What is an ELCB? Types, Working, and Application of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
ELCB or Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a protection device that protects against earth leakage. Initially, the earth leakage circuit breaker were voltage detection devices, now they are switched to current sensing devices. The current ELCB is renamed as RCCB or RCD while the voltage ELCBs are still known as ELCB but they are obsolete.
In this article, we are going to discuss ELCB in detail with both types.
What is Earth Leakage?
The electrical current that flows from the live conductor to the earth through an unintended path is called earth leakage. It may flow between their poor insulation or through a person’s body and cause electrical shock. The consequence of electrical shock may prove fatal if the leakage current exceeds the only 30mA. Therefore, protection devices are used to disconnect the power source when such current leakage is detected
Causes of Earth Leakage?
Earth leakage can occur due to various reasons. It can occur due to damaged insulation of the live conductor or broken conductors. It can also occur when the live conductor comes in contact with the body of the equipment (if the equipment is not properly grounded). Upon touching the conductor or the equipment, the current can pass to the earth through the person’s body.
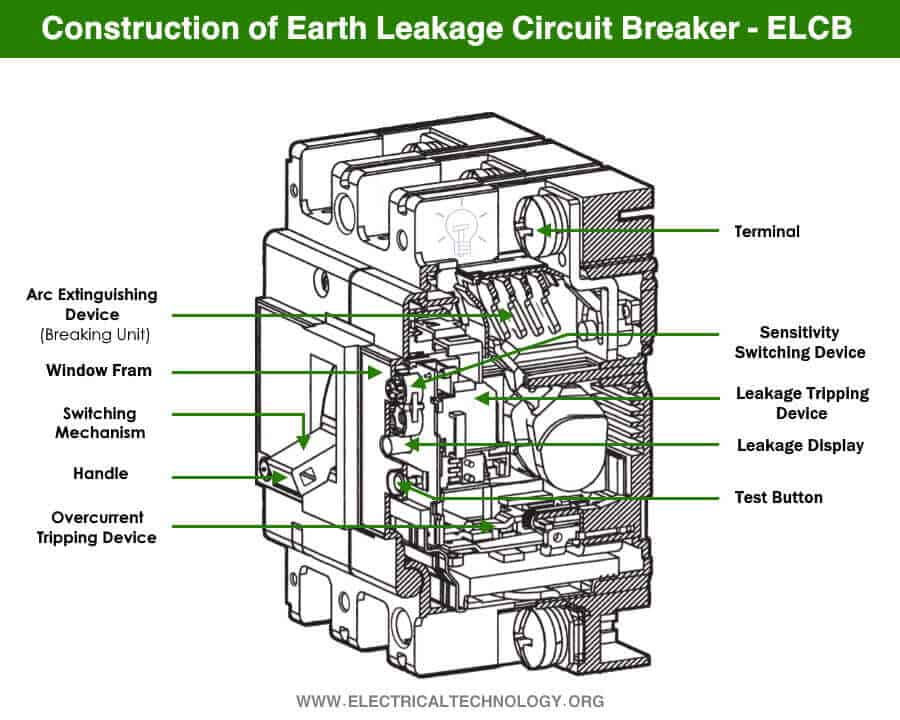
What is an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
ELCB or Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that is used for protection against leakage current. it breaks the circuit and disconnects the power supply to the load when it senses the leakage current. The earth leakage can cause electrical shocks that can be fatal.
ELCB is mainly used for protection against electrical shock. They do not offer protection against overloading or short circuit. Therefore, they must be used in series with an MCB (miniature circuit breaker).
Function of ELCB
ELCB is a safety device whose main function is to prevent electrical shock. It monitors the leakage current that flows out of the circuit through any unintended path. It cannot protect against overloading or short circuit current.
Operation of ELCB
Under normal conditions, the current from the source flows into the load through the live wire and flows out of the load through the neutral wire. In fact, both currents are equal in amount. If the current leaks through any unintended path, an imbalance between the live and neutral wire occurs. The ELCB can sense the imbalance using a current transformer and break the contacts using an electromagnetic relay.
- Related Post: What is an RCD (Residual Current Device)? – RCB and RCCB
Types of ELCBs
There are two types of ELCB classified based on its operation principle;
- Voltage ELCB
- Current ELCB
Both types of ELCBs detect the leakage current but their sensitivity and the level of protection they offer are different. Voltage ELCB was invented before the current ELCB. voltage based ELCB is inferior to current ELCB. Therefore, to avoid confusion, the voltage ELCB is renamed ELCB while the current ELCB is renamed RCCB or RCD.
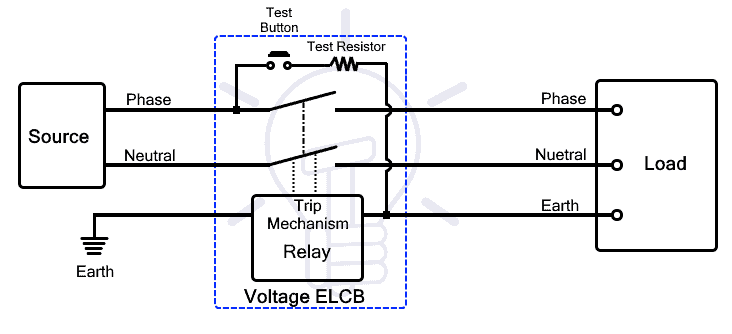
Voltage ELCB
Voltage ELCB operates on the voltage level between the earth and the body of the equipment. The voltage difference is used to detect the leakage current and instantly break the circuit.
It has terminals for both phases and neutral on both supply and load sides. It has two extra terminals that connect with the equipment’s body and the earth. These terminals are actually connected with the electromagnetic relay and they play a vital role in breaking the circuit during current leakage.
Working Principle
One of the terminals of the relay coil is directly connected to the earth while the other terminal is connected to the body of the equipment. The coil can sense the voltage difference between the earth and the body of the equipment.
If the live wire breaks or its insulation fails and comes in contact with the body of the equipment, a voltage difference appears across the terminals of the coil. As a result, the current starts to flow through the coil and it is energized. The relay starts to generate electromagnetic force. When the current exceeds a certain limit, the relay produces sufficient force to pull the latch. By doing so, the latch break opens the contacts and disconnects the power supply to the equipment and prevents electrical shock.
Therefore, the earth connection is necessary as the relay only operates when the leakage current flows through it. if the current leaks through any other parts of the circuit and flows through any other unintended path, it will not break the circuit as the current must flow through the relay in order to break the circuit.
- Related Post: Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications
Advantages
Here are some of the advantages of voltage ELCB
- It helps in protection against electrical shocks.
- They are less sensitive and do not trip unnecessarily.
- They are less expensive.
Disadvantages
Here are some of the disadvantages of voltage ELCB
- It cannot sense the current leakage from phase to any other earthed body.
- It cannot prevent electrical shock in case of touching the phase conductor directly.
- It only trips when the leakage current flows through the earth conductor.
- It requires an extra connection with the body of the equipment and earth.
- It is less sensitive and cannot detect low leakage current.
- Electrical equipment that normally leaks voltage might trip ELCB unnecessarily.
It has far more disadvantages than advantages and they are obsolete. Therefore, if you have installed any old voltage ELCBs in your home, replace them with current ELCB or RCCB. They are more efficient, reliable and best at providing protection against any kind of leakage current.
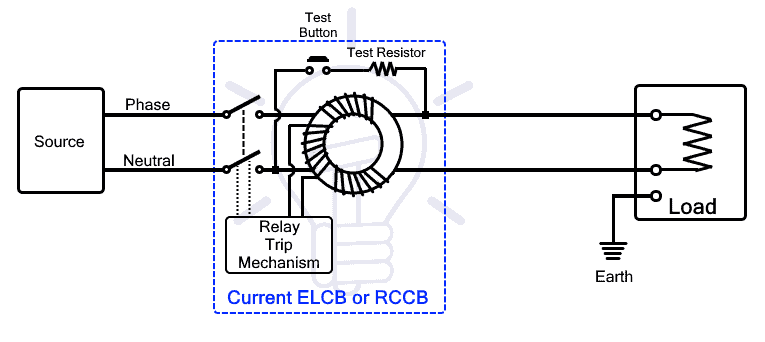
Current ELCB (RCCB or RCD)
Current ELCB or commonly known as RCD (Residual Current Device) or RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is another type of ELCB that breaks the circuit upon sensing any leakage current. It operates on the current difference between the phase and neutral line. The difference appears when the current leaks from the phase line. Therefore, RCCB can provide protection against any kind of current leakage.
It has four terminals having two input and two output terminals for phase and neutral. The phase-in and neutral in are connected to the supply while phase-out and neutral out are connected to the load. It does not have that extra terminal for earth connection.
Working Principle
The RCCB working is based on the current imbalance between the phase and neutral line. It continuously monitors the phase and neutral current. Under normal conditions, both phase and neutral current are equal because it is the same current flowing back from the load. If, the current leaks through any unintended path, the neutral current reduces and causes imbalance. When the imbalance exceeds a certain limit, the RCCB breaks the contacts and disconnects the power supply.
RCCB works on the principle of Kirchhoff’s current law, according to which the amount of current entering the load through the hot wire must be equal to the amount of current leaving the load through the neutral wire. The difference between the two currents known as residual current should be zero. If there is a difference then the current is leaking somewhere that causes the imbalance.
RCCB includes a zero-sequence current transformer that has three coils i.e. phase coil, neutral coil and search coil. It is used for detecting the imbalance or difference between two currents. The phase coil and neutral coil is wounded around the toroidal core in such a way to cancel out each other’s flux.
if the currents are equal as should be under normal conditions, the resultant flux will cancel out each other and there will be no induced current in the search coil. suppose, there is a leakage current, the current difference will produce flux that will induce a voltage in the search coil. as the search coil is connected to the relay trip mechanism, it will break the contacts and disconnect the power supply to the load.
Advantages
Here are the advantages of the current ELCB or RCCB
- RCCB breaks the circuit when the current leaks from any part of the circuit.
- It is very reliable in providing protection against electrical shock.
- It is far more sensitive than voltage ELCB.
- It continuously monitors the residual current and instantaneously breaks when it exceeds its rated limit.
- It does not require an earth connection.
Disadvantages
Here are the disadvantages of the current ELCB or RCCB
- It does not provide protection against short circuit current.
- It does not have overload protection.
- It is expensive than ELCB.
- It cannot provide protection against electrical shock due to touching both phases and neutral wire because the current still remains equal.
- Due to high sensitivity, it may trip unnecessarily when used with old appliances having small current leakage.
- It operates only on normal supply waveforms and cannot operate reliably on non-standard waveforms.
Related Post: Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCD
Types based on Poles
According to the poles of circuit breakers, the ELCB is classified into three types.
2-Pole ELCB: it is used for protection in a single-phase system. It has 2 ingoing and 2 outgoing terminals having phase and neutral connections.
3-Pole ELCB: It is used for protection in a three-wire three-phase system. It has three ingoing and three outgoing terminals.
4-Pole ELCB: It is used for protection in a four-wire three-phase system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ELCBs
Advantages
- ELCB instantly breaks the circuit to avoid electrical shock.
- It prevents damage caused due to broken wires or damaged insulation.
Disadvantages
- ELCB cannot protect against overloading and short circuit current.
- It cannot protect against live-neutral shock.
- It may trip unnecessarily due to small current leakages in old appliances.
Applications of ELCBs
ELCB is used for protection against current leakage. The current leakage causes electrical shock and faults in the system. It breaks the circuit instantly to prevents damage to the connected circuits. They are essential in wet locations having increased risks of electrical shocks.
Related Posts:
- HVDC Circuit Breaker – Types, Working and Applications
- Electronic Circuit Breaker – Schematic and Working
- Smart WiFi Circuit Breaker – Construction, Installation and Working
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Read MCB Nameplate Data printed on it?
- Why Circuit Breaker Capacity Was Rated in MVA and Now in kA and kV?
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit and Vice Versa?
- AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
- GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications

 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Rotor Balancing in the Motors – Types, Methods and Importance
Rotor Balancing in the Motors – Types, Methods and Importance Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?