Difference between LED and Photodiode
What is the Difference between Photodiode and LED?
LED or Light Emitting Diode and photodiode both are semiconductor-based components whose function is the conversion between light energy and electrical energy. The LED converts electrical energy into light energy while the photodiode converts light energy into electrical energy. Apart from the working principle, they have quite a lot of differences explained below.
- Related Post: Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
Before going into the list of differences, let’s look into their basics first.
What is LED?
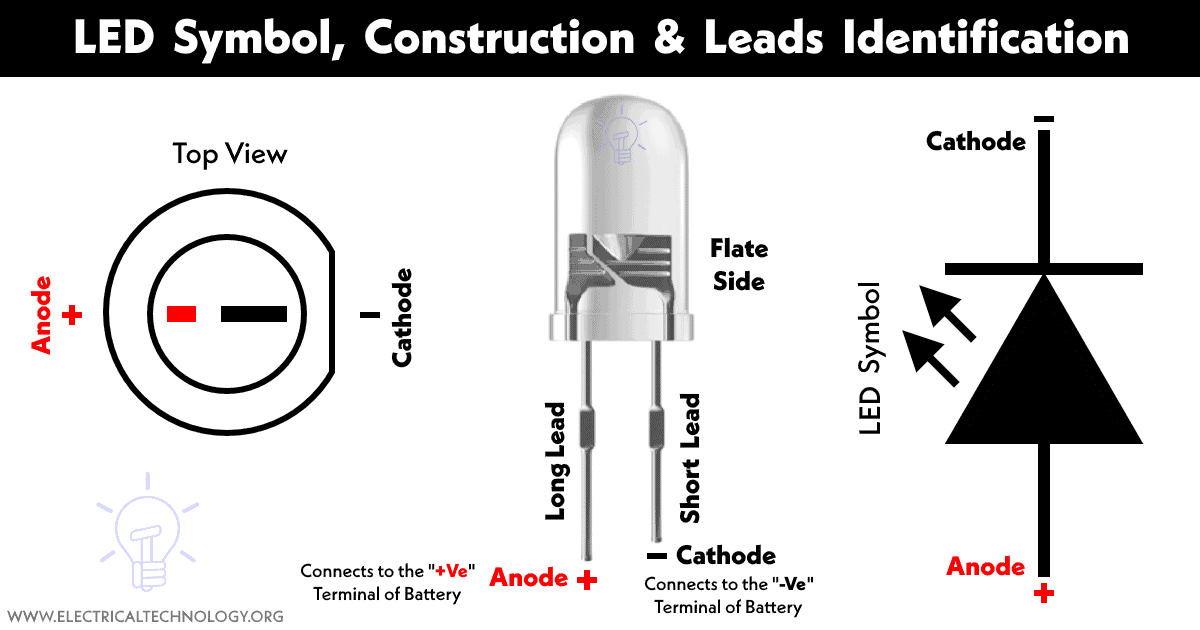
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. It is a type of diode that works on the principle of Electro-Luminance. Electro-Luminance is a phenomenon in which a material emits light when an electric current passes through it. The light can be infrared, visible, and ultraviolet. The symbol of LED resembles a diode with outward-pointing arrows representing light emission.
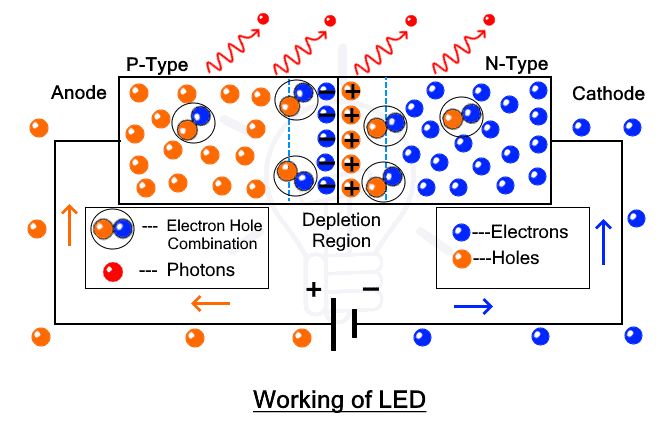
It is a simple PN junction diode that radiates light in forward bias. The junction is covered in transparent epoxy to direct the light emitting from the junction in all directions.
LED is a semiconductor-based component but certain semiconductors only possess such property to emit light such as gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, and indium phosphide compounds. Silicon and germanium emits heat instead of light, therefore they are not used in LEDs. Different materials are selected based on the color of light.
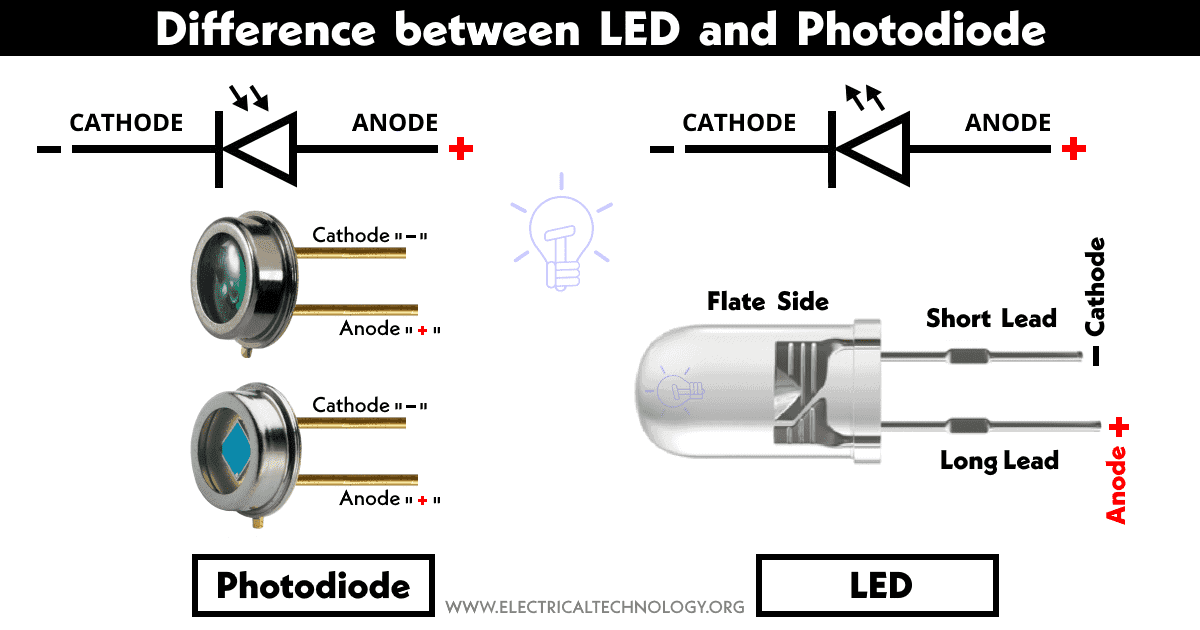
LED has two terminal anode (+) and cathode (-). It only operates in forward bias and reverses bias can permanently damage it.
LED emits light or photons due to the recombination of electrons and holes. When the LED is forward biased, the source energizes the electrons which move towards the junction and recombine with the holes. During recombination, the electrons that are in the conduction band (having higher energy than the valance band) fall back into the valance band (holes) and release energy. This energy is equal to the difference in these bands and it is in the form of light. Now the color of the light depends on the semiconductor material.
What is Photodiode?
The photodiode is a type of diode that works on the principle of the photoelectric effect. In the photoelectric effect, light energy is converted into electrical energy. The symbol of a photodiode is similar to LED except arrows pointing inward showing light falling on the photodiode.
The material used to manufacture photodiodes are but are not limited to silicon, germanium, and indium gallium arsenide. The type of material and the doping concentration determines the performance parameters of photodiode such as response time, sensitivity, breakdown voltage, dark current and cost benefits.
It has two terminals anode and cathode. But it is operated in reverse bias when light or photons fall on it. Even in the absence of light, there is a leakage current called the dark current. However, it induces errors in the reading of the photo-detector.
Photodiode converts light or photon into electrical current due to the photoelectric effect. When a photon strikes the exposed junction of the photodiode, it generates electron-hole pairs. Due to the built-in electric field between the P-type and N-type semiconductor, the electron and hole flows in the opposite direction and eventually into the external circuit.
We can say that LED and photodiode are completely opposite to each other in operation i.e. LED converts electrical energy into light energy and photodiode converts light energy into electrical energy.
Comparison between LEDs and Photodiodes
The following table shows some of the major differences between light emitting diode (LED) and a photodiode.
| LED – Light Emitting Diode | Photodiode |
| LED or light-emitting diode converts electrical energy into light energy. | Photodiode converts electrical energy into light energy. |
| Symbol of LED: |
Symbol of Photodiode: |
| It works on the principle of Electro-Luminance i.e. material emits light energy when a current pass through it. | It works on the principle of the photoelectric effect. |
| The electron-hole recombination emits a photon. | The photon striking the junction energizes the electrons forming electron-hole pairs that generate current. |
| It is used to emit light. | It is used to detect light. |
| Its symbol shows arrows pointing outward. | Its symbol shows arrows pointing inward. |
| Silicon and germanium does not emit light. Gallium, arsenide, and phosphide compounds are used. | Any semiconductor not limited to silicon and germanium can be used depending on its performance. |
| LED is covered in dome-shaped epoxy resin that uniformly scatters light in all directions. | The photodiode has a large lens that focuses the light onto the junction. |
| It is only used in forward bias. | It is used in reverse bias. |
| Reverse biasing an LED can permanently damage it. | It can be used in both forward and reverse bias. |
| There is no reverse leakage current. | There is a significant reverse saturation current since it operates in reverse bias. |
| There is no light emission in absence of electrical current. | In the absence of light, current flows through it called the dark current. |
| LED is used for illumination, lighting, and display in alpha numeric and sign boards. | The photodiode is used for light sensing, circuit protection using optocoupler, high-speed optical communication. |
Related Posts:
- Difference between LDR (Photoresistor) and Photodiode
- Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
- Difference between LED and LDR
Main Differences between Photodiode and LED
Here are some of the main differences between LED and Photodiode
Definition
- LED or light-emitting diode emits light when a current pass through it.
- A photodiode is a type of diode that generates current when light falls on it.
Function
- An LED function is to convert electrical energy into light energy.
- Photodiode’s function is to convert light energy into electrical energy.
Working principle
- LED works on the principle of Electro-Luminance.
- Photodiode works on the principle of the photoelectric effect.
Material
- LED requires materials that emit light during electron-hole combination such as Gallium, arsenide, and phosphide compounds. Silicon and germanium only emit heat energy.
- Photodiode uses any semiconductor such as silicon and germanium.
Biasing
- LED is only used in forward bias. Reverse bias can permanently damage it.
- A photodiode is used in reverse bias. Reverse bias increases its sensitivity.
Reverse Leakage Current
- There is no reverse leakage current.
- There is a significant reverse current since it operates in reverse bias.
Applications
- LED is used for illumination purposes due to its energy-saving feature and it is also in digital displays such as digital watches, and advertisement boards. Last but not least they are extensively used for decoration in children’s toys.
- Photodiode as a sensor is used for sensing light intensity in different electronic circuits. It is used in solar panels to convert solar energy into electrical energy. It is also used to electrically isolate two circuits.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Thermistor and Thermocouple
- Difference Between Sensor and Actuator
- Difference between Sensor and Transducer
- Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between Transistor and Thyristor (SCR)?
- Difference between Active and Passive Components
- Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
- Main Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET
- Difference Between BJT and FET Transistors
- Difference between RTD and Thermocouple
- Applications of Diodes