Difference Between DOL Starter and Soft Starter
What is the Difference between Soft and DOL Starter?
The electrical motor draws a huge amount of current during its startup. The huge current draws causes voltage dips in the system that could potentially damage other electronics as well as the motor itself (due to high current). It also reduces the mechanical life due to the sudden jerk at startup. In order to safely start an electric motor, we need to use motor starters. For this reason, there are multiple motors starters available in the market.
Direct on-line (DOL) starter & soft starter are both two different types of motor starter. They are used for the safe starting & stopping of an induction motor. Both of these motor starters are very different from each other. The DOL hooks up the motor to the full line voltage allowing maximum starting current (full speed) but it does offer low voltage & overcurrent protections. The soft starter, on the other hand, provides a smooth starting & stopping of the motor with low-voltage and overcurrent protections.
Related Posts:
Before going into the differences between DOL & soft starter, let’s discuss their basics first.
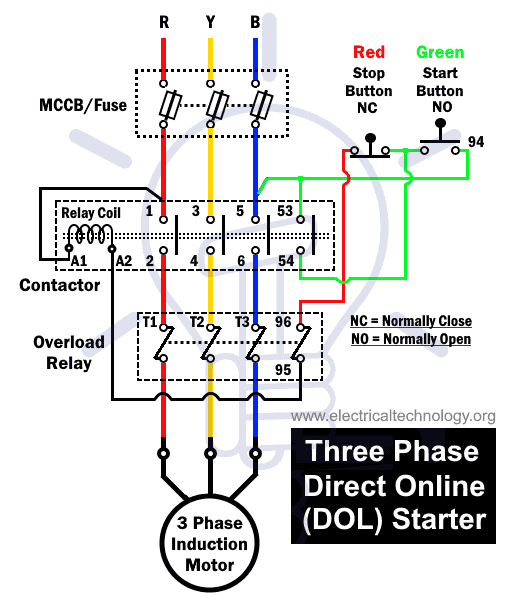
DOL (Direct On-Line) Starter
The direct on-line starter aka DOL is a type of motor starter that directly connects the motor to the full line voltage. The motor starting technique used here is called full voltage or across the line starting technique where the voltage at motor startup is not reduced. Hence, such a starter cannot reduce the starting inrush current. Therefore, the motors used with DOL starters must be rated below 5 HP. However, they do provide protection against overcurrent.
Since there is no voltage reduction at startup, the starting current & torque is very high. So it must be used with a low-power motor because they can tolerate the high current due to their high winding resistance. & it must be used in proper applications that require high starting torque.
The DOL starter creates mechanical stress on the motor, which needs to be frequently maintained in order to work smoothly. Other than that, it is the simplest and cheapest motor starter there is.
Related Posts:
- Main Difference between Contactor and Starter
- DC Machine – Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Speed Control of DC Motor – Voltage, Rheostatic & Flux Control Methods
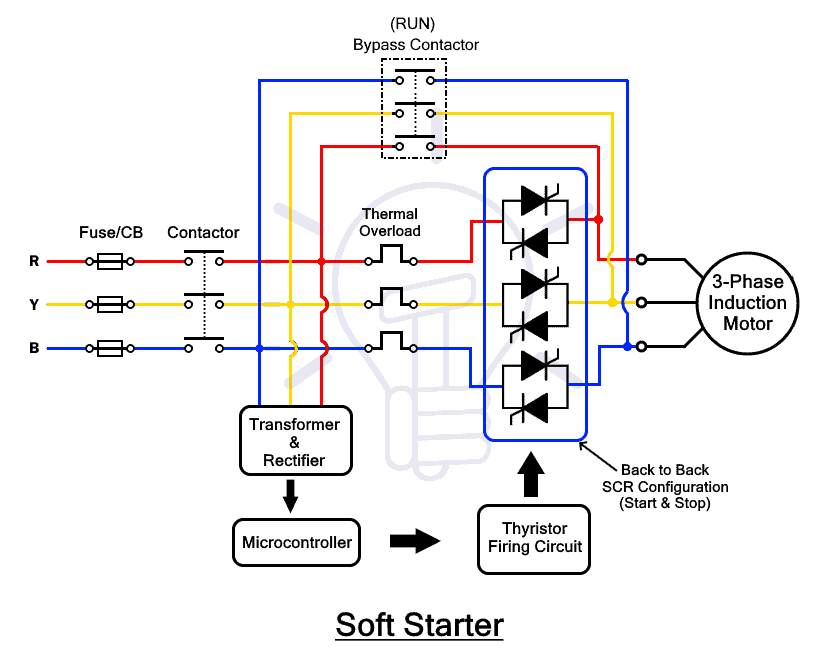
Soft Starter
The soft starter is a semiconductor-based motor starter that uses thyristors to regulate the voltage supply to the motor. The voltage at startup is reduced to reduce the inrush current that can damage the motor windings. The voltage is gradually increased until the motor attains its rated speed.
Three pairs of thyristors in back-to-back formations are used to control the voltage supply to the motor. The firing angle of the gate signal to the thyristor controls its conduction period. Therefore, the soft starter utilizes this feature to vary the voltage supply to the motor during the starting & stopping of a motor.
During the motor startup, the voltage supply is kept minimum to reduce the starting current. With a gradual increase in the voltage, the motor smoothly picks up the speed. Once the motor reaches its rated speed, the starter is bypassed using a contactor & the full voltage supply from the mains is resumed. The same process is done to gradually reduce the speed during stopping of the motor.
The Low voltage at startup protects the motor from damaging a high inrush current that could burn its windings. Also, the smooth increment in speed avoids the jerks that could potentially damage the belts & pulleys & reduce the mechanical life of the motor.
Since it reduces the input voltage that corresponds to the input current which is directly proportional to the starting torque of the induction motor, it significantly reduces the starting torque. This is why Soft starters are used for low or medium starting torque applications.
It offers a fully adjustable acceleration & deceleration of the motor. Varying the firing angle slowly or quickly can control the acceleration during startup & deceleration during stopping of the motor. This is used in applications where startup acceleration needs to be adjusted.
There are no power surges in the mains due to the sudden draw of a huge current by the motor at startup. The DOL can cause voltage dips in the system that could damage other equipment.
Some applications require the motor to start & stop multiple times in a small period of time. Such motor if used with a DOL starter will experience overheating due to high starting current. However, soft starters drastically increase the number of startups for a motor in a specific duration.
The overheating of a motor is a very serious problem. It occurs due to the high winding current during its startup. The soft starter allows a very small amount of starting current which prevents the overheating of the motor.
The soft starter as compared to a DOL starter improves the lifetime of the motor. It is due to the smooth operation & absence of electrical & mechanical stress on the motor.
The DOL motor starter supply full voltage (very high inrush current) to the motor that consumes too much energy. A soft starter significantly reduces it & allows a gradual increase in energy consumption. Also, the power switches are controlled using a very low voltage level. It improves the overall efficiency of the motor.
Since it offers a gradual and smooth increase in speed & it is more reliable, it can be used for heavy motor such as in cranes, conveyor belts, etc.
Related Posts:
- Single-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Three-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
Differences between DOL & Soft Starter
The following table shows the main differences between DOL and SOFT Motor starters.
| Direct On-Line Starter | Soft Starter |
| A type of motor starter that supply full voltage to the motor at startup. | A type of motor starter that reduces the voltage to the motor at startup. |
| It does not reduce the starting inrush current. | It reduces the starting inrush current. |
| It is used for low rated motors below 5 HP. | It is used for heavy motors above 5 HP. |
| It cannot prevent the mechanical jerks at startup. | There are no mechanical jerks at starting & stopping of the motor. |
| The huge current draw causes voltage dips in the circuit. | It does not cause any voltage dip in the line. |
| It offers high starting torque. | It offers low to medium starting torque. |
| There is no acceleration or deceleration control. | The acceleration & deceleration can be programmed for starting & stopping a motor. |
| It has a very simple design. | It has a complex design with logic circuitry. |
| It is very cheaper. | It is very expensive. |
| The startup cycles are limited to a few times in a minute otherwise the winding would overheat. | It increases the startup cycles of the motor significantly. |
| It is smaller in size. | It is larger in size due to complex circuitry & large heat sinks required for thyristors. |
| The motor needs frequent maintenance. | It needs less maintenance than DOL starter |
| Its efficiency is less than a soft starter. | It has high efficiency. |
Overall, the DOL starter being cheaper & due to its full voltage supply at startup should be used for low power machines to avoid any damage. While the soft starter must be used for high power machines where low or medium starting torque & smooth starting & stopping is necessary like in conveyor belts, cranes. Water pumps etc.
Related Posts:
- What is Soft Starter? Its Working, Diagram and Applications
- Direct Online Starter – DOL Starter Wiring Diagram for Motors
- Star Delta Starter – (Y-Δ) Starter Power, Control and Wiring Connection
- STAR-DELTA Starter Motor Starting Method Without Timer
- What is Motor Starter? Types of Motor Starters and Motor Starting Methods
- Motor Protection – Types of Faults and Protection Devices
- Types of Electric Motors – Classification of AC, DC & Special Motors
- What is a Contactor ? Types, Working and Applications
- Why We Need to Install a Starter with a Motor?




Thank you for clear explanation.