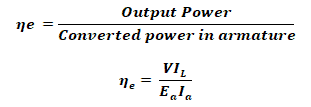DC Generator Formulas and Equations
DC Series and Shunt Generator Formulas & Efficiency, Power & EMF Equations
Shunt Generator:
Terminal Voltage:
V = Ea – Ia Ra
Where
- Ea is the armature induced voltage
- Ia is the armature current
- Ra is the armature resistance
Terminal Current:
Ia = If + IL
where If Is the field current & IL is the load current
The Field Current:
If = V / Rsh
Where
- If is the field current
- Rsh is the shunt field resistance
EMF Equation For DC Generator:
The EMF generated per conductor in a DC generator is:
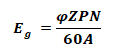
Where
- Z = number of conductors
- P = number of Poles
- N = Speed of rotor in RPM
- A = number of parallel paths
The EMF generated per path for a wave winding & lap-winding;

So the generalized equation for generated EMF of DC generator is:
Eg = kΦω
Where
- K = ZP/2πA = constant of the DC machine
- ω = 2πN/60 = angular speed in rads per second
Related Posts:
- EMF Equation of an Alternator and AC Generator
- EMF Equation of a Transformer
- EMF Equation of a DC Motor
Torque of DC Generator:
the torque of generator is directly proportional to the armature current & it is given by:
T = kfΦIa
Where
- Kf is a constant based on machine construction
- Φ is the magnetic flux
- ω is the angular speed

Where N is the speed in Rotation Per Minute (RPM)
Power Generated & Load Power
The power generated by a shunt generator is given by:
Pg = ωT = EaIa
PL = VIL
Where IL is the load current
Series Generator:
Terminal Voltage:
V = Ea – (Ia Ra + Ia Rse)
V = Ea – Ia(Ra + Rse)
Where
- Ea is the armature induced voltage
- Ia is the armature current
- Ra is the armature resistance
- Rse is the series field resistance
The series field current is equal to the armature current;
Ia = Ise
Armature Induced Voltage & Torque:
The armature induced voltage Ea is proportional to the speed & armature current whereas the torque T of series generator is directly proportional to the square of armature current & it is given by:
Ea = kfΦωIa
T = kf Φ Ia2
Where
- Kf is a constant based on machine construction
- Φ is the magnetic flux
- ω is the angular speed

Where N is the speed in Rotation Per Minute (RPM)
Power Generated & Load Power
The power generated by a series generator is given by:
Pg = ωT = EaIa
PL = VIL
Where IL is the load current
Input Power:
Pin = ωT
Where
- ω is the angular speed of armature
- T is the torque applied
Converted Power:
Pcon = Pin – Stray losses – mechanical losses – core losses
Pcon = EaIa
Where
- Ea is the induced voltage
- Ia is the armature current
Output Power
Pout = Pcon – Electrical losses (I2R)
Pout = VIL
Where
- V is the terminal voltage
- IL is the load current
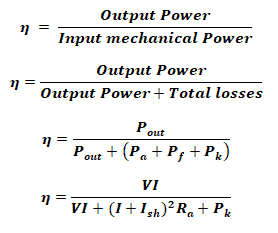
Efficiency of DC Generator:
Mechanical Efficiency:
Related Posts:
- What is Motor Efficiency and How to improve it?
- Transformer Efficiency, All day Efficiency & Condition for Maximum Efficiency
Electrical Efficiency:
Overall Efficiency:
- Pout is the useful output power
- Pa is the armature copper loss
- Pf is the field copper loss
- Pk is the constant losses that contains core losses & mechanical losses
Maximum Efficiency:
The efficiency of the dc generator is Maximum, when;
Variable power loss = Constant power loss
Copper loss = Core & mechanical loss
Copper loss (I2R) such as armature and field copper loss are variable loss because they depend on current. While the core loss such as hysteresis and eddy current loss, mechanical loss such as friction losses are all constant losses.
Related Formulas and Equations Posts:
- Power, Voltage and EMF Equation of a DC Motor – Formulas
- Synchronous, Stepper and AC Motors Formulas and Equations
- Induction Motor & Linear Induction Motors Formulas & Equations
- Transformer Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Generator and Alternator Symbols