Types of Diodes and Their Applications – 24 Types of Diodes
Various Types Of Diodes With Their Characteristics & Uses
The diode is the most used semiconductor device in electronics circuits. It is a two-terminal electrical check valve that allows the flow of current in one direction. They are mostly made up of silicon but germanium is also used. Usually, they are used for rectification. But there are different properties & characteristics of diodes which can be used for different application. These characteristics are modified to form different types of diodes. Nowadays, several different types of diodes having different properties are available.
- Related Post: Different Types of Sensors with Applications
Some of the different types of diodes with their properties and applications are discussed below:
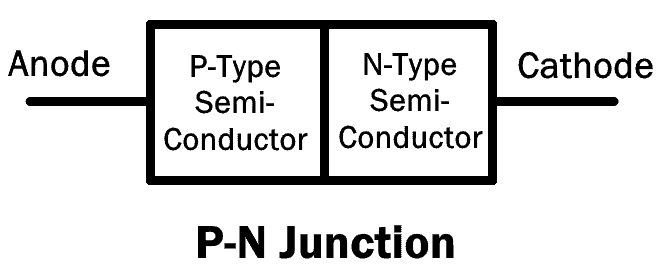
P-N Junction Diode
The P-N junction diode is made up of semiconductor material. It consists of two layers of semiconductors. One layer is doped with P-type material and the other layer with N-type material. The combination of these both P and N-type layers form a junction known as the P-N junction. Hence the name P-N junction diode.
It allows the flow of current in the forward direction and blocks it in reverse direction. They are also known as rectifier diode used for rectification.
There are different types of diodes that use the P-N junction with variation in doping concentration. They are discussed below.
Small Signal Diode
It is a type of P-N junction diode which operates on low voltage signals. Its junction area is very small. Due to which, the junction has less capacitance & low charge storing capacity. It enables the small signal diode to have high switching speed with very fast recovery time. However, its limitations are low voltage and current parameters.
Due to its high switching speed, these types of diodes are used in circuits with high frequencies.
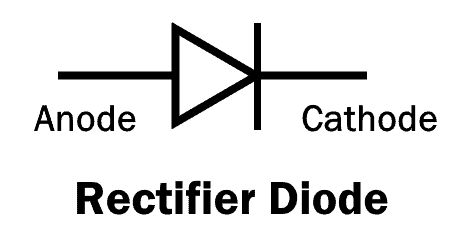
Rectifier Diode
A rectifier diode is a type of P-N junction diode, whose P-N junction area is very large. This results in high capacitance in reverse direction. It has low switching speed.
This is the most common and most used type of a diode. These types of diodes can handle heavy current and are used in converting AC into DC (Rectification).
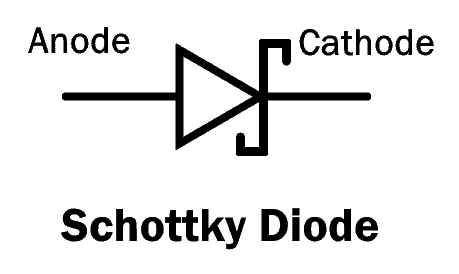
Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode, named after a German physicist Walter H. Schottky, is a type of diode which consists of a small junction between an N-type semiconductor and a metal. It has no P-N junction.
The plus point of the Schottky diode is that it has very low forward voltage drop and fast switching. As there is no capacitive junction (P-N junction), the Schottky diode switching speed is very fast.
The limitation of Schottky diode is that it has low reverse breakdown voltage and high reverse leakage current.
Super Barrier Diodes
Super barrier diodes (SBR) are also rectifier diodes but they have a low forward voltage drop just like a Schottky diode. They have low reverse leakage current just like a normal P-N junction diode.
SBR uses MOSFET by making short contact between its gate and source.
SBR has a low forward voltage drop, less reverse leakage current and fast switching capability.
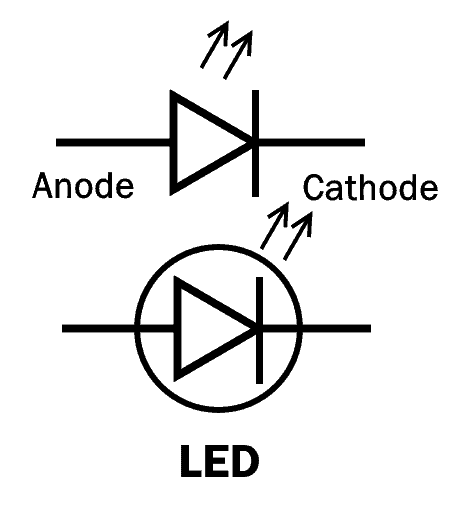
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
The Light Emitting Diode (LED) is also a type of P-N junction diode that emits light in the forward bias configuration.
LED is made up of a direct-band semiconductor. When the charge carriers (electrons) cross the barrier and recombine with electron holes on the other side, they emit photon particles (light). While the color of the light depends on the energy gap of the semiconductor.
LED converts electrical energy into light energy.
Photodiode
The photodiode is a type of P-N junction diode that converts the light energy into electrical current. Its operation is opposite to that of an LED.
Every semiconductor diode is affected by optical charge carriers. It is why they are packaged in a light blocking material.
In the photodiode, there is a special opening that allows the light to enter its sensitive part.
When the light (Photon particles) strikes the PN junction, it creates an electron-hole pair. These electron and hole flow out as electrical current. To increase its efficiency, a PIN junction diode is used.
A photodiode is used in reverse bias and they can be used in solar cells.
Laser Diode
A laser diode is similar to LED because it converts electrical energy into light energy. But unlike LED, Laser diode produces coherent light.
The laser diode consists of a PIN junction, where electron and holes combine together in the intrinsic (I) region. when they combine, it generates a laser beam.
Laser diodes are used in optical communication, laser pointer, CD drives and laser printer etc.
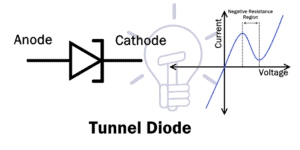
Tunnel Diode
Tunnel diode was invented by Leo Esaki in 1958 for which he received Nobel prize in 1973, which is why it is also known as Esaki diode.
A tunnel diode is a heavily doped P-N junction diode. It works on the principle of the tunneling effect. Due to heavy doping concentration, the junction barrier becomes very thin. This allows the electron to easily escape through the barrier. This phenomenon is known as tunneling effect.
The Tunnel diode has a region in its VI curve where the current decreases as the voltage increases. This region is known as the negative resistance region. The tunnel diode operates in this region in different applications such as an oscillator and a microwave amplifier.
The symbol with VI characteristic curve of tunnel diode is given below:
The tunnel diode also conducts current in reverse direction & it is a fast switching device.
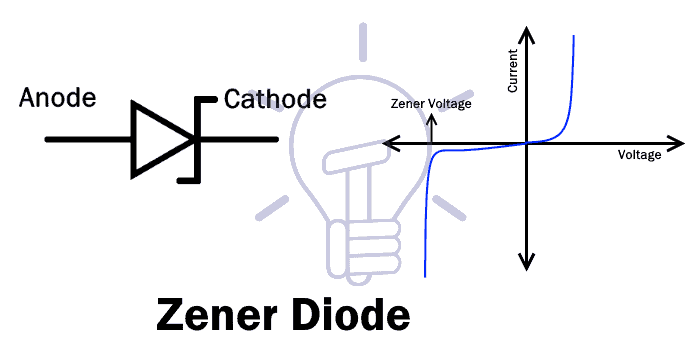
Zener Diode
Zener diode is named after Clarence Malvin Zener who discovered the zener effect.
It is a type of diode, which not only allows the flow of current in the forward direction but also in reverse direction. when the reverse voltage reaches the breakdown voltage known as Zener voltage it allows the current flow.
The Zener diode has heavier doping concentration than a normal P-N junction diode. Hence, it has a very thin depletion region.
In forward bias, it operates as a simple P-N junction diode (Rectifier).
In reverse bias, it blocks until the reverse voltage reaches breakdown. After that, it allows the current flow with a constant voltage drop.
Zener reverse breakdown is caused due to two reason i.e. electron quantum tunneling and Avalanche breakdown.
A Zener diode is mainly used in reverse bias configuration. It provides a stabilized voltage for protection of circuits from overvoltage.
Backward Diode
The backward diode or the back diode is a P-N junction diode, whose operation is similar to that of tunnel diode and Zener diode. But the operating voltages are much lower.
A backward diode is essentially a tunnel diode, whose one side of the junction has relatively less doping concentration compared to the other side.
In the forward bias, it operates as a tunnel diode but its tunneling effect is much reduced as compared to tunnel diode. Otherwise, it operates as a normal P-N junction diode.
In reverse bias, it operates as a Zener diode but the breakdown voltages are much lower.
It is not widely used but it can be used for rectification of a small voltage signal (0.1 to 0.6v). Due to its fast switching speed, it can be used as a switch in RF mixer and multiplier.
Related Post:
Avalanche Diode
The Avalanche diode is a P-N junction diode that is specifically designed to operate in the avalanche breakdown region.
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon where sufficient reverse voltage is applied to the P-N junction. Due to which, the minority carrier ionizes & starts a heavy current flow in reverse direction.
Avalanche diode works electrically similar to the Zener diode. However, the doping concentration of a Zener diode is relatively higher as compared to an avalanche diode.
The heavy doping inside the Zener diode creates a small junction & low voltages can easily break it. However, the avalanche diode has a wide junction because of light doping concentration. Thus, it requires a high voltage for its breakdown. This wide junction makes it a better surge protector compare to a simple Zener diode.
Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) Diode
Transient voltage suppression diode or TVS diode is a type of avalanche diode that protects the circuit form high voltage surges.
TVS diode has the capability of handling high voltages as compared to avalanche diode.
Unidirectional TVS diode operates similar to avalanche diode. it acts as a rectifier in forward bias & surge protector in reverse bias.
Bidirectional TVS diode acts as two avalanche diodes opposing each other in series. It is manufactured as a single component. It operates both ways and provides surge protection when used in parallel with a circuit.
- Related Post: Types of Latches – SR & D Latches
Gold Doped Diode
In such type of diode, Gold or platinum is used as the dopant (doping material). It enables the diode to operate at fast switching speed but at the expense of increasing the forward voltage drop. Also, its reverse leakage current is higher than a normal P-N junction diode.
Constant Current Diode
The constant current diode AKA the current-limiting diode (CLD) is a two terminal diode made from JFET. It regulates the current flow through it up to a fixed level.
CLD is made by making short contact between the gate and the source of JFET. It limits the current just like Zener diode limits voltage.
Step Recovery Diode
Step recovery diode or snap-off diode is a P-N junction diode which abruptly ceases the flow of current when its direction is reversed.
The SRD (Step Recovery Diode) is made of a P-N junction with very low doping concentration near the junction. Due to which, the charge carriers (electron and holes) near the junction also decrease in number. Hence, the charge storing capacity near the junction becomes negligible. This enables the SRD to switch from ON to OFF very fast.
In a normal diode, when it is switched from forward conduction to reverse cutoff, the current flows briefly because of the stored charge. Due to which, the normal diode takes some time in switching. The SRD does not store charge, So it can cease the current flow instantaneously.
- Related Post: Various Types of Electronic Counters
Peltier Or Thermal Diode
Peltier or thermal diode is a type of diode whose thermal resistance is different in one direction than the other direction. So the heat generated flows in one direction to one side (terminal) and leaving the other side cooler.
This diode is used in the application of heat monitoring in microprocessor and in refrigerators for cooling effect.
Vacuum Diode
It is the simplest form of a diode made from a vacuum tube and two electrodes (cathode and anode). The Anode and Cathode are enclosed inside the vacuum tube (empty glass).
When the cathode heats up it emits electrons, the anode picks up the electrons and the flow continues.
The cathode can be heated directly or indirectly.
In forward bias, the free electron on cathode release into the vacuum after getting heat up. The anode collects these electrons and the current flows.
In reverse bias, the free electron in the vacuum gets repelled by the anode as it is connected to the negative terminal, therefore the current does not flow.
Thus, the current flows in only one direction.
Related Posts:
Varactor Diode
Varactor diode also known as Vericap diode are voltage controlled capacitors. They have a P-N junction with variable junction capacitance.
The varactor diode operates under reverse bias conditions. The depletion layer between the P and N-type material is varied by changing the reverse voltage.
All diode’s junction capacitance varies with reverse voltage but Varactor diode is able to use this effect with a high range of capacitance.
The applications of Varactor diodes are as a voltage controlled oscillator in the phase-lock loop, in RF tuning filters and frequency multipliers.
Related Post: Types of ICs. Classification of Integrated Circuits and Their Limitation
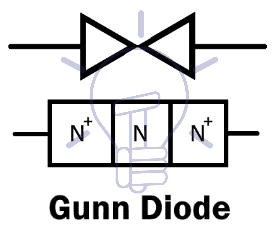
Gunn Diode
Gunn diode AKA “Transferred Electron Device” (TED) is a type of diode having negative resistance like tunnel diode. It is named after a British physicist J.B Gunn who discovered the “Gunn Effect” in 1962.
The Gunn diode does not have P-N junction. In fact, it consists of only N-type material, which is why it does not rectify AC or work like a normal diode. It is also the reason many people call it “Transferred Electron Device” (TED) instead of a diode.
It consists of three N-type layers; two of them which are on the terminal’s side have a higher doping concentration whereas the middle thin layer has a lighter doping concentration.
When the voltage is applied to Gunn diode, initially its current increases with increase in voltage.
At higher voltage, the resistance of the middle layer starts increasing with voltage. It results in the fall of the current flow. This is the negative resistance region & Gunn diode operates in this region.
The Gunn diode is used in an oscillator for generating microwaves of high frequency.
- Related post: Types of Circuits, Network & Parts Of Circuit
PIN Diode
PIN diode is a three-layer diode i.e. P-layer, I-layer & N-layer. The ‘I‘ intrinsic semiconductor layer is placed between heavily doped P and an N-type semiconductor.
The electron and holes from N and P-type region respectively flow to the intrinsic region (I). Once the “I” region fills completely with electron-holes, the diode starts conduction.
In reverse bias, the wide intrinsic layer in the diode can block and tolerate high reverse voltages.
At higher frequency, the PIN diode will act as a linear resistor. It is because of the fact that the PIN diode has poor reverse recovery time. The reason is that the heavily charged “I” region does not get enough time to discharge during fast cycles.
While at low frequency, it acts as a rectifier diode. Because it gets enough time to discharge & turn off during the cycle.
If a photon enters the “I” region of a reversed bias PIN diode, it produces an electron-hole pair. This electron-hole pair flows out as current. So it is also used in photodetectors and photovoltaic cells.
PIN diodes are used in high voltage rectification, in RF application as attenuator & switching element.
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
SCR is a four-layer P-N-P-N semiconductor switching device. It has three terminals Anode, Cathode, and Gate.
SCR is essentially a diode with an external control input known as the gate input. It allows current flow in one direction.
When SCR is connected in the forward bias, it won’t yet allow the flow of current. This is known as the forward blocking mode.
To make SCR conduct in the forward mode, it either needs the necessary voltage to cross its breakover limit or by applying a positive pulse to its gate input.
To turn off SCR, either decrease the current below the holding current point or turn off the gate input and short circuit the anode-cathode momentarily.
In reverse bias, the SCR does not allow current even after applying gate input. But if the reverse voltage reaches reverse breakdown voltage, the SCR starts conduction due to avalanche phenomena.
SCR is used for controlling high power circuits, rectification of high power AC.
- Related Post: Types of Rectifiers and their Operation
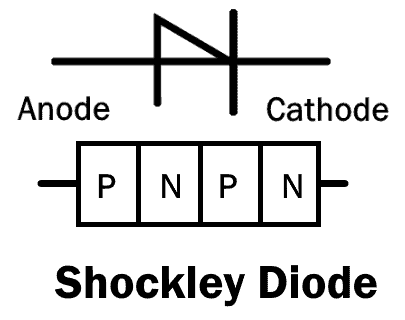
Shockley Diode
Shockley diode is a four layer PNPN diode. It resembles SCR but it has no control or gate input.
Shockley diode tends to stay ‘ON’ once it is turned ‘ON’ & tends to stay ‘OFF’ when it is turned ‘OFF’.
As we know that the Shockley diode has no gate input so the only way to switch it ‘ON’ is by applying Forward voltage greater than its breakdown voltage.
After applying the voltage greater than its breakdown voltage, it will allow the current flow.
During conduction state, it won’t turn off even if the voltage decreases from its breakdown voltage. To make it switch ‘OFF’, the voltage needs to be sufficiently lower than its breakdown voltage.
Point Contact Diode
Point Contact Diode is also known as Cat Whisker diode or crystal diode.
It is a type of diode in which a small point junction is formed between a metal wire & N-types semiconductor crystal.
“cat whisker” is a thin springy wire made of Phosphorus bronze or tungsten. It makes a point contact junction with an N-type semiconductor, Hence the name point-contact diode.
As the junction formed is very small so the junction capacitance of point contact diode is very low. Thus, there is very low charge storage capacity, which makes it a fast switching device.
During manufacturing, passing a relatively large current through the cat whisker wire results in the formation of small a P-region upon the N-type semiconductor. This small junction acts as a P-N junction.
Point contact diodes are used for low voltage signal & in microwave mixer & detectors.
These are some of the most common types of diodes used in designing and operation of electronic circuits. If you want to add more kinds of diodes, let us know in the comment box below.
Related and Descriptive Articles on Different Kinds of Diodes:
- What is Diode? Construction and Working of PN Junction Diode
- Fast Recovery Diode: Construction, Working and Applications
- Step Recovery Diode – SRD: Construction, Working and Applications
- Schottky Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages and Applications
- Shockley Diode: Construction, Working, Characteristics and Applications
- LED – Light Emitting Diode: Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Photodiode: Types, Construction, Operation, Modes, Performance and Applications
- PIN Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Point Contact Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Constant Current Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Gunn Diode: Symbol, Construction Working and Applications
- Varactor Diode – Symbol, Construction, Working and Applications
- Backward Diode: Construction, Operation, Characteristics and Applications
- What is a Laser Diode? Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- What is Avalanche Diode? Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Tunnel Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages, and Applications
- Zener Diode – Symbol, Construction, Circuit, Working and Applications
- Blocking Diode and Bypass Diodes in a Solar Panel Junction Box
- Diode Formulas and Equations – Zenner, Shockley and Rectifier
- Diode Symbols – Electronic and Electrical Symbols
- Applications of Diodes
Additional Different Types of Electronic Components and Devices
- Types of SSR Relays – Construction & Operation
- Types of Binary Multiplier – Binary Multiplication Calculator
- Types of Binary Encoder – Construction, Working & Applications
- Types of Binary Decoder – Construction, Working & Applications
- Types of Binary Adder & Subtractor – Construction, Working & Applications
- Types of 555 Timer ICs – Construction, Working & Application
- Types of Inverters and their Applications
- Types of Digital Logic Gates













intersting and well informed.. Ecellent notes.
Two small additions:
The SCR diode is also called a thyristor;
The Shockley diode is also called a diac.