Constant Current Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
Constant Current Diode: It’s Symbol, Working, Construction, Characteristics, Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications
A diode is a semiconductor-based component very extensively used in every electronic circuit. It is a unidirectional switch that allows current in only one direction. It offers nearly zero resistance in one direction but very high resistance in the other direction. Its two terminals are named anode and cathode.
The diode has several other types designed for their special functions such as LEDs, Zener diode, and Schottky diode. One of those types of diodes is a constant current diode which we are going to discuss in this article.
What is a Constant Current Diode?
Constant current diode or CCD is a special type of diode that allows a constant amount of current of its maximum limit. It is also known as the Current Limit Diode “CLD” or Current Resisting Diode “CRD”. It allows current through it to rise to a specific level and then stay constant. It works analogously to the voltage limiting of a Zener diode. The current does not change even if the voltage across it changes. However, unlike Zener, it only operates in forward bias and does not work in reverse bias.
It is a protection device used to protect a circuit from overcurrent or short circuits.
Related Posts:
- What is Diode? Construction and Working of PN Junction Diode
- Types of Diodes and Their Applications – 24 Types of Diodes
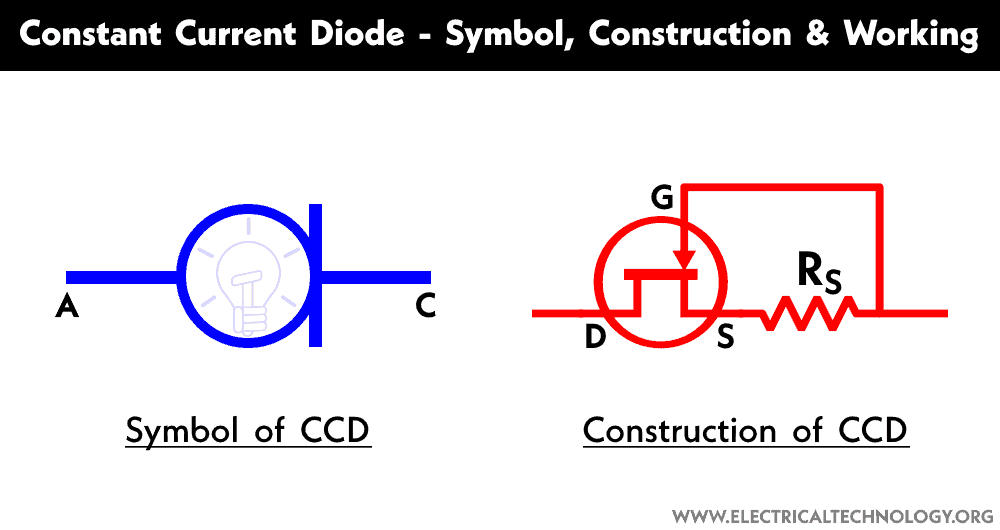
Symbol
The symbol of the constant current diode does not resemble a conventional diode, however, the bar represents the cathode terminal of the CCD as shown in the figure below.
Construction
The constant current diode is made of an N-channel JFET. The gate and source terminal of the JFET is shorted through a resistor Rs. Thus making it a two-terminal device. The drain acts as the anode terminal and the other terminal acts as the cathode. The configuration makes it a current source or current limiter similar to a Zener diode. It allows a current to rise up to a specific limit.
Working
A constant current diode limits the current flow similar to the voltage limiting of a Zener diode. It regulates the current. It only works in forward bias. Initially, with the increase in applied voltage, the diode current rises until the pinch-off occurs and the current starts to stabilize. Further increase in the voltage does not vary the current. This current is known as pinch-off current.
The CCD can tolerate the forward voltage up to a certain limit without changing the current. Once the voltage exceeds this limit, the junction breaks and the current violently increases. This voltage is known as the breakdown voltage. This causes irreversible damage to the device and must be avoided.
In reverse bias, it acts as a normal PN junction diode. It does not allow current flow until the reverse voltage exceeds the reverse breakdown voltage and infinite current start flowing.
Related Posts:
- Fast Recovery Diode: Construction, Working and Applications
- Step Recovery Diode – SRD: Construction, Working and Applications
IV Characteristic of Constant Current Diode
The IV characteristic curve shows the relationship between the applied voltage and the diode current. The given graph shows the IV characteristic curve for a constant current diode. The VAK is the applied voltage to the anode-cathode represented by the horizontal axis while the ID is the diode current represented by the vertical axis.
As shown in the graph, the right portion of the curve is the forward bias characteristic while the left portion is the reverse characteristic of CCD.
Initially with the increase of forward voltage, the diode current increase. With further increase in the voltage, the current increases up to the pinch-off current Ip. The diode current Id stabilizes and does not increase above the Ip. Further increase in the voltage does not vary the current up till the breakdown voltage. At this voltage, breakdown occurs and the current increases rapidly.
In reverse bias, the diode does not allow current. However, there is a reverse leakage current. When the reverse voltage increase above the reverse breakdown voltage VR the diode starts conduction in reverse.
CCD in a Circuit
CCD is used to control the current flow through the load. For example, an LED is connected to a battery through a CCD. It will limit the current flow through the LED. However, the current ratings should match the requirement of the LED.
In case the permissible current of the CCD is low, a parallel combination of CCD will increase its allowable limit.
To have a stable current with increased voltage, a Zener diode in addition to CCD will do the job.
Related Posts:
- Schottky Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages and Applications
- Shockley Diode: Construction, Working, Characteristics and Applications
Advantages and Disadvantages of CCD
Advantages
Here are some advantages of constant current diode
- It provides a constant current.
- It protects against current spikes and short circuits.
- Voltage fluctuation does not affect its current flow.
- It is simple and easy to use. It doesn’t require biasing.
- Its performance is not affected by the change in temperature.
- Easier to modify its current capacity by using the parallel combination.
Disadvantages
Here are some disadvantages of constant current diode
- It only operates in forward bias.
- A reverse voltage spike can permanently damage it.
Applications
CCD due to its compact design and small size is used in numerous applications as given below.
- It is used in any application that requires constant current irrespective of the load.
- It is used in battery chargers, power supplies, etc.
- It is used as a current source for driving a long string of LEDs.
- It is used for stabilizing the brightness of LED.
- It is used to provide the control signal to an SSR (solid state relay).
- It is used as a constant current source for various sensors.
- It is used in waveform generators and other timing circuits.
- It is used for testing other semiconductor devices.
Related Posts:
- PIN Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Point Contact Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Gunn Diode: Symbol, Construction Working and Applications
- Varactor Diode – Symbol, Construction, Working and Applications
- LED – Light Emitting Diode: Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Photodiode: Types, Construction, Operation, Modes, Performance and Applications
- Backward Diode: Construction, Operation, Characteristics and Applications
- What is a Laser Diode? Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- What is Avalanche Diode? Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Tunnel Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages, and Applications
- Zener Diode – Symbol, Construction, Circuit, Working and Applications
- Blocking Diode and Bypass Diodes in a Solar Panel Junction Box
- Diode Formulas and Equations – Zenner, Shockley and Rectifier
- Diode Symbols – Electronic and Electrical Symbols
- Applications of Diodes