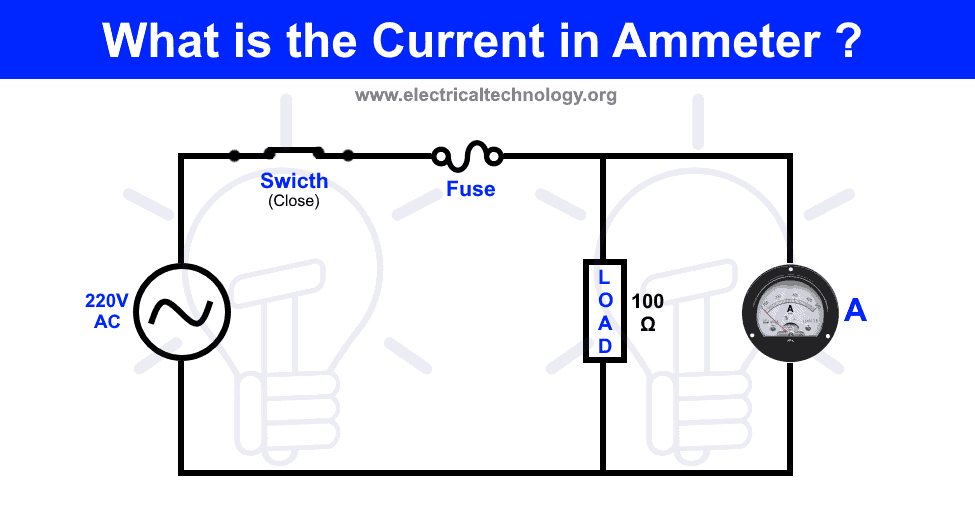
If an Ammeter is Connected in Parallel with Load, What is the Deflection?
Basic Electrical Engineering Interview Question Series: An Ampere meter is connected in parallel with the 100 ohms load and 220V AC Supply. What is the current value flowing through ammeter?
Short Answer: Boom and Ammeter will blow if there is no fuse or circuit breaker.
Explanatory Answer:
Ammeter (short version of Ampere meter) is always connected in series due to the low internal resistance and proper current measurement as compared to voltmeter which is connected in parallel. If an ammeter is connected in parallel, the circuit current will chose a least resistive path for flow of electron i.e. current will ignore the load in resistance and flow the ammeter circuit which may destroy the ampere meter.
As shown in the fig above, ampere meter is connected such a way like a short circuit path in the basic circuit.
Now, If we analyze the circuit where ampere meter is connected in parallel with the supply voltage and load. As we know that current always chose a low resistance path to flow, hence the current will bypass the 100 Ohms (current will not flow through the 100 Ohms) load in the circuit and start to flow through the ampere meter due to low internal resistance.
The current flow in this basic circuit is shown with the blue line with arrow around the circuit.
Theoretically, the flowing amount of current through the ammeter circuit is infinite if we neglect the internal resistance of ammeter.
According to the ohm’s law
I = V / R
Putting the values
I = 220V / 0Ω
I = Infinite.
As a result:
- Current will be infinite due to short circuit.
- Ammeter may start to smoke and burn if there is no fuse in the circuit.
Similar Basic Electrical Engineering Question and Answers:
- Will the Bulb Connected in This Strange Circuit Glow? And What is the Current in Ammeter?
- Clear Your Concept. What will be the Current In ampere-meter in This Basic Circuit.?
- Batteries Configuration. These Batteries have Connected in series or parallel? Clear Your Concept.
- Ammeter Basic Concept: What is the Current in Ampere Meter ?

 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode