Transistors, IGFET and MOSFETS Symbols
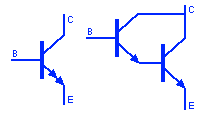
NPN BJT Transistor
An NPN bipolar Junction transistor (BJT) made up of 3 layers of semiconductor material. A P type semiconductor material is sandwiched between two N type materials. It is a current controlled current device used for switching or amplification. The current entering through the base terminal is amplified into the current entering through the collector.
PNP BJT Transistor
This symbol represent a PNP BJT Transistor. it is made up of N type semiconductor meterial sandwiched between two P type materials. PNP transistor amplify when its base is negative with respect to collector & emitter. In other words it ampify the current flowing out of its base terminal.
Tunnel FET
TFET or Tunnel Field effect transistor is a type of MOSFET whose structure looks similar to that of a traditional MOSFET but its switching mechanism differs. They use the phenomenon of quantum tunneling that makes it a perfect candidate for low power electronics.
Unijunction Transistor N Type
Unijunction transistors are made up of lightly doped base with a heavily doped emitter creating only one junction. it is also known as “double base diode”. The potential at the emitter with respect to the base controls the current through the base. N type UJT is made up of lightly doped P-type base (B1 & B2) with a heavily doped N type emitter (E). They are mostly used for triggering thyristors.
Unijunction Transistor P Type
This is a P-type unijunction transistor made from a bar of lightly doped N-type material with a heavily doped P-type part near the base 2. It operation is similar to N type UJT but the voltages polarities are reversed,
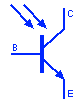
Photo Transistor
Photo transistor is a light dependent transisitor that converts the light energy into electrical current between the collector & emitter. It operates the same as Photo-diode but it is more sensitive with the extra gain factor. They are used in light sensing applications.
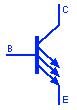
Multi-Emitter NPN Transistor
It is a special type of BJT (bipolar junction Transistor) that has multiple emitters. The emitters are independent of each other & the current through each emitter depends on its individual voltage with respect to the base of the transistor. These are mostly used in TTL (Transistor-transistor Logic) NAND gates.
Avalanche NPN Transistor
This is a type of BJT specially designed to operate in the avalanche breakdown region where the phenomenon of negative differential resistance occurs. At this point, increasing the voltage causes to decrease the current. Thus the avalanche transistor has the ability of very fast switching of heavy currents.
Schottkey NPN Transistor
It is made up of a schottkey diode and a transistor. The schottkey diode is connected between the base and the collector. It keeps the transistor from saturating by shunting the excessive current. it helps in fast switching due to the time delay in removing the stored charges in saturated mode.
JFET Transistor N channel
JFET or junction field effect transistors are unipolar transistors because the current flow is due to single carrier type. JFET are voltage controlled i.e. the current flow is controlled by the voltage at its gate terminal. The voltage increase or decrease the depletion region controlling the current flow. The N channel JFET has N-type channel between Source & drain while the gate is made of P-Type material.
JFET Transistor P channel
This symbol represents a P-channel JFET (denoted by arrow pointing outwards). A P channel JFET is made up of P-type channel made between Drain & Source while the gate is made of N-type material. The P channel JFET switches off by maintaining positive gate to source voltage.
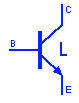
PUT Programmable Unijunction Transistor
PUT or programmable UJT is a four PN layer device just like the thyristors but it operate like UJT if programmed with two external resistors. It has anode, cathode & a gate terminal. The voltage at the gate terminal switches the PUT on & off when it crosses its cutoff level.
NPN Darlington Transistor Pair
It is a special type of transistor made by connecting the emitter of one BJT with the base of another BJT to increase the current gain & sensitivity. It can be made from NPN or PNP transistors by connecting it in this configuration. the total gain of Darlington transistor is the product of gains of individual BJT & the voltage drop is twice at base-emitter.
Sziklai Transistor Pair
The Sziklai transistor is made from combining two NPN & PNP transistors in Darlington pair formation. The main advantage of this Sziklai pair is that it switch on with 0.7v while the total gain remains the same as in Darlington pair.
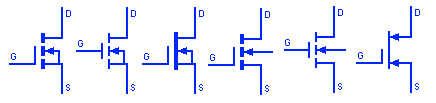
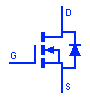
Depletion Type MOSFET
MOSFET or Metal-oxide Semiconductor FET is another field effect transistor whose gate is completely isolated from the current carrying channel that is why it is also known as IGFET (insulated Gate FET). It is a voltage controlled current device. The Depletion type MOSFET is normally ON at zero gate-source voltage. They switch OFF by applying positive or negative gate-source voltage for P channel or N channel MOSFET respectively.
Enhancement Type MOSFET
The Enhancement type MOSFET do not normally conduct when gate-source voltage is at zero. They turn ON by applying positive gate-source voltage for N channel & by negative gate-source voltage for P channel Enhancement MOSFET. Enhancement type resembles a normally open switch while Depletion type resembles normally closed type switches.
Enhancement Type MOSFET with Bulk
Such type of enhancement MOSFET has four terminals. The extra terminal is known as Bulk or body terminal. It is neither an input nor an output terminal but it is used for grounding the substrate. It is usually internally connected with the source terminal which is why they are omitted from their symbol to show a clear schematic with less clunky wiring.
Depletion type MOSFET with Bulk
This depletion type MOSFET has an extra separate terminal for the bulk or body. It is shorted with the source terminal of MOSFET for operation. It grounds the substate.
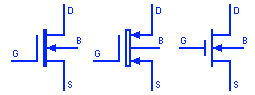
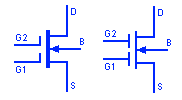
Dual Gate Depletion Type MOSFET
Dual gate MOSFET is a special type of MOSFET that incorporate two individual gates in series. The gates control the amplification factors more precisely. For example, the amplification factor of signal at gate 1 can be controlled by varying the signal at gate 2 thus providing automatic control for signal of various magnitude.
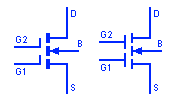
Dual Gate Enhancement Type MOSFET
This is an enhancement type dual gate MOSFET. They operate the same as depletion type MOSFET but the only difference is that depletion type normally conducts while enhancement type normally don’t conduct when there is zero gate-source voltage.
Logic Level FET Transistor
Logic level FET transistors are designed to be used with digital logic systems. They are used for switching heavy loads when applied with digital logic i.e. positive logic voltage usually of 5v at gate-source starts conduction of maximum current.
Photo FET Transistor
Photo FET Transistor is a light dependent FET that switches when the light intensity upon its junction changes. They are used in opto-couplet or opto-isolator to electrically isolate two circuits by using an LED between them.
Related Electrical and Electronic Symbols:
- Basic Electrical and Electronic Symbols
- Transformer Symbols
- Motors Symbols
- Generator and Alternator Symbols
- Resistor Symbols
- Capacitor Symbols
- Inductor Symbols
- Fuse and Circuit Breaker Symbols
- Switch and Push Button Symbols
- Relay Symbols
- Diode Symbols
- Thyristor, DIAC and TRIAC Symbols
- Electronic Logic Circuits and Programming Symbols
- Digital Logic Gates Symbols
- Digital Flip-Flop and Latches Symbols
- Electronic Filters Symbols



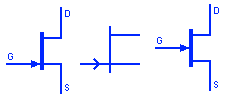
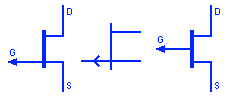





 Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode Difference Between Amplifier and Operational Amplifier
Difference Between Amplifier and Operational Amplifier Difference Between Static RAM & Dynamic RAM – SRAM vs DRAM
Difference Between Static RAM & Dynamic RAM – SRAM vs DRAM Difference Between Digital Latch and Flip-Flop Circuits
Difference Between Digital Latch and Flip-Flop Circuits