ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Operation, Types, Advantages and Applications
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is a device, which is capable to:
- Break a circuit automatically under fault conditions (like overcurrent, short-circuit, etc.).
- Make or break a circuit manually or by remote control under normal conditions.
- Make a circuit manually or by remote control under the fault conditions.
A circuit breaker is used for switching mechanism and protection of the system. Other associated devises and components are also used for this purpose associated with circuit breakers like fuses, relays, switches etc.
Circuit breakers are widely used in industries as well as power system for controlling and protection of different parts of the circuit like switchgears, transformers, motors, generators/alternator etc., which leads the system stable and reliable.
There are different types of air circuit breakers available in the market and we will discuss one by one in detail.
- Related Post: Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications
What is an Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)?
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is an electrical protection device used for short circuit and overcurrent protection up to 15kV with amperes rating of 800A to 10kA. It operates in air (where air-blast as an arc quenching medium) at atmospheric pressure to protect the connected electric circuits. ACB has completely replaced by oil circuit breaker because it is still a preferable choice to use an ACB because, there is no chance of oil fire like in oil circuit breaker.
An air circuit breaker:
- Operates in air (where air-blast as an arc quenching medium) at atmospheric pressure.
- It has completely replaced by oil circuit breaker.
- No chance of oil fire like in oil circuit breaker.
- Rated Current up to 10k A.
- Trip thresholds and delays are adjustable.
- Electronically and microprocessor controlled.
- It is used in large industrial plant for main power distribution.
Construction of Air-Circuit Breaker
The following fig shows the main and external parts of an ACB. (ABB EMax Low Voltage, Current Limiting and Selective (Non-Current Limiting) Air Circuit Breaker).

- OFF button (O)
- ON button (I)
- Main contact position indicator
- Energy storage mechanism status indicator
- Reset Button
- LED Indicators
- Controller
- “Connection”, “Test” and “isolated” position stopper (the three-position latching/locking mechanism)
- User-supplied padlock
- Connection “,” Test “and” separation “of the position indication
- Connection (CE) Separation, (CD) Test (CT) Position indication contacts
- Rated Name Plate
- Digital Displays
- Mechanical energy storage handle
- Shake (IN/OUT)
- Rocker repository
- Fault trip reset button
The following fig shows the Internal Construction of Air Circuit Breaker
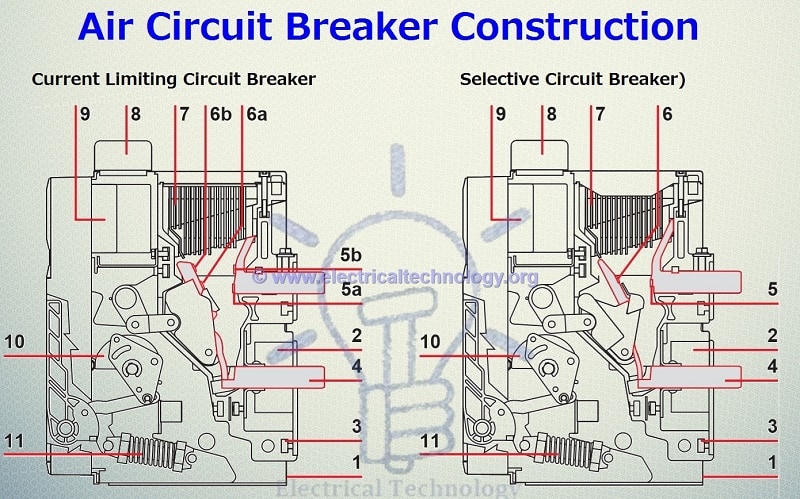
- 1. Sheet Steel Supporting Structure
- 2. Current Transformer for Protection Trip Unit
- 3. Pole Group insulating box
- 4. Horizontal rare terminals
- 5a. Plates for fixed main contacts
- 5b. Plates for fixed arcing Contacts
- 6a. Plates for Main moving contacts
- 6b. Plates for Moving Arcing contacts
- 7. Arcing Chamber
- 8. Terminal box for fixed version – Sliding Contacts for withdrawable version
- 9. Protection Trip Unit
- 10. Circuit breaker Closing and Opening Control
- 11. Closing Springs
Principle of Operation of ACB
The working principle of Air Circuit breaker is rather different from other types of circuit breaker. The main aim of circuit breaker is to prevent reestablishment of arcing after current zero where the contact gap will withstand the system recovery voltage. It does it same work, but in a different manner. During interruption of arc, it creates an arc voltage instead of supply voltage. Arc voltage is defined as the minimum voltage required for maintaining arc .The circuit breaker increases the voltage in three different ways:
- Arc voltage can be increased by cooling arc plasma. As soon as the temperature of arc plasma motion of particle in arc plasma is reduced, more voltage gradient will be required to maintain the arc.
- By splitting the arc into a number of series will increases the arc voltage.
- Arc voltage can be increased by lengthening the arc path. As soon length of arc path is increased the resistance path will increase more arc voltage is applied across the arc path hence arc voltage is increased.
It is operated within voltage level up to 1 KV. It contains two pairs of contact. The main pair carries the current and the contact made of copper. An additional pair of contact is made of carbon. When the breaker is opened, the main contact opens first. During opening of the main contact, the arc contact remains in touch with each other. The arcing gets initiated when arc contacts are separated. The circuit breaker is obsolete for medium voltage.
Types of Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs)
There are four types of ACBs used in the control and protection to maintain and stable operation of switch gears and indoor medium voltage.
- Plain Break Type Air Break Circuit Breaker or Cross-Blast ACB
- Magnetic Blowout Type Air Break Circuit Breaker
- Air Chute Air Break Circuit Breaker
- Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Related Post: MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
Plain Air Circuit breaker or Cross-Blast ACB
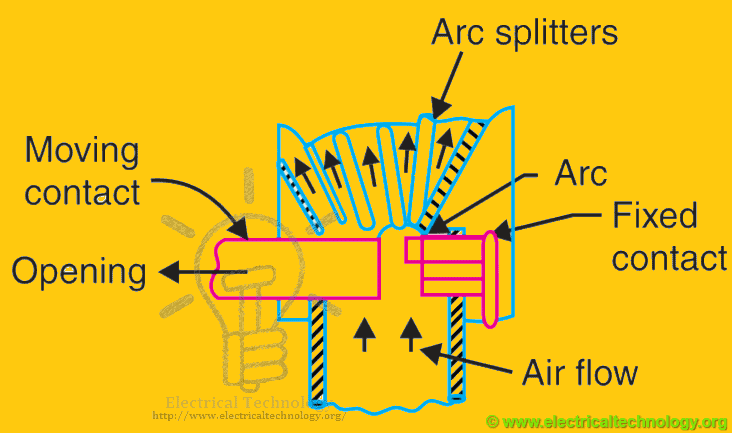
The circuit breaker is fitted with a chamber surrounding the contact. The chamber is known as “arc chute”. The arc is made to drive in it. The arc chute will help in achieving cooling. Arc chute is made from some refractory material. The inner walls of arc chute are shaped in such a way that arc is not only forced into close proximity, but will drive into the serpentine channel projected on arc chute wall.
The arc chute is divided into a number of small compartments by using metallic separation plates. Metallic separation plates are arc splitters and each of small compartments behave as a mini arc chute. Initial arc will split into a series of arcs this will make all arc voltages higher than system voltage. They are preferable choice in low voltage application.
Air Chute Air Break ACB
In air chute air circuit breaker, there are two types of contacts namely “main contact” and “auxiliary or arcing contacts”. The main contacts are made of copper and the silver plates having low resistance and conducts the current in closed position. Auxiliary or arcing contacts are made of copper alloy as they are heat resistance and used to prevent from damaging the main contacts due to arcing and can be easily replaced when needed in case of wear and tear. During the circuit breaker operation, the arcing or auxiliary contacts are closed before and open after the main contacts of the circuit breaker.
Magnetic Blowout Type Air Break ACB
Magnetic blowout air circuit breakers provide magnetic control over the arc moment to make arc extinction within the devices. The arc extinction is controlled using magnetic field provided by the current in blowout coils connected in series with the circuit being interrupted. These coils are known as “blow out the coil”. Magnetic field does not control and extinguish the arc made in the breaker, but it moves the arc into chutes where the arc is lengthened, cooled and extinguished accordingly. These types of circuit breakers are used up to 11kV.
Air Blast Circuit Breaker:
This type of circuit breaker is used for system voltage of 245 KV, 420 KV and even more.
- Axial blast breaker
- Axial blast with sliding moving contact.
Related Post: Tripping Curves of Circuit Breakers – B, C, D, K and Z Trip Curve
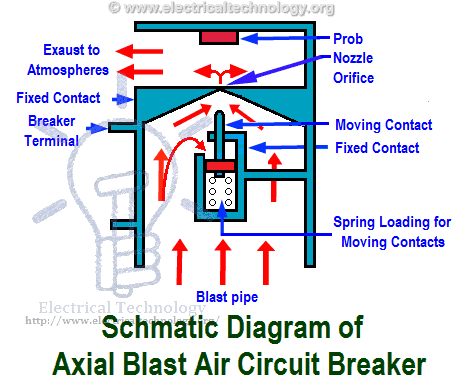
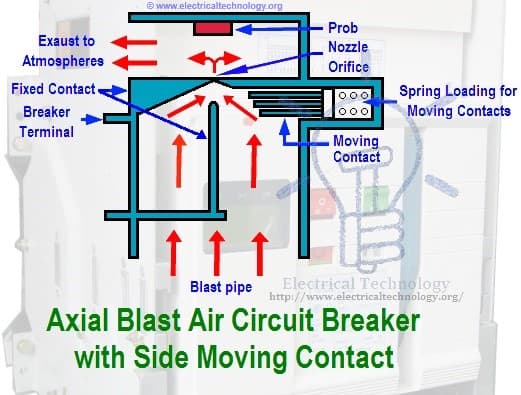
Axial Blast Breaker
The moving contact is in contact. There is a nozzle orifice in fixed contact at normal closed condition of breaker. When a fault occur high pressure is introduced into the chamber. High-pressure air will flow through nozzle orifice voltage is sufficient to sustain.
Axial Blast with Sliding Moving Contact
The moving contact is fitted over a piston supported by a spring. The blast transfers arc to arcing electrode.
Related posts: Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB and RCD Circuit Breakers
Advantages & Disadvantages of Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Advantages
- Air blast circuit breaker is a suitable option to use where frequent operation is required because of lesser arc energy
- The risk of fire is eliminated in the operation of Air blast circuit breaker.
- Air blast circuit breaker is small in size, because of the growth of dielectric strength is so rapid (which final contact gap needed for arc extinction is very small).
- Speed of circuit breaker is much higher during operation of the air blast.
- Arc quenching is much faster
- The duration of the arc is same for all values of current.
- Stability of operation can be maintained and depends on speed operation of circuit breakers.
- It requires less maintenance.
Related post: HRC Fuse (High Rupturing Capacity Fuse) and its Types
Disadvantages
- The air supplier plant requires additional maintenance.
- It contains high capacity air compressor.
- There is a chance of air pressure leakage from the air pipes junction.
- There is chance of a high rate rise of re-striking voltage and current chopping.
- The air has relatively lower arc extinguishing properties.
Application and Uses of Air Circuit Breakers
- It is used for protection of plants.
- It is used for common protection of electrical machines.
- It used for protection of transformers, capacitors and generators.
- ACB is also used in electricity sharing system and NGD about 15kV.
- Also used in Low as well as High voltage and Currents applications .
Related Posts:
- HVDC Circuit Breaker – Types, Working and Applications
- Electronic Circuit Breaker – Schematic and Working
- Smart WiFi Circuit Breaker – Construction, Installation and Working
- Tripping Curves of Circuit Breakers – B, C, D, K and Z Trip Curve
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- Why Circuit Breaker Capacity Was Rated in MVA and Now in kA and kV?
- How to Read MCB Nameplate Data printed on it?
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit and Vice Versa?
- AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
- GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
 Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference between Voltage Source Inverter & Current Source Inverter
Difference between Voltage Source Inverter & Current Source Inverter Difference Between Voltage Stabilizer and Voltage Regulator (AVR)
Difference Between Voltage Stabilizer and Voltage Regulator (AVR) Difference Between Shunt Capacitors and Shunt Reactors
Difference Between Shunt Capacitors and Shunt Reactors