Difference between RTD and Thermocouple
What is the Difference Between Thermocouple and RTD?
RTD or Resistance Temperature Detector and thermocouple are two of the different types of temperature sensors used in electrical and electronic engineering to monitor the temperature. Other temperature sensors such as thermistors and thermostats can also be used to accurately measure temperature. However, they are quite different in operation as well as other parameters. The main difference between RTD and thermocouple is their operation. The former uses electrical resistance to measure temperature while the latter uses the thermoelectric effect to generate voltage due to the temperature change.
- Related Post: Difference Between Thermistor and Thermocouple
Before going to enlist the difference between RTD and thermocouple, we are going to discuss their basics first.
RTD
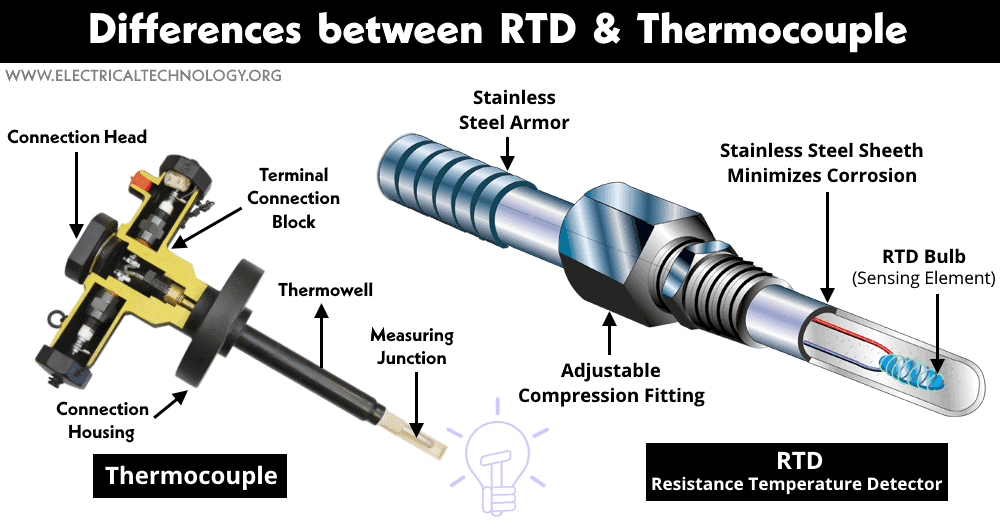
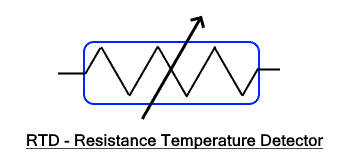
RTD is an acronym for Resistance Temperature Detector. It is a type of temperature sensor that is used to measure temperature using the change in electrical resistance of an electrical wire. It can be used to measure temperatures up to 600°C.
In RTD, an electrical conductor is used as a sensor whose resistance increases with an increase in temperature & decreases with a decrease in the temperature. The resistance of the RTD element is measured using another signal conditioning circuit. The change in temperature changes the resistance of the RTD element which can be used to measure the rise or fall in the temperature.
RTD is a passive sensor that requires an external power source to operate. Its performance depends on the battery’s health. It requires a very complicated signal conditioning circuit that converts the resistance into a voltage signal. The resistance is measured by passing a fixed current through the element.
RTD uses pure metals that has high temperature coefficient so that the change in resistance is significant. Therefore, copper, nickel and platinum is usually used as RTD element. They offer a very linear change in resistance with the change in temperature which constitutes into the high accuracy of the RTD.
It can have two, three or four terminals depending on its design. Four terminals RTD has higher accuracy than three terminal and three terminal RTD has higher accuracy than two terminal RTD. The difference in accuracy is due to the lead wire resistance which is compensated in these other designs.
The resistance of its element may also increase due to the heat generated due to current flowing through it called the self-heating effect.
Related Post:
Thermocouple
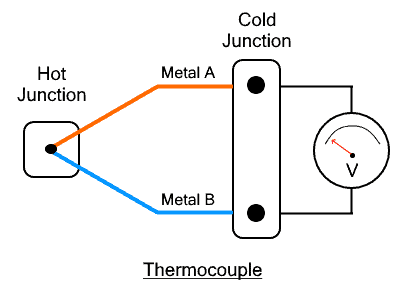
Thermocouple is a temperature sensor that allows us to measure temperature by converting the temperature into voltage signal of proportional strength. It is used to measure very high Temperature up to 2000° C. It is used in low cryogenic applications as well.
Two dissimilar metals having different thermoelectric properties are joined together at one end while separated at other end. The temperature at the joined end called hot junction produce thermoelectric potential at the other end. The potential is measured using a volt meter which is proportional to the temperature at the hot junction.
Thermocouple is an active sensor; it does not require any power source to operate. It generates very small voltage in microvolts per degree Celsius of temperature change. As the temperature changes, the potential difference between its two terminals also changes but the relationship between these two is non-linear and more like a curve. Therefore, thermocouple has lower accuracy than RTD.
Related Post:
- What is a Thermistor? Types of Thermistors and Applications
- Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
Key Differences between RTD and Thermocouple
The following comparison table shows the major differences between a thermocouple and a Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD).
| RTD | Thermocouple |
| It is used to measure temperature by measuring the change in resistance of the wire. | It is used to measure temperature by measuring the thermoelectric potential due to temperature change. |
| It converts temperature into electrical resistance | It converts temperature into voltage. |
| It is a passive sensor that requires external power source to operate. | It is an active sensor that does not requires external power source. |
| It requires complex signal conditioning circuit. | It requires any ordinary of voltmeter. |
| Its sensing element is made of pure metal such as copper, nickel & platinum. | Its sensing element is made of two dissimilar metals. |
| It can measure temperature up to 600° C | It measures temperature up to 2000° C. |
| It has a slower response time | Thermocouple has more fast response time. |
| Due to slower response time, it has lower sensitivity. | It has higher sensitivity able to measure small changes in temperature. |
| It has more linear relationship between its resistance and temperature. | It has nonlinear relationship between its resistance and temperature. |
| The lead wire resistance affects the accuracy | The non-linearity affects its accuracy. |
| Self-heating can affect its measurement. | There is no self-heating effect. |
| RTD has higher accuracy than thermocouple | It has lower accuracy. |
| It is immune to EMI & RFI | It is prone to EMI & RFI |
| It has longer life span with much more stability. | It has smaller life span and comparatively lower stability. |
| It has a higher overall cost | It has cheaper overall cost |
| It is larger & bulkier in size than a thermocouple | It is smaller in size than RTD |
| Due to large size, it is no suitable for point sensing. | Due to their small junction size, they are suitable for point sensing. |
Main Differences between RTD and Thermocouple
Operations
- RTD works on the principle of change in resistance of a conductor due to the temperature.
- A thermocouple works on the principle of thermoelectric potential generated due to the difference between their two junctions.
Sensing Unit
- The RTD sensing unit is an electrical conductor with high temperature coefficient.
- A thermocouple’s sensing unit is the junction of two metals having different thermoelectric properties.
Sensing System
- RTD has a very complicated sensing system that must be able to measure the resistance of the element excluding the lead wire resistance as well as the self heating effect.
- A thermocouple only requires a voltmeter to measure the thermoelectric potential.
External Source
- RTD is a passive sensor that requires external power source.
- A thermocouple is an active sensor that does not require external power source.
Operating Range
- RTD is used for measurement of moderate temperature. It can measure up to 600 °C.
- A thermocouple is used for measuring very high temperature up to 2000 °C.
Sensitivity
- RTD is less sensitive compared to thermocouples.
- A thermocouple has higher sensitivity thus able to measure small changes in the temperature.
Accuracy
- RTD has better accuracy as compared to thermocouple but they are not suitable for high temperature applications.
- Thermocouple has lower accuracy but are best for high temperature measurement.
Response Time
- The RTD has slower response time of about 1 – 50s.
- Thermocouple has quicker response time of about 0.1 – 10s.
Immunity to Interference
- RTD is immune to interference such as RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) & EMI (Electromagnetic Interference).
- Thermocouples are susceptible to RFI & EMI which also causes error in the measurement.
Size
- RTD’s element or sensor is bulkier and larger in size. Therefore they are unable for point sensing.
- The thermocouple’s sensing junction is smaller in size. Therefore it is best for measuring temperature at a small point.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
- Difference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET
- Difference Between BJT and FET Transistors
- Difference Between Diode and SCR (Thyristor)
- Difference Between Diode and Transistor
- Difference Between NPN and PNP Transistor
- Difference Between DIAC and TRIAC
- Difference Between Transistor & Thyristor (SCR)?
- What is a Transducer? Types of Transducers and Applications
- LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer and Inductive Sensors
- Capacitive Sensor and Transducer and Its Applications
- What is Piezoelectric Sensor? Construction, Working and Applications
- Types of Resistive Sensors and Transducer, Potentiometer and Strain Gauge
- What is a Thermistor? Types of Thermistors and Applications
- Thermocouple – Types, Construction, Working and Applications