How to Find the Value of Resistor for Different Types of LEDs Circuits
The following step by step tutorial will help you to find the proper value of a resistor (or resistors) for one or more LEDs and LEDs string circuits to design and connect with battery and power supply.
In the following guide, you will be able to learn how to:
- Calculate the value of resistors for different LEDs circuits.
- Calculate the forward current of LEDs.
- Calculate the Forward Voltage for different LEDs circuits.
- Connect LEDs in series with a battery.
- Connect LEDs in parallel with a battery.
- Connect LEDs in series-parallel combination circuits.
Update: You can Also use this LED Resistor Calculator for the same purpose i.e. finding the value of exact or nearest standard value of resistor for LEDs circuits.
Related Posts:
- How to Find the Value of Burnt Resistor ( By Four Handy Methods )
- How to Find the Value of SMD Resistors – (SMD Resistor Codes)
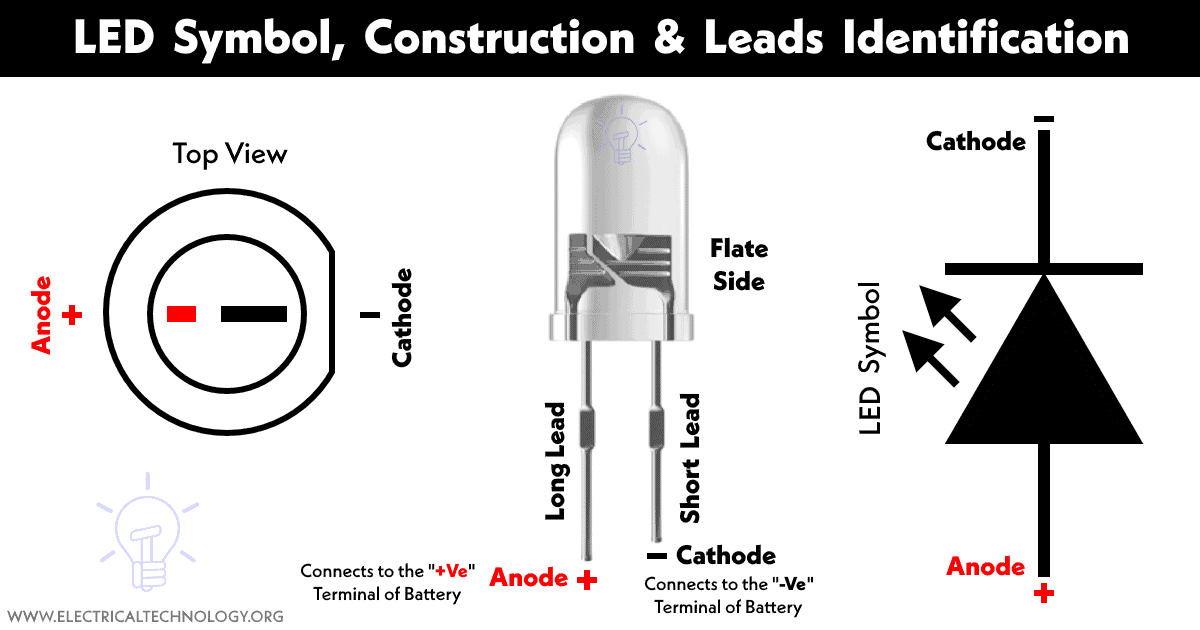
Typical LED Symbol, Construction and Leads Identification
Click Image to enlarge
Formula For Finding the Value of Resistor for an LED Circuit
Value of Resistor = (VSupply – VF) ÷ IF
Where:
- VSupply = Supply voltage
- VF = Forward Voltage
- IF = Forward Current
The following formula can be used to calculate the value of power rating of the resistor.
Power Rating of Resistor = IF2 × Value of Resistor
Finding the Value of Resistor to Connect with an LED
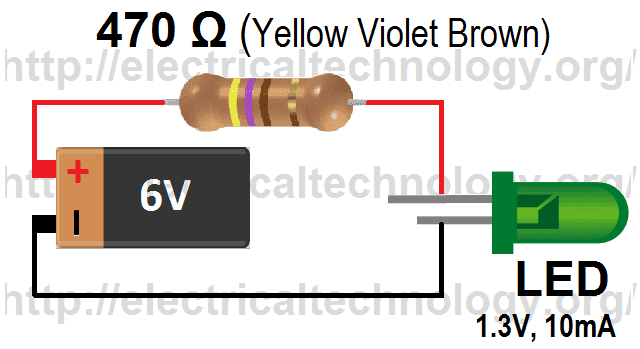
Before we go into details, let’s try to evaluate the following simple circuit. This way, it will be easier to determine the value of resistors for other complex circuits.
Click Image to enlarge
Example:
In the above simple LED circuit, the supply voltage is 6V, LED forward voltage (VF) is 1.3 Volt and forward current (IF) is 10mA.
Now the value of resistor (which we will connect in series with LED) for the above circuit would be:
Resistor Value = (VSupply – VF) ÷ IF = (6 – 1.3) ÷ 10mA = 470 Ω
Current draw = 20mA
Resistor Power rating formula for this circuit
Resistor Power Rating = IF2 × Resistor’s Value
= (10mA) 2 × 470 Ω = 0.047W = 47mW
But this is the minimum required value of resistor to ensure that the resistor will not overheat, so it’s recommended that to double the power rating of the resistor that you have calculated, therefore, choose 0.047W × 2 = 0.094W = 94mW resistor for this circuit. Resistor power rating (Value is doubled) = 0.094 W = (94 mW)
Good to Know:
- It is too difficult to find the exact power rating resistors that you have calculated. Generally, Resistors come in 1/4 watt, 1/2 watt, 1 watt, 2 watt, 5 watt, and so on. Therefore, select the next higher value of power rating. For example, if the calculated value of power rating of the resistor is 0.789W = 789mW, then you would select 1W Resistor.
- It is too difficult to find the exact value of resistors that you have calculated. Generally, Resistors come in standard values. If you are not able to find the exact value of a resistor that you have calculated, and then select the next coming value of the resistor that you have calculated, For Example, if the calculated value is 313.5Ω, you would use the closest standard value, which is 330 Ω. if the closest value is not close enough, then you can make it by connecting resistors in series – parallel configuration.
- IF = Forward Current of LED: This is the amount of maximum current that LED can accept continuously. It is recommended to provide 80% of LED forward current rating for long life and stability. For example, if the rating current of the LED is 30mA, then you should run this LED on 24mA. Value of current over this amount will shorten LED life or may start to smock and burn.
- If you are still unable to find the LED forward current, then assume it is 20mA because a typical LEDs run on 20mA.
- VF = Forward Voltage of LED: This is the forward voltage of LED i.e. the voltage drop when we supply the rated forward current. You can find this data on LEDs Packages, but it is somewhere between 1.3V to 3.5V depending on type, color and brightness. If you are still unable to find the forward voltage, simply connect the LED through 200Ω with a 6V battery. Now measure the voltage across the LED. It will be 2V and this is the forward voltage.
Related Posts:
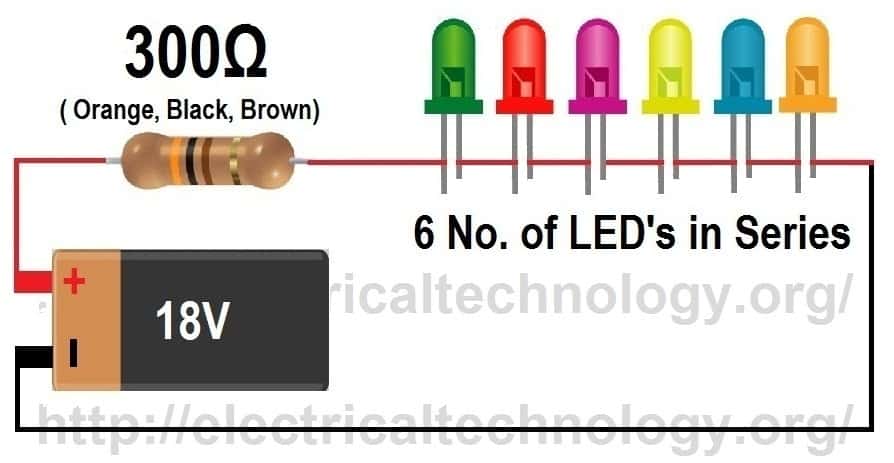
Finding the Value of Resistor to Connect with LEDs in Series
Below is another simple LEDs (LEDs Connected in Series) Circuit. In this circuit, we have connected 6 LEDs in Series. Supply Voltage is 18V, The Forward Voltage (VF) of LEDs is 2V and the forward Current (IF) is 20mA each.
Formula:
Value of Resistor for LEDs in Series = (VSupply – (VF × No. of LEDs)) ÷ IF
Click Image to enlarge
Example:
In the above series LEDs string circuit, the total forward voltage (VF) of 6 LEDs = 2 × 6 = 12V
and forward Current (IF) is same (i.e. 20mA)
(Note: this is a series circuit, so current in series circuit in each point is same while voltages are additive) Now, the value of resistor (for series circuit) would be:
= (VSupply – (VF × No. of LEDs)) ÷ IF = (18 – (2 × 6)) ÷ 20mA
= (18 – 12) ÷ 20mA = 300 Ω
Total Current draw = 20mA
(This is series circuit, so currents are same)Resistor Power Rating
= IF2 × Resistor Value = (20mA) 2 × 300 Ω = 0.12 = 120mW
But this is the minimum required value of resistor to ensure that resistor will not explode. This way, it is recommended to double the value of power rating of the calculated resistor. therefore, choose 0.12W × 2 = 0.24W = 240mW resistor for this circuit. Resistor power rating (Value is doubled) = 0.24 W = (240 mW).
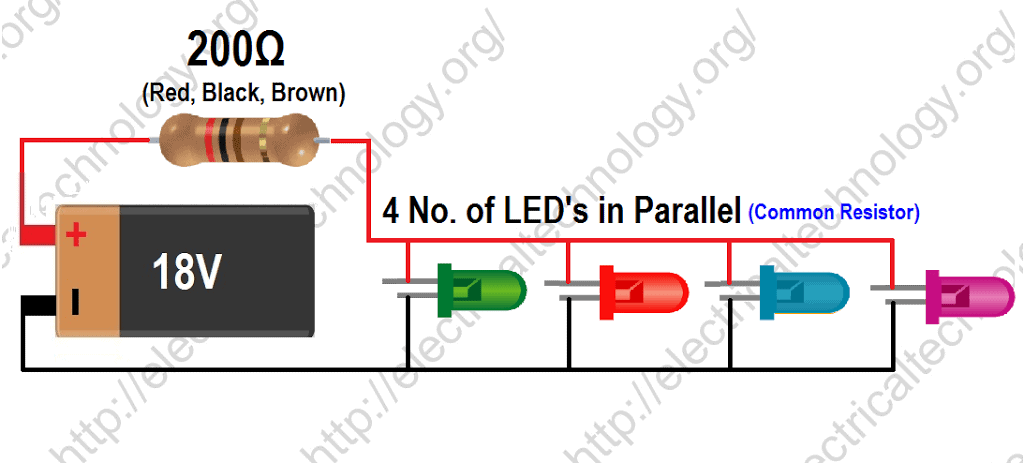
Finding the Value of Common Resistor to Connect with LEDs in Parallel
Click Image to enlarge
In this circuit, we have connected LEDs in parallel with a common resistor. Supply Voltage is 18V, The Forward Voltage (VF) of LEDs is 2V and the forward Current (IF) is 20mA each.
Formula:
Value of Common Resistor for LEDs in Parallel = (VSupply – VF) ÷ (IF × No. of LEDs)
Example:
Here, the total forward Current (IF) of 4 LEDs = 20mA × 4 = 0.08A, and forward Voltage (VF) is same (i.e. 2V)
(Note: this is a parallel circuit, so voltage is the same in each point while currents are additive).
Now, the value of resistor (for parallel Circuit with common resistor) would be:
= (Vsupply – VF) ÷ (IF × No. of LEDs)
= (18 – 2) ÷ 0.08
= 200 Ω
Total Current draw = 20mA × 4 = 80mA
(This is parallel circuit, so currents are additive)
Resistor Power Rating = IF2× Resistor Value= (20mA) 2 × 200Ω = 0.08 W = 80mW
As before, this is the least required value of resistor that will will not overheat and explode. Therefore, it’s recommended to double the power rating of the calculated resistor. This way, choose 1.28W × 2 = 2.56W resistor for this circuit. Resistor power rating (Value is doubled) = 2.56W (280 mW).
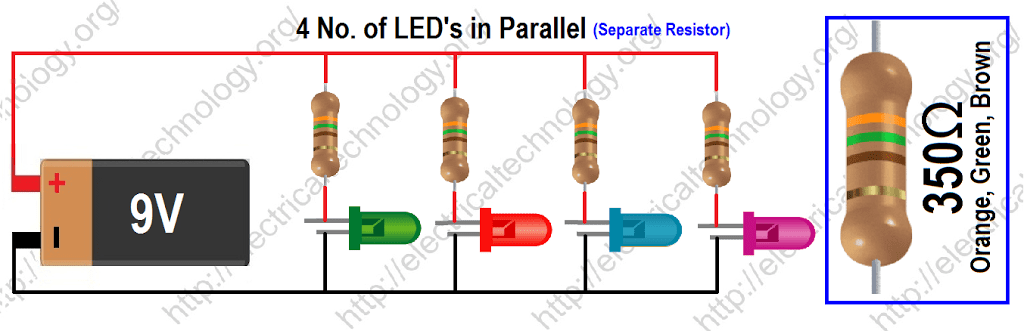
Finding the Value of Separate Resistor to Connect with LEDs in Parallel
Click Image to enlarge
This is another way to connect LEDs in parallel with separate resistors. In this circuit, we have connected 4 LEDs in parallel with separate resistors. Supply Voltage is 9V and the Forward Voltage (VF) of LEDs is 2V and the forward Current (IF) is 20mA each.
Formula:
Value of Separate Resistor for LEDs in Parallel = (VSupply – VF) ÷ IF
Example:
In this case, the total forward voltage (VF) of LEDs = 2 and forward Current (IF) 20mA (i.e. 20mA)
(Note: this is a parallel circuit, but we are finding the value of the resistor for each section, not for the whole circuit. So in each section, the circuit becomes in Series position (refer to the Series Circuit formula or the 1st simple circuit above, you will find that these are same)
Now, the value of resistor (for parallel Circuit with separate resistors) would be:
= (VSupply – VF)/ IF= (9 – 2) ÷ 20mA = 350 Ω
Total Current draw = 20mA × 4 = 80mA (This is parallel circuit, so currents are additive)
Resistor Power Rating = IF2 × Resistor Value= (20mA) 2 × 350 Ω = 0.14 = 140mW
Same like the above scenarios, the calculated value of the resistor is the minimum required value to safely connect in the LED circuit. To be on a safe side, it is recommended to double the power rating of the calculated resistor. Hence, choose 0.14W × 2 = 0.28W = 280mW resistor for this circuit. Resistor power rating (Value is doubled) = 0.28 W (280 mW).
There is another way to connect LEDs with batteries in series-parallel combination and yes, you will need a proper resistor(s) for that purpose too. But if you understand this simple calculation based tutorial, then I’m sure that you can easily determine the value of resistors for series-parallel combination based LEDs connections and circuits as well.
Related Posts:
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker? Breaker Calculator & Examples
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation? – Examples in Imperial & Metric System
- Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- How to Find the Number of Lights on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Size and Find the Numbers of Ceiling Fan in a Room?
- How to Find P.F Capacitor in µF & kVAR?
- How to Find the Size of Earth Conductor, Earthing Lead & Earth Electrodes?
- How to Calculate the Right Size Battery? Battery Bank Size Calculator
- How to Calculate the Right Size of Solar Charge Controller?
- How to Calculate the Number of Fluorescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Number of Incandescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Suitable Capacitor Size in µ-Farads & kVAR for P.F Improvement
- How to Calculate the Battery Charging Time & Battery Charging Current – Example
- How To Calculate Your Electricity Bill. Electric Bill Calculator with Examples
- How to Determine the Suitable Size of Inverter for Home Appliances?
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Size a Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer in kVA? Calculator
- How to Size a Generator? Portable, Backup & Standby for Home & Commercial Applications
 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode