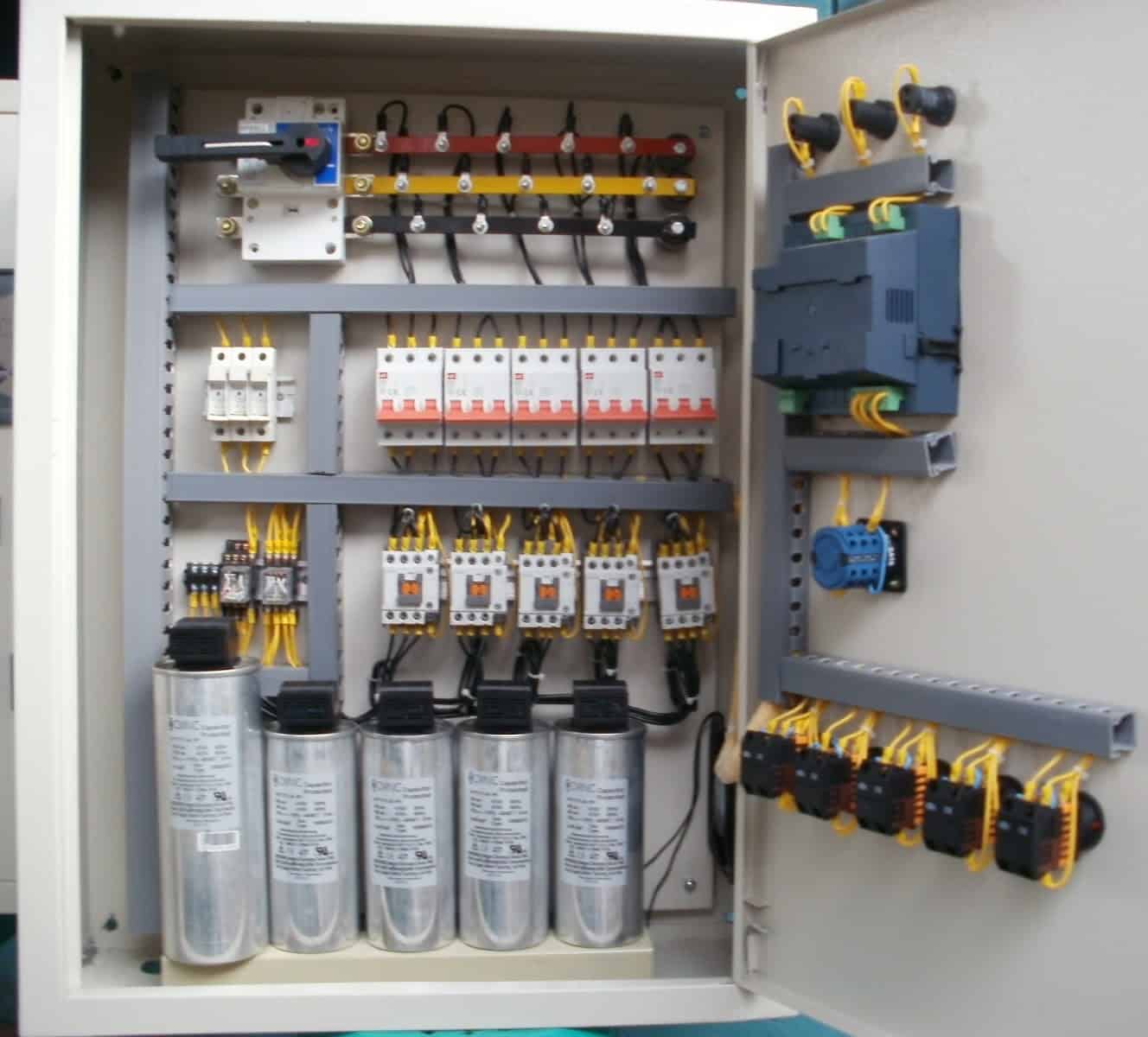
The switchgear arrangement on each distribution side is housed in metal-enclosed structures called as LT (low tension) panels. These LT panels are responsible for distributing the power to various sub LT panels by receiving it from the transformer. These are rated for 430 V, 3-phase, 50Hz three or four wire system.
It is a floor mounted free standing unit and it is totally closed and extensible type. Its design includes all provisions for safety of operation as well as for maintenance personnel.
The internal connection for the LT panel is shown in figure below.
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
It makes or breaks the circuit either manually or remotely controlled during normal operating condition and break the circuit during fault condition automatically. These can be 3/4 pole type with a rating decided by the load current (or breaking capacity) and can be either drawn out or fixed type.
ACBs (Air Circuit Breaker) consist of necessary bus bars to connect the terminals with bolted type neutral links. These are provided with microprocessor systems to enable protection systems like overload, earth fault and short circuits. ACB also gives the necessary indication and metering requirements with the use of CTs, lamps, ammeter, voltmeters, etc.
Bus Bar and Connections
Bus bars are made with high conductivity copper (in some cases, aluminum bus bars are used to reduce the cost). LT panel consists of a system of main horizontal bus bars and auxiliary vertical bus bars in bus bar alleys on which panel could be arranged with front access to connect cables.
The outgoing cables are connected to the bus bars either as a solid or flexible connection depends on the panel manufacturer. All bus bars are suitably insulated / sleeved in approved manner.
Bus bars collect the supply from transformer terminals and supply it to the various elements in the panel such as ACBs, capacitor bank switch gear, and other connected loads. The bus bars can be run at either top or bottom, or both sides of the panel, but mostly top side bus bars takes the transformer supply while bottom side bus bars take the supply from DG (Diesel Generator) set.
Bus Coupler
It couples one bus bar with other bus bar of different source (but the rating should be same) without creating any arcs or interruption to the supply system. In case of maintenance of other circuit breakers on the same panel this bus coupler diverts the supply source to the other. It is also a switchgear arrangement with ACB and provided with interlocking facility.
Capacitor Bank
It is a separate panel that consisting of bus bars, MCCBs, tuned reactors, capacitor units, contactors, metering equipment, and cables. It is also called as automatic power factor correction panel (APFC). This panel is connected to the LT panel with ACBs and other switchgear arrangements through cables.
The capacitors and reactors are of an indoor type with air cooled units. The capacitor banks are connected across the supply to improve the power factor o f the system. Capacitors are switched automatically (through programmable devices) or manually (by switches) depending on the amount of reactive power to be compensated.
Metering and indication
Voltmeters, ammeter and power factor meters in LT panel indicate various parameters and these are protected with MCBs. On all LT panels, indicating lamps (mostly LED lamps) are provided for each phase for indicating live or fault condition. Start and stop push buttons also provided on metering panel to give input commands such as turn ON supply and emergency stop.
Sub-LT Panels
These panels are similar to the LT panels, however rating of these panels is somewhat less than LT panels and also these are placed in a particular section of an industry (such as assembling section or dispatching section) instead near the transformer as in case of LT panel. These are acts as mains for various SDBs, because these panels distribute the power to the SDBs by receiving it from LT panels.
The internal circuitry is same as that of LT panel such as bus bars, capacitor bank connections, ACBs, metering panels (bus couplers may not be included in most cases).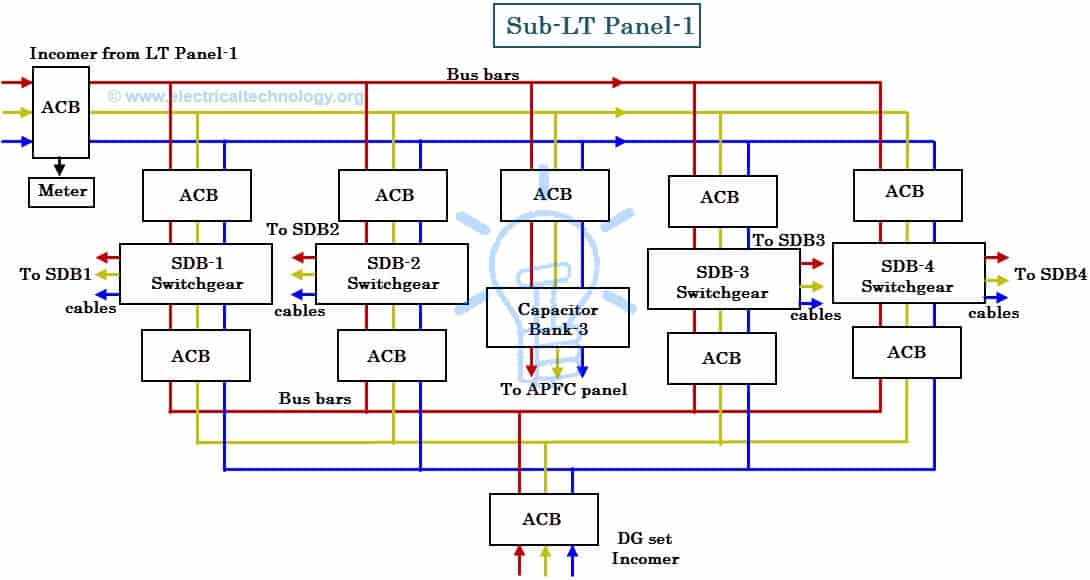
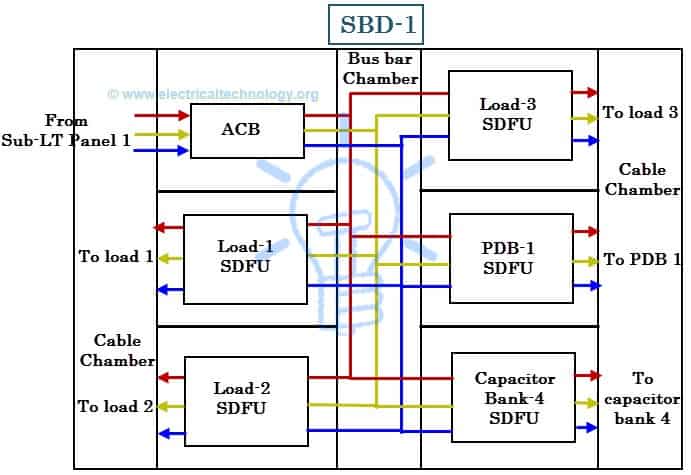
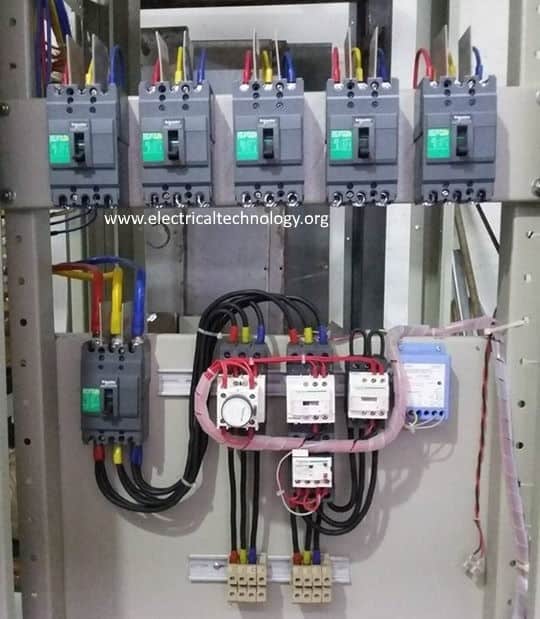
Sub-Distribution Boards
These are available in standardized and customized designs from various manufacturers. SDBs consist of bus bars (copper or aluminum) that receive power supply from either sub-LT panels or main LT panels and then distribute it to various heavy rated machineries (such as furnaces, chillers, water pumps, ovens, etc.) and PDBs (power distribution boards).
It receives the power (i.e., incomer) through ACB or MCCB and distributes through outgoing MCCBs or SDFUs (Switch-Disconnect-Fuses). The SDFUs consists of switches in series with fuse links (high breaking capacity HRC fuses) with mechanical structure for manual operation. These switching units are used for load switching, isolation and short circuit protection.

Some SDBs also consists of capacitor banks especially that (SDBs) are provided to supply heavy inductive loads in order to improve the power factor. SDBs use bus bars to enable connection of all the SDFUs and other devices inside of it through the bus bar chamber, also enables the outgoing connections though high capacity cables in the cable chamber.
Each load switching compartment is provided with permanent identification labels, indication lights and metering equipment (if necessary). The figure below shows the schematic diagram of an SDB.
Power Distribution Boards (PDBs)
These are designed to distribute the power to various machines and equipment, even in big building we can observe such arrangement of power distribution through PDBs. PDBs are built with short circuit as well as overload protection systems. These are fitted with different protective relays that can trip the different CBs (of high capacity) against various types of faults.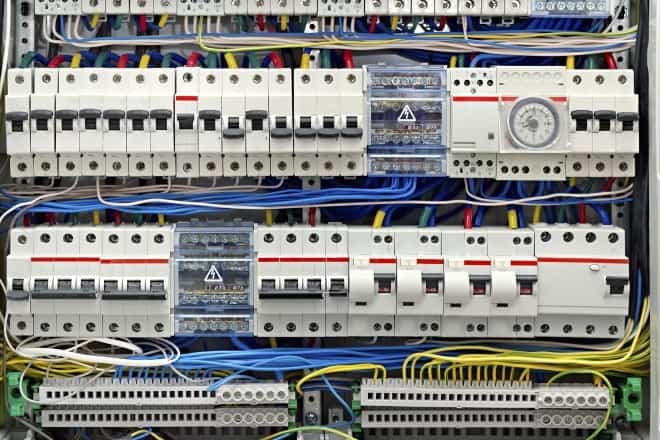
PDBs receives the power from various SDBs and correspondingly supplies to the loads adjacent to it. So these are placed near the application concerned, such as conveyor switching, lift and hoist machinery, pump control sets, etc.
These can be wall mount or floor mount depends on the customer requirement as well as power it is rated for. In addition to SDBs incomer, some PDBs are supplied with UPS (uninterrupted power supply) as an auxiliary power source to enable continuity of service of the equipment during power outages.
Lighting Distribution Boards (LDBs)
These are the final switch boards (In electrical wiring & installation) and are located at small electrical loads switching areas including lighting, air conditioners, small motors switching, distribution boards for plugging portable devices like blowers, etc. We can also observe these LDBs in our homes and offices as they are employed in low switching operations.
Click here to view the wiring diagram of lighting distribution board
LDBs consist of various MCBs where each MCB acts as a switch for individual loads (some cases two or more lights can be connected to single MCB). These MCBs protects the loads against overload as well as short circuit conditions. These MCBs are mounted or fixed to the metal racks. These boards receive the power from PDBs and then supplies to the lighting loads. Mostly these are of wall mounted type boards.













Got knowledge
Wow! Great tools to Learn or just to refresh your knowledge, from time to time is ideal to read and go through all these very important articles.
THANKYOU SO MUCH SIR FOR GIVING THESE DETAILS