HRC Fuse (High Rupturing Capacity Fuse) and its Types
HRC Fuse (High Rupturing Capacity Fuse) and its Types
A high rupturing capacity fuse contains a fuse wire that safely carries the short-circuit current for a given time period. During this period, if the fault is removed, the fuse does not blow off; otherwise, it will melt and disconnect the circuit from the electrical supply, ensuring the circuit remains safe.
The common material used to make an HRC fuse is glass, but this is not always the case. Other chemical compounds are also employed in the manufacturing and construction of HRC fuses based on different factors. The external enclosure is made fully airtight to prevent the atmosphere’s effect on the fuse materials. A major concern with HRC fuses is the low and uncertain breaking capacity of semi-enclosed fuses.
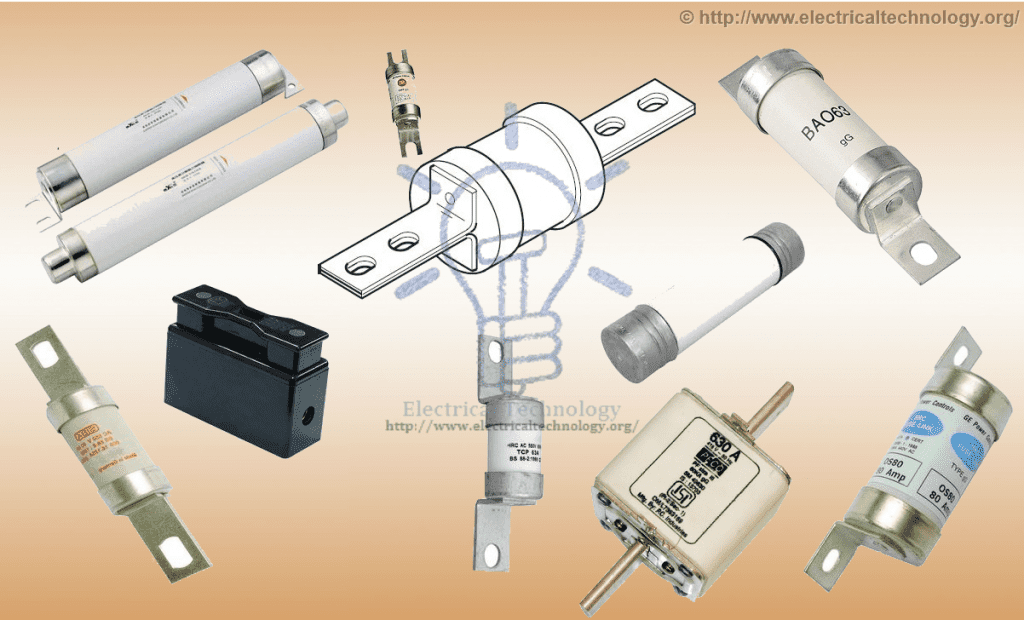
Construction and Operations of HRC Fuse:
An HRC Fuse consists of a highly heat-resistant material (such as ceramic) body with metal end caps, which are welded to a silver current-carrying element. The internal space of the fuse body is completely filled with a powder. The material used to fill the inner space may include plaster of Paris, quartz, chalk, marble, dust, and cooling mediums, among others. This filling prevents overheating, allowing the fuse to carry normal current.
The heat produced vaporizes the silver element. A chemical reaction occurs between the silver vapor and the filling powder, resulting in a high-resistance substance. This substance helps quench the arc in the fuse
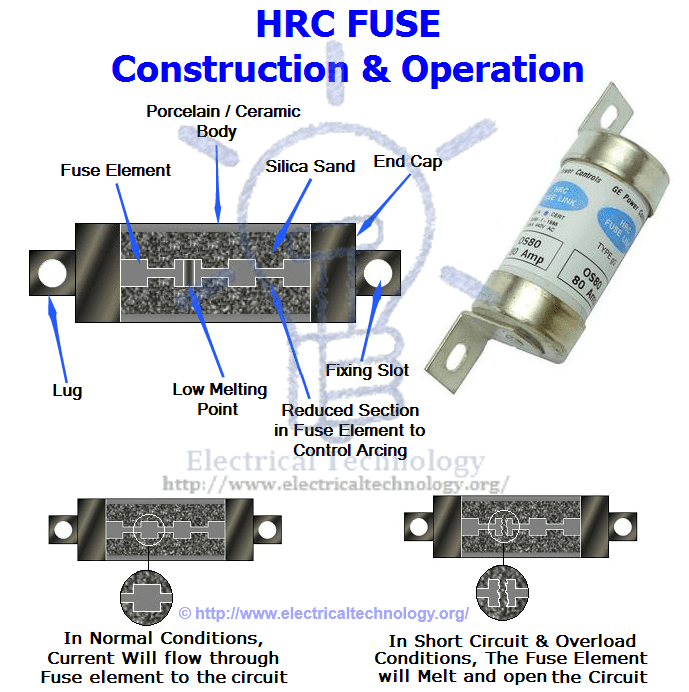
HRC Fuse with Tripping Device:
When a fuse blows out due to a fault condition, it triggers the tripping device, causing the circuit breaker to operate. The fuse body is made of ceramic material with a metallic cap fixed at each end, connected by a series of silver fuse elements.
At one end, there is a plunger that hits the tripping mechanism of the circuit breaker under fault conditions, prompting it to operate and interrupt the circuit. The plunger is connected through a fusible link and a tungsten wire to the other end of the cap.
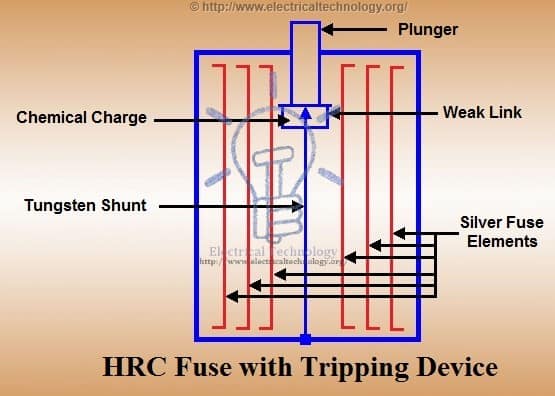
When a fault occurs, the first element to be blown out is the silver fuse, and the current is transferred to the tungsten wire. The travel of the plunger is set in such a way that it is not ejected from the fuse body during fault conditions.
Advantages of HRC Fuse with Tripping Device:
- During a single-phase fault on a three-phase system, the plunger trips the circuit breaker, which opens all three phases, preventing single-phase supply.”
- The effects of the short circuit need to be considered in a circuit breaker to allow the use of an inexpensive circuit breaker.”
- The fuse-tripped breaker is capable of handling small currents, eliminating the necessity of replacing the fuse (except in cases of high current).
Low-voltage H.R.C. fuses are available in capacities ranging from 16,000A to 30,000A at 400V (also available in the range of 80kA to 120kA). HRC fuses are used for protection on low-voltage distribution systems against overload and short-circuit conditions.
Types of HRC Fuse:
NH Type H.R.C Fuse:
The NH fuse provides overload and short-circuit protection for low and medium voltage. It serves as backup protection for motor starters and other equipment against short circuits and overloads. The fuses are light in weight with compact dimensions.
Din Type HRC Fuse:
DIN-type fuses are available in a wide range of rated currents. They are used for various purposes, each with specific characteristics under different temperature conditions. These types of fuses are available for different voltage levels and can be utilized in transformer protection even in cases where there is no Low-Voltage (LV) secondary or backup protection. They exhibit excellent clearing capability for ideal low overcurrent with short-circuit performance. DIN fuses also find applications in air and gas-insulated switchgear, mining, transformers, and feeder sectionalizing.
Blade Type HRC Fuse:
This type of fuse, also known as spade or plug-in fuses, comes with a plastic body and two metal caps to fit into the socket. Mostly used in automobiles for wiring and short-circuit protection, they are lightweight and have a low cutoff current. These fuses are also employed for short-circuit and backup protection of motors. They are available in various sizes and shapes with different current rating capacities, which are printed on the top.
Advantages & Disadvantages of HRC Fuse:
Advantages
- Clears both high and low fault currents.
- Does not deteriorate with age.
- Operates at high speed.
- Provides reliable discrimination.
- Requires no maintenance.
- More cost-effective than other circuit interrupting devices with the same rating.
- Ensures consistent performance.
- Fast fusing operation without noise and smoke.
Disadvantages
- They need to be replaced after each operation.
- The heat produced by the arc may affect the associated switches.
Application of H.R.C Fuses:
- Transformer Protection: H.R.C fuses are commonly used to protect transformers from overcurrent and short-circuit conditions.
- Motor Protection: They are used as backup protection for safeguarding motors against overloads and short circuits.
- Automobiles: H.R.C fuses find application in automotive electrical systems, providing protection for wiring and components.
- Motor Stators: Specifically used in motor stators to ensure proper protection against electrical faults.
- Backup Protection: H.R.C fuses serve as backup protection for various electrical equipment and systems.
- Low Voltage Distribution Systems: These fuses are utilized in low voltage distribution systems to prevent and mitigate the impact of faults.
- Industrial Applications: H.R.C fuses are employed in diverse industrial settings for protecting electrical circuits and equipment.
- Feeder Sectionalizing: They are used in feeder sectionalizing, ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical distribution.
- Air and Gas Insulated Switchgear: H.R.C fuses play a role in protecting components within air and gas-insulated switchgear.
- Mining Operations: These fuses are applied in mining operations for electrical circuit protection.
Final Taught
After reviewing the advantages and disadvantages of H.R.C fuses for low-voltage installations, it’s evident that they can be easily replaced. These fuses offer high-speed operation for short-circuit and overcurrent protection. Moreover, they contribute to the stability of industrial power distribution and semiconductor protection. In a low-voltage system, both the fuse and circuit breaker complement each other. They can be used to provide backup protection to the circuit breaker with high breaking capacity.
Related Posts:
- Fuse and Types of Fuses
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCD & (RCB or RCCB) Circuit Breakers
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB): Construction, Operation, Types and Uses
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
- ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
- Wiring of the Distribution Board with RCD
- Types of Switches
- Basic Electrical Wiring Tutorials







Technology
nyc and teaching
LAWSON FUSES
I want to have alot ov experience as an electritian
Sr# Description UOM Quantity
1 Fuse Hrc
.IN 700 500 VAC CURR.50KA Nos. 10
2 Fuse Hrc
AR 125A 660 VAC Nos. 10
3 Fuse Hrc
Type=Rs31 (As Per Sample)
AR 35A AC 660V
Type=Rs31 (As Per Sample) AR 35A AC 660V
DELIXI Nos. 10
4 Fuse Hrc
AR 315A 660 VAC Nos. 10
5 Fuse HRC
AR 160A 660 VAC Nos. 10
Dear sir,
3 units of efo medium voltaqge h.r.c. fuse:
Type: outdoor/indoor
Class: back-up fuse
Rated voltage ur:7.2kv
Rated current ir: 2a
Max. breaing current i1: 16kA
Min. breaking curren lmin: 8a
Rated freq: 50ha
Thanks