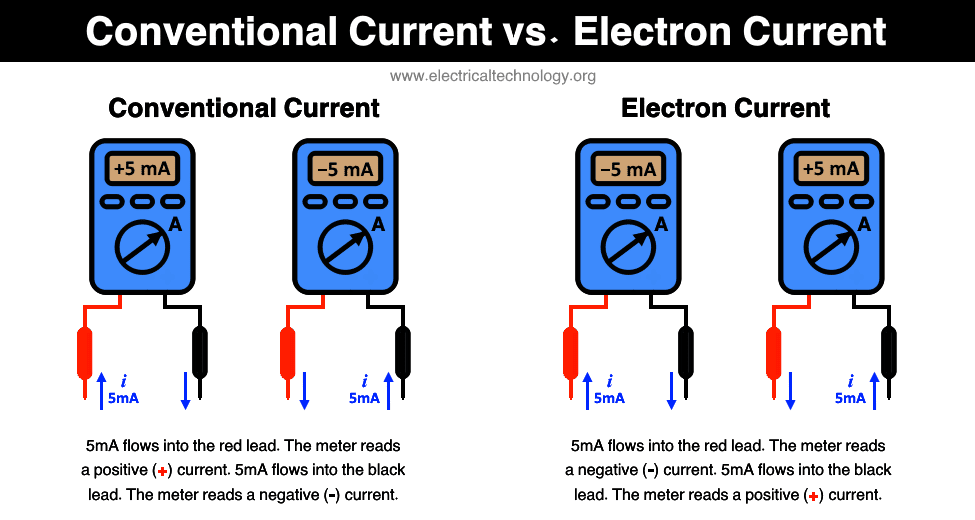
Difference between Electron Current and Conventional Current
What is the Difference between Conventional Current and Electron Current?
The electrical & electronics engineering is the study that revolves around the electric current. Electric current can be classified into electron current & conventional current. One has to understand the basics of electron current, conventional current & the difference between them.
You may have heard the debate; which is the correct current electron current o conventional current. Some say the conventional current is correct, others say the electron current is true. You might know the answer if you have studied it before. This article explains both types of current & the differences between them. They are quite the same since both of them are the flow of charges also known as Electric current but they are different in some aspects.
Related Posts:
- Difference between AC and DC (Current & Voltage)
- Difference Between Electric Current and Electric Charge
- Difference Between Current and Voltage
Before going into the differences between them, let’s learn their basics first & how they came to be.
Electric Current
The flow of charge particles or the rate of flow of electric charge through a point in a conducting medium is called electric current. The charge particles can be negative or positive.
The electric current is divided into two types of current based on its directions.
Electron Current
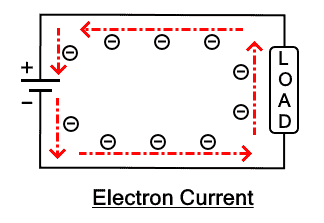
The flow of negatively charged particles also known as electrons is called electron current. It flows from the negative terminal of the power source to the positive terminal.
Conventional Current
The current produced due to the flow of positively charged particles is called conventional current. It flows out from the positive terminal of the battery into the negative terminal. Another words, the rate of flow of holes through a conductor through a fixed point is called conventional current.

Related Posts:
- Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power Supply
- Difference between Electrical Engineering and Electronic Engineering
Why Conventional Current when Electron Current is Correct?
The electricity was discovered before the discovery of the electron. It was assumed to be the flow of positively charged particles & that it moves from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. But their assumption was found wrong once the electron was discovered. So in practice, the electric current is the flow of electrons (negatively charged particle) & it moves from the negative terminal out to the external circuit & then into the positive terminal of a cell.
Since the conventional current was used way before the discovery of electron current, many rules, laws & formulas were established that would cause confusion in the new students if it were to change at that time. Such as the arrowhead shape of a diode represents the current direction & in the transistors. Also, the left-hand-rule & the right-hand-rule is based on the conventional direction of the current. However, the direction of the current does not affect the properties of the circuit as long as you keep it consistent. Therefore, the conventional current is taken as the standard current direction.
For example, Kirchhoff’s current law says that the sum of current going into a node is the same as the sum of current going out of the node. Changing the directions does not matter as long as you keep them consistent throughout the circuit. The law is still true for inverting the directions.
Related Posts:
- What is Resistance? Resistivity (ρ) & Specific Resistance Ω.
- What is Voltage? its Unit, Formula, Types & Applications
- What is Electrical Power? Types of Electric Power and their Units
Differences between Electron Current & Conventional Current
The following comparison list shows some of the differences between electric and conventional current.
| Electron Current | Conventional Current |
| The electron current is the flow of negative charges or electrons through a conductor. | The conventional current is the flow of positive charges or holes through a conductive medium. |
| Electron current flows from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of the battery. | The conventional current flows from the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal. |
| It flows from electronegative potential to electropositive potential. | It flows from the electropositive potential to electronegative potential. |
| The electronegative potential has a high density of electrons compared to the electropositive potential. | The electropositive potential has a high density of positive charge compared to the electronegative potential, therefore, it flows out. |
| Electron current flow is technically the correct direction of current flow. | Its direction is considered by convention & it is technically wrong. |
| It is discovered after the discovery of electricity. | This direction was assigned at the discovery of electricity. |
| The electrical rules such as right-hand & left-hand and many other would change using this direction. | Many electrical components symbols were designed based on its direction such as a diode, transistor |
| It is the real and actual direction of electric current. | It is assumption to solve and analyze electric circuits easily. |
| It is used in the recent books and circuit analysis techniques especially in electronic engineering books. | It is an old school consideration mainly used in electrical engineering books. |
To conclude this article, the direction of the current flow does not matter. What matters is to keep consistency in a circuit while considering either of the two directions. Technically, the electron flow is the correct direction but the conventional flow has made its way through many electrical formulas, rules & graphical representation of components. Therefore, it is much easier to use now.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Grounding, Earthing and Bonding
- Difference Between Active and Reactive Power – Watts vs VA
- Difference Between EMF and MMF
- Difference Between Voltage and EMF?
- Difference between Analog and Digital Multimeter
- Difference between Analog and Digital Circuit
- Difference Between GFCI and AFCI
- Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- Difference Between 8085 & 8086 Microprocessor
- Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit