Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor / Ultra-Capacitor
Both Supercapacitor and conventional capacitors stores charge in the form of electrostatic field. They are passive components while supercapacitive a type of polar capacitors. While the function of normal capacitor and ultra-capacitor is same to store charge, there are some difference between them which we will discuss as follow.
- Related Post:Difference Between Conductor and Superconductor
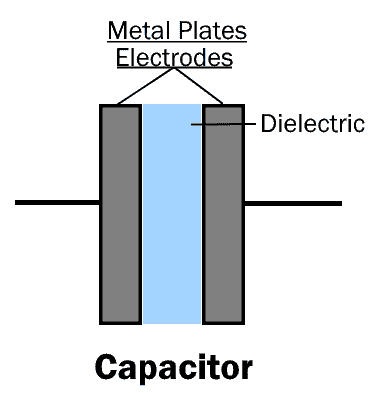
Capacitor
A Capacitor is a two-terminal passive electronic component that stores charge in the form of electric field between its metal plates. it is made up of two metal plates (electrodes as anode and cathode) separated by an insulator known as the dielectric.
When source voltage is applied across the two terminal of a capacitor, the current want to flow through the insulating material but it opposes the flow of electrons. When the voltage across the capacitor terminal is equal to the applied voltage, the insulation medium still resist to the flow of electrons. This resist phenomena makes a changes which create an effect to store energy in the form of electrostatically field.
- Related Post: Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
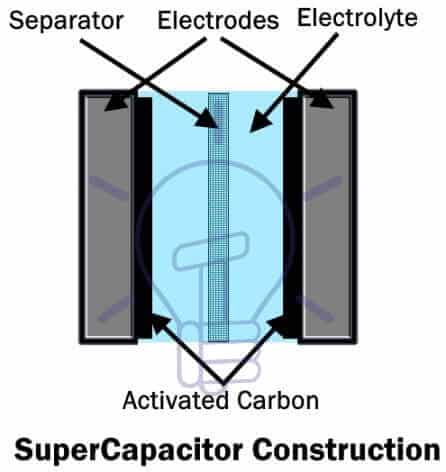
Supercapacitor
Supercapacitor is also known as Super Cap, Double Layer Capacitor or Ultra-capacitor. The electrodes of supercapacitor is coated with active carbon as electrode material. A separator is used between Anode and Cathode in Supercapacitor, whereas a dielectric materials are used in conventional capacitor.
The supercapacitors store charge either using electrostatic double-layer capacitance (EDLC) or electrochemical pseudocapacitance or both known as hybrid capacitance.
Supercapacitors are made of metal foil (electrodes), each layered with activated carbon. These foils sandwich the separator in between. The separator is an ion-permeable membrane such as graphene (used in modern supercapacitor) which provides the insulation and exchange of ions of the electrolyte between the electrodes.
Good to Know:
Supercapacitors are considered between Capacitors and Batteries. The main reason is that Supercapacitor charges very fast like a capacitor and its capacity is high and discharge rate is slow like a Battery.
- Related Post: Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
Main Differences between Capacitors and Supercapacitors
There are key differences between a capacitor and ultra-capacitor which are shown in the below table as comparison.
| Characteristics | Capacitor | Supercapacitor |
| Construction | Capacitor is a two metallic terminals (Electrodes) device with dielectric medium in between. Electric energy is stored in the electrostatic field in it. | Supercapacitoir is a type of polar capacitor and electrolytic solution is used instead of dielectric. The activated carbon is used on electrodes to enlarge the area. |
| Definition | A Capacitor stores potential energy in the form of electric field (electrostatically) and release to the circuit as electrical energy. | A Supercapacitor lays in between Capacitor and battery. Also known as Super Cap, Double Layer Capacitor or Ultra-capacitor. Supercapacitor has very high capacitance and low voltage rating as compared to a normal Capacitor. |
| Working | Capacitor store energy in the form of electric field. | Supercapacitor stores energy between the ions of the electrolyte & electrode in a double layer of charge. |
| Types |
|
|
| Dielectric Material
|
Aluminum oxide, polymer films or ceramic are used in capacitor as dielectric medium in between the electrodes.
|
In Supercapacitor, activated carbon is used as medium. When voltage applied, a double electric field is generated which acts like a dielectric medium.
|
| Charge / Discharge Time | Charging and discharging of conventional capacitor is normal as compared to supercapacitor i.e. 10-3-10-6 seconds. | Supercapacitors can deliver charge much faster than a battery and store charge more than an electrolytic capacitor per volume unit. That is why it is considered between a battery and an electrolytic capacitor. |
| Charge / Discharge Efficiency | > 0.95 | 0.85 – 0.98 |
| Operating Temperature | -20 to 65 °C (-4 to 149°F) | -40 to 65 °C (-40 – 149°F) |
| Energy | <0.1 Wh/kg | 1-10 Wh/kg |
| Energy Density | Low | Very High |
| Specific Power | Upto 100,000 Wh/kg | Upto 10,000 Wh/kg |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Applications |
|
|
Related Posts:
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference between Contactor and Starter
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCB, RCD or RCCB Circuit Breakers
- Difference between AC and DC Resistance & How to calculate it?
- Difference between Star and Delta Connections – Comparison Of Y/Δ
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector

 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering