Which One Carries More Current – Solid Conductor or Stranded Conductor?
The war is still on and there is no winner yet between solid wire and stranded wire. One can not decide which one is the better as each wire type offers some advantages (as well as disadvantages) in special applications. In short, the following article will help you to decide which one is the best option in case of flexibility, routing, protection, distance, cost of indoor/outdoor applications and current carrying capacity (ampacity) etc.
Related Posts:
- Why are US Homes Wired Using Solid Wire rather than Stranded Wire?
- Types of Electrical Wires and Cables
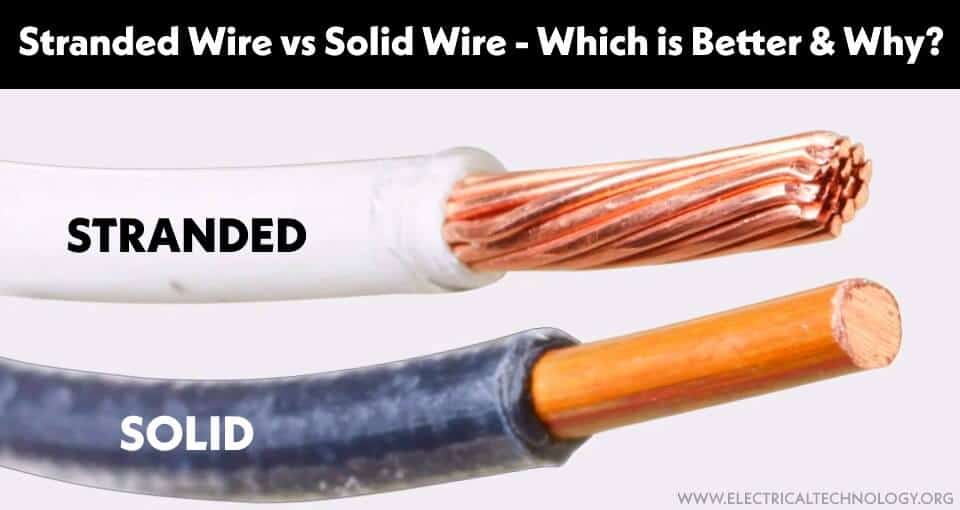
What is Stranded Wire?
A stranded wire is a bundle of multiple thin strands of conductors (twisted-pair in insulation). They are available in different sizes for specific applications. For example, the size of wire in UK is 3/0.029″, 7/0.036″, 7/0.042″ where the first digit (e.g. 3 or 7 shows the number of stranded conductors and the second part of numbers (e.g. 0.029″, 0.042″ shows the size of the conductor i.e. 0.036″ means 0.036 inches2). The size of wire in the US is 7/32 where the number of “7” shows the number of strands where 32 shows the AWG size of conductor.
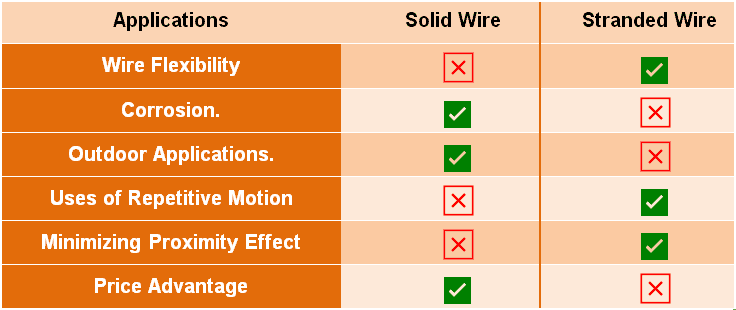
Stranded wire offers flexibility as compared to solid wire thus the suitable option for electrician stranded wire in applications where wires need to be bent or twisted as it is easier to route through pipes and conduit in walls. In addition, current flows safely in the stranded wire as the heat generated in the wire conductor (due to flow of current) can be easily dissipated as there is air-gap among the stands of conductors.
The stranded wire is also used in applications of repetitive motion such as opening/closing the doors etc. These are the better choice in case of short distance and easily can be fitted in patch cords.
You may also notice the stranded wire instead of solid wire for power transmission and distribution lines which is used to reduce the skin effect (a property of alternating current (AC) flowing on the outer surface of the conductor instead of the whole conductor). To eliminate the skin effect, stranded wire is the appropriate solution to do so.
On the other hand, stranded wires are costly, faces corrosion problems especially in humidity and outdoor applications. Finally, the ampacity of stranded wire is lesser as compared to the same size of solid wire as there is air gap between the conductors in case of stranded wires.
Related Posts:
- What are the Tiny Cylinder in Power Cords & Cable?
- Why Coaxial Cables are Highly Insulated?
- How To Locate Faults In Cables? Cable Faults, Types & Causes
Advantages of Stranded Wire
- More flexibility
- Easy routing & bending with longer flex life in motion applications
- Less heating & safe current flow
- suitable for crimp termination & patch cords connection
- Less skin effect in case of longer and high voltage and power transmission
Disadvantages of Stranded Wire
- High chance of corrosion especially in outdoor applications
- Less current capacity as compared to the solid conductor having the same size.
- More voltage drop
- Noisy sound with attenuation of 20-50% and medium transmission performance of high frequencies
- Complex termination and connection
- Costly as compared to solid wire
Related Post:
What is Solid Wire?
As the name suggests, a single solid conductor covered in insulation which is thicker and heavier than stranded wire is known as solid wire. As we know that stranded wire has some advantages over solid wire but still it is used in home wiring especially in US for 120/240 main panel and its applications for some reasons like better connection and higher ampacity etc.
The current carrying capacity of solid wire is more than the stranded wire due to the air-gaps between the conductors. It has less resistance due to the thickness of the conductor and offers perfect termination and connection.
In addition, solid wire has more capacity and there is less voltage drop, less corrosion, lossless sound (less noise ratio), more long lasting and stable connection. Moreover, solid wires are less costly and suitable in outdoor applications.
On the other hand, solid wire has less flexibility and it is difficult to bend and twist the wire due to its stiffness. So it might damage and break the solid wire if used with multiple bending and routing especially in movement based applications.
Related Posts:
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation? Examples in Imperial & Metric System
- Cable and Wire Tester Circuit Diagram
Advantages of Solid Wire
- Perfect termination and connection
- High ampacity as compared to stranded wire having the same size.
- Clear sound (less noise due to low attenuation) and good transmission performance with high frequencies
- Lesser resistance and anti-corrosive in indoor/outdoor applications
- low voltage drop and suitable for long distance applications
- Less costly as compared to stranded wires.
Disadvantages of Solid Wire
- Less flexible
- Might damage the cable if used in repetitive motion applications
- Problems of skin effect in case of high voltage and power transmission lines
- Not suable in electronics, digital communication and computer applications
The following table shows the differences and comparison between solid conductor and stranded conductor in accordance with special conditions and applications.
Current Carrying Capacity of Solid & Stranded Wire
If the diameter of both wires are the same, the solid wire will carry more current than the stranded wire. This is because the cross sectional area of the solid wire is bigger than the stranded wire as there is air-gap between the strands of the conductor in it. For this reason, an electrician must select an appropriate wire size based on the wire gauge and ampacity for desired application.
One another phenomenon known as skin effect (current flowing on the outer surface of the conductor instead of the whole conductor) occurs in AC current having frequency. That’s the reason they use stranded wires for high power transmission. But skin depth may be neglected in case of copper wire (up to 6mm) used for home wiring having the frequency of 50/60 Hz.
Which One is Best – Solid or Stranded Wire & Why?
You must select a wire and cable type based on initial & long term cost, indoor/outdoor & specific applications, load types, motion, right ampacity and other weather & environmental factors etc. As a conclusion, the selection of solid wire vs stranded wire depends on multiple factors. In short:
If you need durability, simplicity, smoothness and especially cost effective solution based on your required applications, Solid wire is for you.
If you are looking for long term flexibility and special motion based applications, stranded wire is the best choice for you then.
Related Posts:
- ABYC Cable & Wire Color Codes for Yacht, Boat & Marine Wiring
- Treeing in XLPE Insulated Medium & High Voltage Cables
- MV & HV Cable Termination to Equipment & Joints
- Electric Stress Control in Cable, Joints & Terminations
- Cables Feeder Protection – Faults, Types, Causes & Differential Protection
- Submarine Cables – Construction, Characteristics, Cables Laying & Joints
- Choice of Wiring System – Types Of Cables Used In Internal Wiring
- Types of Control & Communication Cables
 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering