The Main difference between Neutral, Ground and Earth?
To understand the difference between Neutral, Ground and Earth, we must first understand the purpose of these elements.
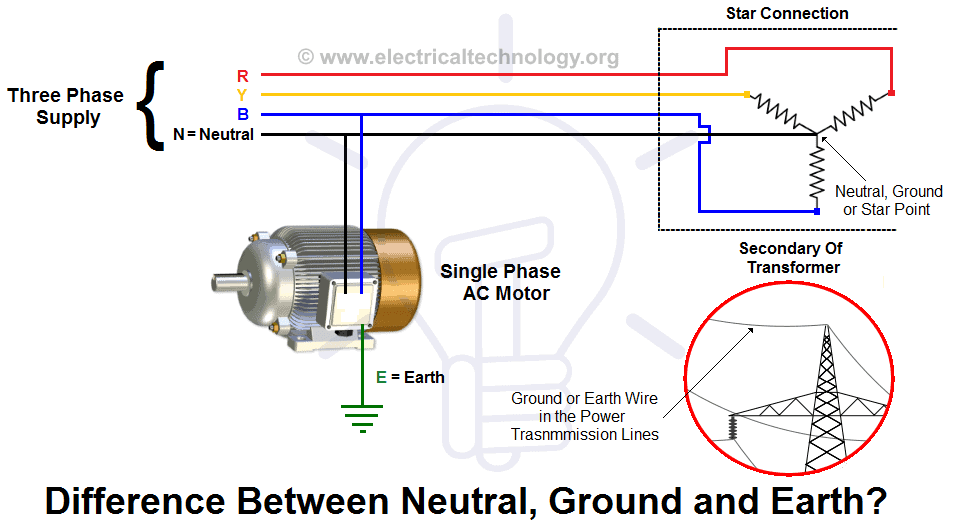
Neutral
Neutral is the return path for electric current in an electric circuit which is intended to carry current in normal condition. This current may result from various factors, primarily due to phase current imbalances and occasionally as a result of the presence of 3rd and 5th harmonics.
The neutral wire provides a return path for the current to flow back to the power source, completing the circuit. In household wiring, it usually carries current from various electrical loads back to the electrical panel or distribution point.
In a properly functioning electrical system, the voltage on the neutral wire should be close to zero volts. It helps stabilize the voltage and maintain a relatively constant potential difference between the live (hot) and neutral wires.
The neutral wire is designed to carry current under normal operating conditions. If there is an imbalance between the current on the live (hot) wire and the neutral wire, it can indicate a fault or short circuit, which can be detected and used to shut off power for safety reasons.
There may be other reasons too but the magnitude of this current is in fraction of phase current and in few cases it can be even double of phase current. So Neutral wire is always assumed to be charged (in active circuit). This neutral wire is connected to the ground (by grounding as in a domestic power supply the Ground is bonded to Neutral, to provide a return path to the transformer at the sub-station) to make the second terminal of neutral wire at zero potential.
Good to Know: The commonly practiced color code for the Neutral wire is white in the National Electrical Code (NEC), while light blue is used in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
- Related Post: Why Earth Pin is Thicker and Longer in a 3-Pin Plug?
Earth or Ground
Earth or Ground is used for safety purposes to divert leakage or residual currents in the system through the path of least resistance. While Phase and Neutral are connected to the main power wiring, the earth may be connected to the body of equipment or to any system that, under normal conditions, doesn’t carry current. However, in case of insulation failure, it is designed to carry a minor current.
This current does not directly originate from the Live or Phase (Line or Hot) wire but instead comes from secondary connections that are not in contact with the live system under normal conditions. This current is typically much lower than the main Line or Phase current, often on the order of milliamperes (mA). However, this leakage current is still capable of causing electrocution or posing a fire risk with potentially severe damages. To mitigate these risks, such current is provided with a low-resistance path and directed to the earth via the ground/earth wire.
Due to differences in their applications, we never mix the grounding of Neutral and Earth. Nonetheless, both are grounded (although the methods may differ). If they were to be mixed, the earth wire, which is not supposed to carry any current under normal conditions, may accumulate charges and become a hazard
Difference Between Earthing and Grounding.
There is no difference between ‘Earthing’ and ‘Grounding‘; these terms are used interchangeably.
Grounding, also known as Bonding, is the term commonly used for earthing in North American standards such as IEEE, NEC, ANSI, and UL, while Earthing is the term used in European, Commonwealth countries, and British standards such as IS and IEC.
In simple words, Earthing and Grounding are synonyms. Both are similar words used for the same thing,
Good to Know:
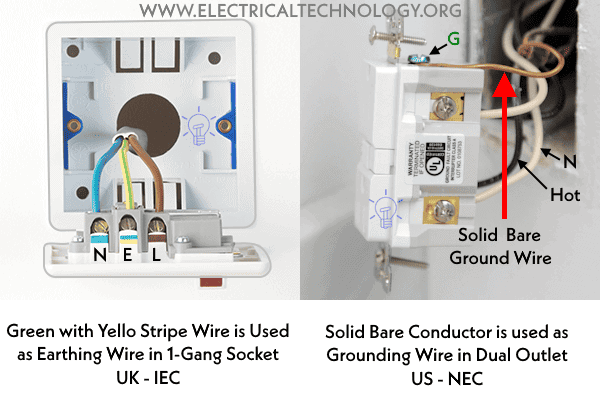
In the US, as per NEC regulations, solid bare conductors are generally used for grounding, while in IEC standards, green or green wires with a yellow stripe are used for earthing.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Grounding, Earthing and Bonding
- Difference between Active and Passive Components
- Main Difference b/w Electrical and Electronics Engineering?
- Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor
- Difference between Power Transformers and Distribution Transformers?
- Difference between Linear and Nonlinear Circuit?
 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Rotor Balancing in the Motors – Types, Methods and Importance
Rotor Balancing in the Motors – Types, Methods and Importance Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?