Current Source – Types of Dependent & Independent Current Sources
What is Current Source? Different Types of Current Sources
Humans have evolved to use different kinds of tools and equipment using different kinds of energy obtained from various sources. One of the most used forms of energy in the modern day is electrical energy. The power that is used to run every machine from a small hair trimmer in your home to heavy machinery in industries. This electrical energy is supplied by an electrical source.
An electrical source is a device that converts any other form of energy into electrical energy. It can be hydel, wind, light, nuclear, thermal, chemical, mechanical energy, etc. An electrical source is a general term that can be classified into two main types
- Voltage Source
- Current Source
In this article, we are going to discuss the current source in detail.
What is Current Source?
A current source is an electrical source that provides constant current irrespective of the voltage across its terminals. The voltage across its terminals is determined by the load impedance connected. It drives a constant current through the impedance & it does not change at any cost. So in theory, such a source can provide the infinite electrical energy which is also termed an ideal current source.
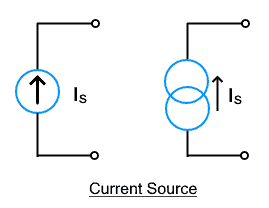
Current sources are rated in Amperes or Amps. Symbolically it is represented by an arrow that shows the direction of the current flow. The direction of the current also determines the polarity of the corresponding voltage.
Related Posts:
- What is Voltage Source? Different Types of Voltage Sources
- Difference Between Voltage Source and Current Source
Types of Current Sources
Current sources can be classified into two main types
- Independent Current Source
- Dependent Current Source
Independent Current Source
A current source that provides current that is not dependent on other variables in the circuit. It is represented by a circle around an arrow showing the current direction. The current supplied is independent of the value of any other parameters in the connected circuit.
An independent source can be further categorized into two types
- Direct Current Source
- Alternating Current Source
Direct Current Source
A direct current source or DC current source is a type of current source that delivers current that does not change with time i.e. its magnitude and direction remain the same. The direction of the current flow is determined by the arrow.
The given direction of the current flow is for the conventional current that is supposed to flow from the corresponding positive terminal into the negative terminal of the source. The direction of the electron current will be opposite to the given direction.
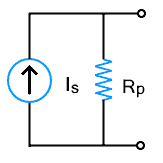
A DC current source has an internal resistance that is connected in parallel with it. The parallel resistor Rp is very high, ideally, it is infinite i.e. open circuit.
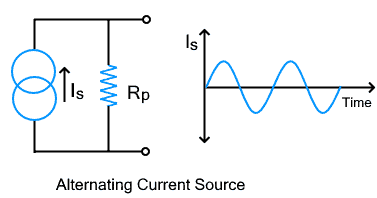
Alternating Current Source
The alternating current source or AC current source provides current that periodically varies with time. However, the RMS value remains constant. The current swings between its positive and negative peak value about its mean position forming a sinusoidal waveform.
As the magnitude swings between positive & negative values, the direction of the current changes periodically at a known frequency. Therefore it doesn’t have a fixed direction as shown by the wavy shape in its symbol.
Related Posts:
- What is Voltage? its Unit, Formula, Types & Applications
- What is Electric Current, its Unit, Formula, Types & Applications
Dependent Current Source
A dependent current source supply current whose magnitude depends on other variables in the connected circuit. It does not supply constant current but it varies with changes in other electrical parameters. Symbolically, it is represented by a diamond shape in a schematic.
Dependent current sources can be classified into a current-controlled and voltage-controlled current sources.
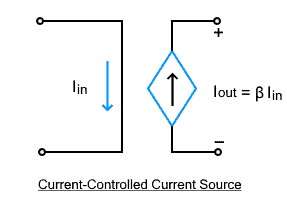
Current Controlled Current Source
Such type of dependent source supplies current to a load that depends on current somewhere else in the circuit is called the current controlled current source or CCCS. Its current can be controlled by varying the value of the controlling current as it is proportional to it. It has four terminals where the dependent current source is represented by a diamond shape.
The input current Iin is the controlling current whereas the output of the dependent source is the controlled current Iout given by βIin. Where the ‘β’ is the multiplying current constant also known as the current transfer ratio or current gain. It is a unitless constant.
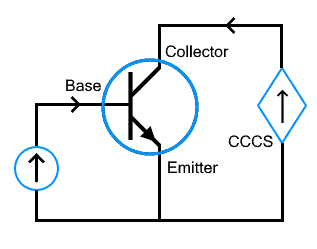
Here is a very basic example of CCCS, a bipolar junction transistor BJT. It is a current controlling current device where the base current Iin controls the emitter current Iout. The emitter current is the dependent current which is β times base current Iin.
Related Posts:
- What is Electrical Power? Types of Electric Power and their Units
- What is Resistance? Resistivity (ρ) & Specific Resistance Ω.
Voltage Controlled Current Source
Such a type of dependent source whose current depends on the amount of voltage somewhere else in the circuit is called voltage controlled current source or VCCS. The current supplied by the dependent current source is controlled by voltage. It has four terminals where the two terminals.
The output current Iout is directly proportional to the input voltage Vin. The Iout is given by ‘αVIN‘ where the α is the multiplying constant or ratio between the output current Iout in input voltage VIN. Its unit is Ampere/Volts or mhos ℧ as it is opposite of ohms.
A basic example of VCCS is a field effect transistor, FET. The voltage applied across its gate & source terminal is the controlling voltage that controls the output drain current. If there is a current source connected between the drain & source terminal, it will be a dependent current source controlled by the gate voltage.
Ideal Current Source
An ideal current source delivers constant current irrespective of the voltage across its terminals or variation in the load. It is an independent source with infinite internal resistance. The current with respect to the voltage/time graph shows a straight line without any change as shown in the figure below.
Theoretically, an ideal current source provides infinite energy which is not possible. However, they are used for circuit analysis.
The ideal current source has the following characteristics
- It provides a constant current independent of the variation in the load or voltage across it.
- Its internal resistance is infinite.
Related Posts:
- What is Electricity? Types, Sources & Generation of Electricity
- What is Electrical Energy? Its Unit, Formula & Applications
Practical Current Source
Particle current source provides current to a load that varies with the change in the load as well as time. As the current source depletes of the charge, the current supply also decreases. It has a very large internal resistance that is connected in parallel with it.
Parallel & Series Operations of Current Sources
Current Source can be connected in parallel & series to increase its performance.
Parallel Operation of Current Sources
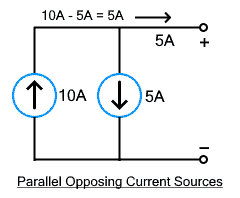
When current sources are connected in parallel their net current is the algebraic sum of the individual current. It acts like a single current source. Their sign is determined by the direction of the current. Therefore, they can be added using two types of configuration parallel aiding and parallel opposing.
In parallel aiding, the current of both supplies adds up where the net current increases. The direction of the current is the same for both current sources. It is mostly used to increase the current of a current source.
In the parallel-opposing type, the current sources are connected in the opposite direction as the direction of the current opposes each other. The net current is the difference between both currents & its direction is determined by the source with the greater current rating. This configuration is not used.
Series Operation of Current Sources
When multiple current sources are connected in series, their current does not add up. Therefore it should not be connected in series even if they have the same current or different current ratings. Therefore there are no series-aiding or series-opposing currents in current ideal current sources.
Related Posts:
- Difference between AC and DC (Current & Voltage)
- Difference Between Current and Voltage
- Difference Between EMF and MMF
- Difference Between Voltage and EMF?
- Difference between Electron Current and Conventional Current
- Difference Between Current Transformer & Potential Transformer
- Difference between Electric Field and Magnetic Field
- Difference Between Electric and Magnetic Circuit
- Differences Between Electrostatic & Electromagnetic Terms
- Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power Supply
- Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit – Comparison
- Difference Between Overcurrent, Overload and Overvoltage
- Difference Between Electric Current and Electric Charge
- Difference Between Active and Reactive Power – Watts vs VA
- Difference between Analog and Digital Multimeter
- Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor