Magnetic Terms used in Magnetic Circuits – Definition & Formulas
Magnetic and Magnetism Important Terms, Definition and Formulas
Magnetic Field or Magnetic Induction (B)
Magnet or Electromagnet produces a Magnetic field. The field where the magnet attracts or repels magnetic materials such as iron, steel, etc. it may be defined as a force on a moving charge,
F = q x v x B
Where
- F = Force,
- V = Speed of Particles,
- B = magnitude of the field.
Good to Know:
It is a vector quantity and The SI Unit of magnetic Field is Tesla where, 1 Tesla = (Newton x second) / (coulomb x meter) 10,000 Gauss. The Formula for the magnetic field in SI is B = µ○ (H+M) and in CGS is B = H+4π M.
A wire carrying a DC current or permanent magnet produces magnetostatic (Stationery) field and its magnitude and direction remain same. While Alternating current or Pulsating DC current carrying conductor creates alternating magnetic field which continuously change their direction and magnitude.
Also Read
Magnetic Field Strength (H)
The amount of magnetizing force (how much force it has to magnetize, magnetic materials such as iron, steel, etc) is called Magnetic field strength which is denoted by (H). It is inversely proportional to the length of wire and directly proportional to the current passing through it. The SI unit of Magnetic Field Strength is Ampere/meter (A/m) and it is a vector quantity and the SI formula for Magnetic Field strength is
H = NI / 1c
Where 1c = magnetic path in meter.
- 10+ Design & Simulation Tools for Electrical/Electronics Engineers Online
- 15 Must Have Android Apps for Electrical & Electronics Engineers & Students
Magnetic Flux (Φ)
In simple words, Magnetic field x area perpendicular to the magnetic field (B) is called Magnetic Flux which is denoted by Φ or Φm or ΦB. Or it is the amount of magnetic field or magnetic lines of force passing through a surface like conducting area, space, air, etc. The SI Unit of magnetic flux is Wb (Weber). The Formula for finding magnetic flux in the SI system is;
Φ = BAc
Where
Ac = area in m2
And CGS unit and formula for Magnetic Flux is Maxwell (M) and Φ = BAc Ac = area in cm2 respectively.
- Maximum Flux Density (Bmax) Calculator. (Formulas & Equations)
- A simple Electrical Project ( Magnet levitation)
Magnetization (M)
The state of a material being magnetized or the process in which magnetic materials are magnetized. It is the density of permanent magnet or electromagnet dipole moments in magnetic materials. Or the magnetic moment (m) per unit volume (v) by a magnetic field is called Magnetization. The SI Unit of Magnetization is Ampere/meter (A/m) and it is also a vector quantity. The SI formula for Magnetization is
M = m/V
Where,
- m = Total magnetic moment
- And V= volume in m3.
The CGS unit and formula of Magnetization is Emu/cm3 and M = m/V respectively, where, m = Total magnetic moment, V = volume in cm3 and EMU = Electromagnetic units. It may also be defined in term of M = (N/V) x m → M = nm ……. (N/V) = n. Where, “m” is the magnetic moment and “n” is the number density of magnetic moments.
Magnetic Permeability of vacuum (µ○)
In funny words, Perm = Permission and ability is the feature or skill to do something. I.e. permeability (µ) it is the ability of a material that how does it easily magnetize?
Magnetic Permeability of vacuum
It is the amount of resistance encountered to the magnetic field when forming in a vacuum.
The SI unit of Permeability is (H·m−1), or Newton per ampere squared (N·A−2). The SI unit and formulas of Magnetic Permeability of vacuum is Newton/Ampere2 and µ○ = 4πx10-7 ≈ 1.2566370614 H·m−1 respectively. The CGS unit of magnetic permeability of vacuum is 1.
Good to know: The opposition of magnetic permeability is Magnetic Reluctivity.
Good to Know: Famous magnetic relation is B = µH where µ is permeability which is a scalar quantity, B is the magnetic field and H is magnetizing force or Magnetic Field Strength.
- Why AC rated in Tons, Not in kW or kVA? A Guide about Airconditioner and Refrigeration
- Testing Electrical and Electronics Components and Devices with Multimeter
Inductance (L)
Inductance is the property of conductor, coil or wire which opposes the change of current flowing through it. The change of current flowing through a conductor produces a voltage called Back EMF or Electro motive force.
Even The change of current flowing through a conductor or coil produces voltage through it which is called Self induced EMF and in any nearby coils or conductors which is called Mutual inductance. The SI unit of Inductance (L) is Henry “H” and formula is
L = µ○ µ N2 Ac/1c
Where
- N = Turns
- Ac = Area in m2
- 1c = magnetic path in meter
CGS unit and formula of Inductance is Henry “H” (Joseph Henry) and L = 0.4π µN2Ac/1c x10-8 respectively
where;
- L = Inductance
- N = Turns
- Ac = Area in cm2
- 1c = magnetic path in cm.
Good to Know: 1 H = 1 Wb/A (One Henry = 1 Weber per Ampere)
Self Inductance formula
L = µ○ (N2xA)/l
Where:
- L = in Henries
- μο = the Permeability of Free Space (4.π.10-7)
- N = the Number of turns
- A = the Inner Core Area (π.r 2) in m2
- l = the length of the Coil in meters
Mutual Inductance formula
M = μο μrN1N2A/l
Where:
- µo = the permeability of free space (4.π.10-7)
- µr = the relative permeability of the soft iron core
- N = in the number of coil turns
- A = in the cross-sectional area in m2
- l = the coils length in meters
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Electric and Magnetic Circuit
- Difference between Electric Field and Magnetic Field
Voltage or E.M.F (V)
The Electric Potential Difference between two points is called Voltage. Or the work done per unit charge in a static electric field to move the charge between two points, so the equation becomes as
V = W/q or E/q.
Where;
- V = Voltage
- E = Energy in joules
- q = Charge in Coulombs
Or the electric potential energy per unit charge is called Voltage.
In Ohm’s Law, Voltage = V = I x R, Where I = Current in amperes and R = Resistance in Ohms (Ω)
The SI unit of Voltage is the Volt (V) or Joules per Coulomb. Where 1V = 1Joule/1Coulomb
The SI formula of Voltage is
V = -N dΦ/dt
Where;
- N = number of coil Turns
- dΦ = rate of the Change in flux
- t = time
Good to know: Other related words used for Voltages and EMF are, Electrical Potential Difference, Electric Tension , Electric Pressure, potential difference, P.d, E.M.F, Electromotive force and it is a scalar quantity and it is a type of Electrical Energy.
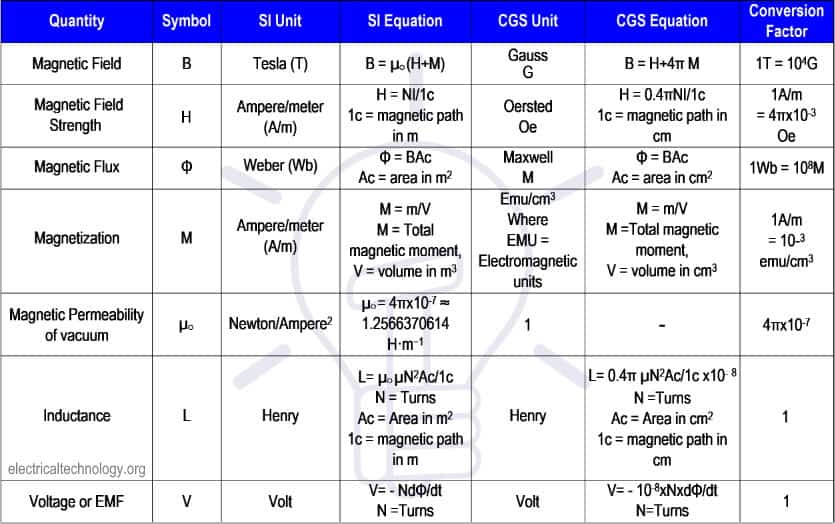
The following table shows all the above basic terms used in magnetic circuits with SI and CGS units and formula.
| Quantity | Symbol | SI Unit | SI Equation | CGS Unit | CGS Equation | Conversion Factor |
| Magnetic Field | B | Tesla (T) | B = µ○(H+M) | Gauss (G) | B = H+4π M | 1T = 104G |
| Magnetic Field Strength | H | Ampere/meter
(A/m) |
H = NI/1c
1c = magnetic path in m |
Oersted
Oe |
H=0.4πNI/1c
1c = magnetic path in cm |
1A/m
=4πx10-3 Oe |
| Magnetic Flux | Φ | Weber (Wb) | Φ = BAc
Ac=area in m2 |
Maxwell
M |
Φ=BAc
Ac = area in cm2 |
1Wb =108M |
| Magnetization | M | Ampere/meter (A/m) | M=m/V
m = Total magnetic moment, V = volume in m3 |
Emu/cm3
Where EMU = Electromagnetic units |
M=m/V
m=Total magnetic moment, V = volume in cm3 |
1A/m
= 10-3 emu/cm3 |
| Magnetic Permeability of vacuum | µ○ | Newton/Ampere2 | µ○ = 4πx10-7 ≈ 1.2566370614 H·m−1 | 1 | – | 4πx10-7 |
| Inductance | L | Henry | L = µ○µN2Ac/1c
N = Turns Ac = Area in m2 1c = magnetic path in m |
Henry | L=0.4π µN2Ac/1c x10-8
N=Turns Ac=Area in cm2 1c = magnetic path in cm |
1 |
| Voltage or EMF | V | Volt | V = – NdΦ/dt
N=Turns |
Volt | V =
-10-8xNxdΦ/dt N=Turns |
1 |
Following is the table in image format as a ref.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between EMF and MMF
- What is a Solenoid and Solenoid Magnetic Field
- Electric circuits / Networks and important terms related to it you must know
- Electric Phase or Line Tester: Construction and Working






hi sir maam i wanna study for free
Make correction in v=i/r
Its actually v=ir
But nice