Main Differences between Isolator / Disconnector and Circuit Breaker
Isolator and Disconnetor
As the name suggests, An Isolator or Disconnector is an isolating or disconnecting switch which disconnects or isolate the whole or a specific part of the circuit. It is used where we need to disconnect a portion of the circuit in case of faults from the main power supply for maintenance purposes. Isolator blocks the DC current and allow the AC current to flow through it (same like a capacitor). HV and MV Switch Disconnectors and Isolators are used in high voltage equipment such as transformer, substation etc. Switch Disconnectors are used in MV installation nowadays. HV/MV Switch Disconnectors And Isolators are used where power installations exceeding 1 kV AC (IEC-61936-1).
- Keep in mind that isolator or disconnector should not open when the current is flowing through it.
- There may a physical and construction difference between Switch Disconnectors, Load Switches, Disconnectors as Isolating Switches but the function is almost same.
Related Post: Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
Circuit Breaker
A Circuit Breaker is a protective device used to control the flow of current same like a fuse. It break the circuit in case of fault conditions like short circuit and overload. It also capable to operate automatically, manually or by remote control in normal and faulty conditions. A relay inside the circuit breaker sense the errors signal and sends to the mechanical switch which make and close the contacts.
- Related Post: Main Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
Differences between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
The following table shows the main differences between Isolators, Disconnectors and Circuit Breakers.
| Characteristics | Circuit Breaker | Isolator / Disconnector |
| Symbol | 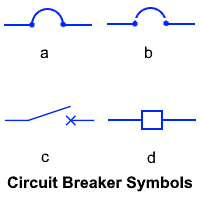 |
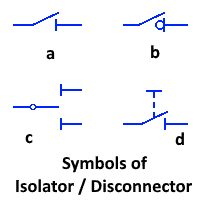 |
| Construction | Circuit Breaker consists of electromechanical switch and a relay in a single box. | Isolators and Disconnectors are types of simple mechanical switch. |
| Working | Circuit Breaker is operated Automatically and Manually. | Isolator and Disconnector are operated Manually. |
| Type of Device | Circuit Breaker is an Electromechanical or electronic device and relay mechanism. | Isolator is a Mechanical Device act as Switch and provides isolation functions. |
| Function and Operation | Circuit Breaker is a protection device (such as MCB, ACB, SF6, OCB etc) which disconnects the circuit in case of overload and short circuit faults. | Disconnector and Isolator switches provide isolating function i.e. disconnecting the supply from all or a portion of installation e.g. in power plants. |
| Types | MCB (Miniature), ACB (Air Blast), OCB (Oil), SF6 etc. | Pantograph ,Knee, Double Break, Center Break, Earthing etc. |
| ON-Load Operation | Circuit Brekaer is an ON-Load and OFF-Load Device i.e. it operates when the power supply in ON or OFF. | Isolator is an OFF-Load Device i.e. Disconnector can be operated when the power supply is totally OFF. |
| Withstand Capacity | At ON-Load Conditions, Circuit breaker has the high withstand Capacity. | Isolators have low withstand Capacity as compared to circuit breakers. |
| Thermal Capability | High | Low |
| Contacts | It has Main as well as Arcing Contacts. | It has Main and Moving Arms / Blades. |
| Power Routes | Circuit Breakers can be used to re-route the power Supply. | Disconnector can be used to re-route the power supply. |
| Trap Charges | It can’t remove the trap charges. | It can remove the trap charges. |
| Insulation | In CB, Air, Oil, Vacuum or SF6 gas are used as insulation medium. | Isolators don’t require insulation or insulation medium. |
| Over-voltage During Switching | In Circuit Breakers, there is a chance of rise in overvoltage during switching operation. | In Isolator, there is no overvoltage rise during switching as it is an OFF-Load device. |
| Earth Switch | Earth Switches are not included in the the circuit breakers. | Single or Double Earth Switches can be included in Disconnector. |
| Interruption | Circuit Breaker interrupts the normal as well as short circuit currents during faults. | Isolator doesn’t interrupt any current. It only isolates the circuit for maintenance purpose. |
| Current Flow Operation | Circuit Breaker can be opened during the flow of current through it. i.e. It can be operated in both cases where the power supply from utility pole is ON or OFF. | Isolator / Disconector should not be opened when the current is flowing through it. Current flow should be disconnected by Turning off the circuit breaker before. |
Different Characteristic of Isolator, Switch Disconnector and Circuit Breaker
Characteristics of Switch Disconnectors
- Rated voltage: 2 kV – 36 kV
- Rated current: 400 A – 1,250 A
- Rated short-time withstand current (3 s): 5 kA – 25 kA
Characteristics of Isolator
- Rated voltage
- MV: 2 kV – 36 kV
- HV:5 kV – 800 kV
- Rated current
- MV: 400 A – 1,250 A
- HV:2,000 A – 5,000 A
- Rated short-time withstand current (3 s)
- MV: 5 kA – 25 kA
- HV:50 kA – 80 kA
Related Post: Main Difference between Contactor and Starter
Characteristic of Circuit Breaker
- Rated Current 10k A and above.
- Electromagnetic Circuit breaker must trip in case of over current.
- Thermal circuit breaker must trip in case of continues overload.
- Mechanical Circuit Breaker must open and close the circuit like a switch.
- A Circuit breaker must prevent the re-connection of the circuit in case of existing short circuit current in the circuit.
- A Circuit breaker must reconnect the load circuit to the power supply automatically or manually in case of no faults currents i.e. short circuit and overload.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
- Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor
- Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth
- Different Types of Electrical Wiring Systems
- Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth?
 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering