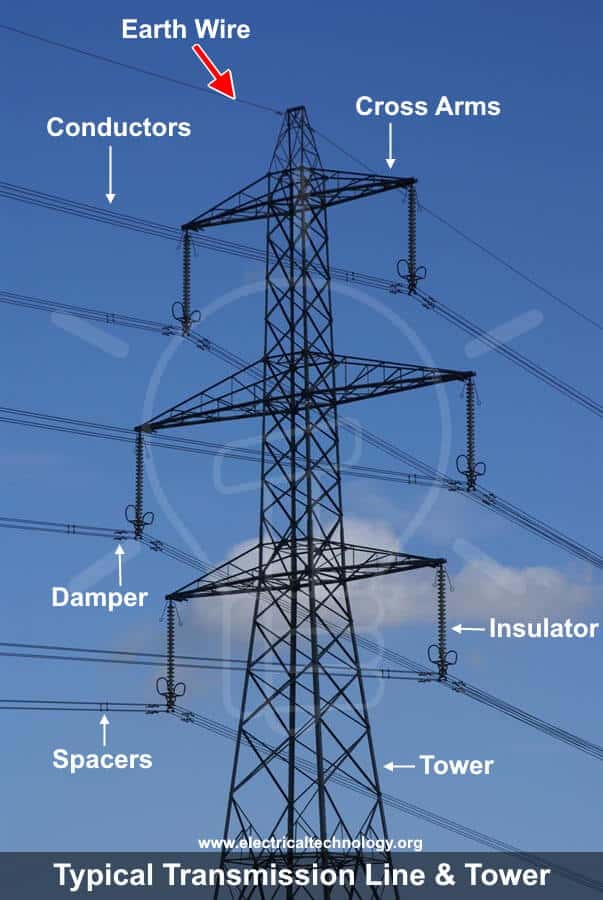
The Role of Earth Wire or Ground Wire in Overhead Power Lines
Ground wire or earth wire (also known as OPGV) is a bare conductor supported at the top of transmission towers. They serve to shield the line and intercept lightning stroke before it hits the current carrying conductors below i.e. power lines.
Ground wires normally do not carry current. Therefore, they are often made of steel. The ground wires are solidly connected to ground at each tower in transmission and distribution system.
Click image to enlarge
In power systems, ground wire is provided in overhead transmission lines having voltages of 110kV and above. In modern power systems, there are two ground wires on transmission tower instead of single for better protection. These earth wires has no effect on switching surges and the coupling effect is higher with low serge impedance as compared to single earth wire.
In case of lightning strikes, the resistance between earth and tower base should be low for effective protection. when lightning hit the ground wire, the produced waves travel along the line in opposite direction and reach to the adjoining tower. The tower passes them safely to the earth which ensures no power outage in case of lightning stroke faults.
The main purpose of ground wire is to protect the power lines conductors from direct lightning strokes. In HV transmission lines, lightning strokes may cause a voltage rise at the tower peak before reaching to the ground wire which may back flash-over from the tower to the conductors and insulators.
To minimize the chances of insulator flash-overs, it is important to reduce the increase in voltage on the top of the tower as ground wire is not enough to protect the insulator set from flash-over. The chance of fault may be reduced by proper grounding and earthing of the poles and tower by deep earthing rods or counterpoise wires.
Related Posts:
- Why is the Ground Wire Always Positioned Above the Overhead Power Lines?
- Why is the Grounding Wire Bare and Not Insulated?
- Why are Overhead Power Transmission Lines Not Insulated?
- Difference Between Grounding, Earthing and Bonding
- Difference Between Real Ground and Virtual Ground
- What is the Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth?
- Why are Salt and Charcoal Added in Earthing Pit for Grounding?
- Why are Stones Used in an Electrical Substation?
 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode