De-Energized Work procedure & Safety in Electrical Engineering
Introduction
Electricity presents to the workers and installations different hazards and for this reason local operations and maintenance of electrical equipment should only be performed after a detailed analysis of risk, definition of appropriated procedures and can only be done by instructed personnel to avoid emergency case.
Policies & Procedures
Each company must develop policies and procedures regarding the safety conditions to perform any kind of work.
These policies and procedures are related to “Quality Management System”, “Management of Work Health and Safety System and “Health and Safety Plan”, subjects that will be discussed under Section 15.
Hazards must be identified, description of work and the way to perform it must be done, forms and records must be produced, “Lockout-Tagout”, “Permit to Work” and “Work Assignment” procedures must be implemented and switching programs must be established.
No matter what operations are necessary to do, they cannot be done without a written authorization from the responsible in charge of the conduction of installation and all paper work (safety documents) shall be done and dully signed by the responsible and the personnel that will perform the work.
To perform any kind of work in switchgear all personnel must be aware of “as built drawings” and of the technical documentation provided by the supplier of the equipment.
Every worker must be fully equipped with protective clothing and protection equipment.
All tools to be used must be adequate to work to be performed; ladders must be safe and used the proper way and scaffolding must be provided with “bodyguards”.
The operations of the equipment and of the global installation shall be carried out only by authorized and instructed personnel that must follow the internal procedures and the safety rules defined on documents produced by the company.
- Related Article: All About Electrical Protection Systems, Devices And Units
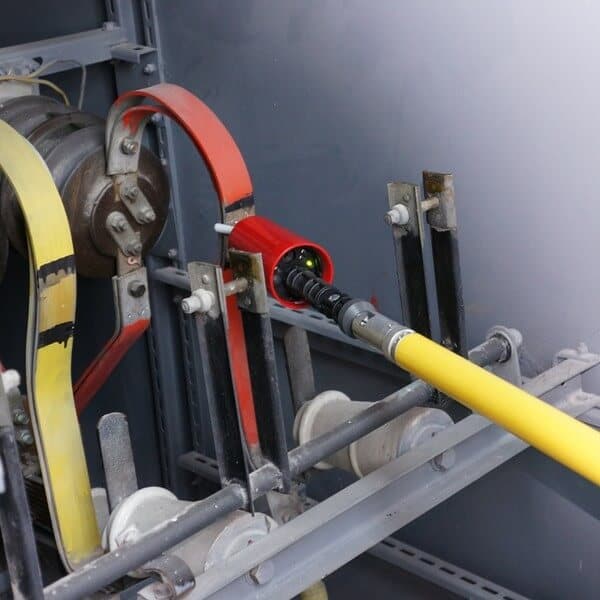
Voltage Detection Equipment
As a safety precaution when works are to be performed it must be assured that the installation is de-energized, prior to the beginning of those works.
For that reason voltage detection equipment must be used, such as multimeters, phase sticks and voltage testers.

Lock Out & Tag Out (LOTO)
Introduction
During normal operation or maintenance of equipment and machines the energy sources used in industry (electrical, mechanical, thermal and others) can be hazardous to the workers, due to unexpected startup of released of that stored energy.
For that reason is necessary to implement procedures to control the flow of that hazardous energy through persons working or standing by the area.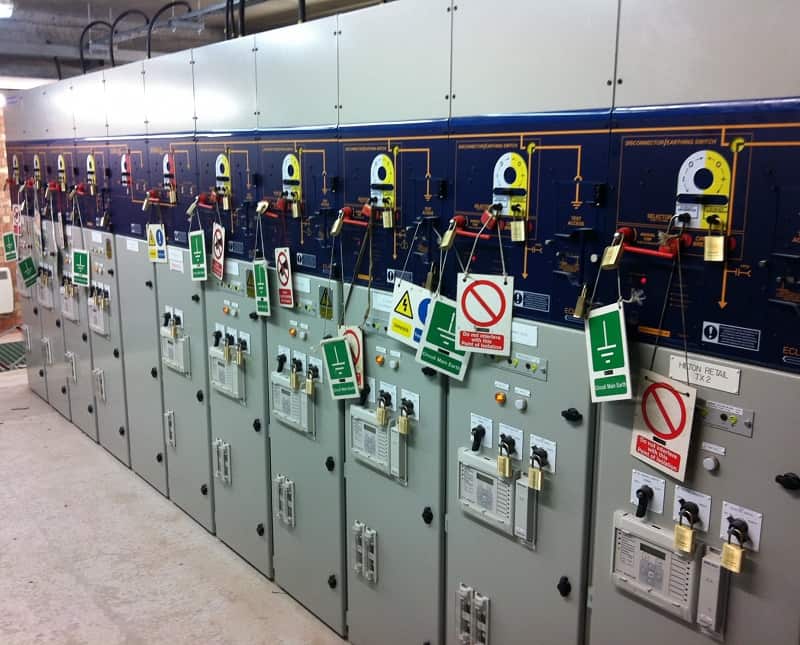
Hazardous Energy Control
Nearly 10% of serious occupational accidents are due to failure to control hazardous energy.
At HV Switchgears the sources of energy that must be considered are the following:
- Generators
- Power transmission lines
- Capacitors banks
- Batteries
Usually to control that energy three methods are used:
- Isolation, breaking the pathway of the energy
- Dissipation of stored energy, being an example the discharge to earth of capacitor banks before any intervention
- Blocking the operation of the equipment
Safety Lockout Procedures
Many countries developed officially procedures to energy control and safety lockout-tagout of equipments and machines to prevent hazards, most of them based on USA standards.
In the USA the existing standards covering this matter are NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) 70E and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) CFR 1910.147 – The control of hazardous energy (lockout / tagout), CFR 1910.269 ( Sub part R – Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution ), CFR 1910.333 (Subpart S – Electrical – Selection and use of work practices ) and CFR 1926 (Subpart V – Power Transmission and Distribution).
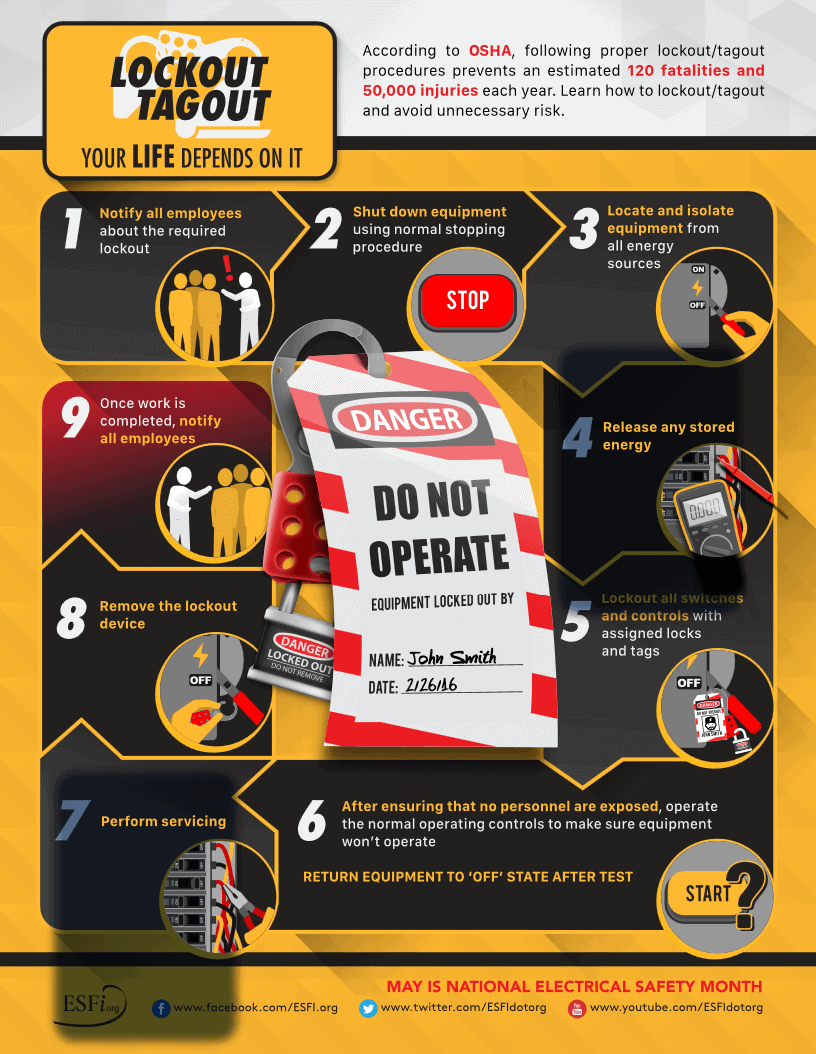
Lockout-tagout, known as LOTO, is a safety procedure to insure that dangerous equipments and machines are properly shut off and not started up again prior to the completion of maintenance or servicing work.
Lockout consists in the insertion of a mechanical device preventing the operation of the equipment and the flow of energy.
Tagout consists in the use of tags to show that the equipment is locked and that must not be operated without prior to specific authorization. Tags must have an identification showing the name of the person doing the lock and tag.
The procedure requires that a tag be affixed to the locked equipment indicating that it should not be turned on.
This procedure is associated to “Permit to Work” and “Work Assignment”.
At HV Switchgears these procedures concern the following equipment and installations:
- Circuit breakers, switches and isolators installed outdoors or at switchboards (local and remote control).
- Doors of fences surrounding equipment with accessible live parts.
LOTO Procedures
Improper use or failure of LOTO procedures may result in:
- Electrical shock
- Human body injuries
- Death
- Fire, explosion and arc flash
LOTO procedure requires that hazardous power sources be isolated and rendered inoperative before any maintenance work starts.
These actions must be performed according to pre-defined sequences of electrical control and coordination between the operation and maintenance departments.
Only authorized and trained workers may be engaged in tasks that require use of LOTO procedures, being an obligation of employers to train and to instruct employees to that purpose.
An employer is required to ensure that each employee knows, understands and is able to follow the applicable provisions of the hazardous energy control procedures and that he can recognize the hazard energy sources at workplace and how to control and isolate that energy.
It is usual that companies impose that only the person who locked and tagged the equipment is authorized to undo the operation and that phone instructions to remove LOTO devices is not acceptable.
Taking into account these facts is strongly advised that a written procedure shall be produced; this procedure may be a check list describing the sequence for access, de-energizing, lockout, clearance, release, and start-up.
Click image to enlarge
Electrical Control & Service Restoring Procedures
The recommend sequence for an electrical shutdown and lockout should meet the usual shutdown procedure:
- Prior to shutdown identify be aware of the hazardous energy you dealing with and notify all affected employees that the installation or the equipment will be out of service.
- Turn the equipment off by using the off/on switch, if any, according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Open all isolation devices – switches, isolators and circuit breakers – and remove fuses to disconnect the equipment from the energy source.
- Shut off all sources of hazardous energy concerning the equipment.
- Identify all hazardous energy control point and equipment with LOTO devices, holding the isolating equipment at “safe” or “off” position.
- Prior to start work witness personally or verify that there it is not present any hazardous energy, testing all lock and tags out following the normal start up procedures. After completion of work and before restoring equipment to service the following steps must be performed by the Maintenance Manager and the employees in charge of work:
- If more than one worker or company is involved in the works each one must place is own LOTO device.
Restoring the Power
After completion of work and before restoring equipment to service the following steps must be performed by the Maintenance Manager and the employees in charge of work.
Procedures for restoring the services are:
- Remove all tools and non-essential items
- Confirm that all equipment components are operationally intact, including guards and safety devices
- Repair or replace defective guards before removing lockouts
- Make a visual check before restoring energy to ensure that everyone is physically clear of the equipment
LOTO Devices
Common LOTO devices used by maintenance personnel are keys, padlocks, hasps (hardware device that mechanically joins objects together) and warning tags, uniquely identifiable to a specific worker. In the market is possible to find complete kits with LOTO devices.
LOTO devices must be:
- Durable for the environment in which they are used
- Sturdy enough to minimize accidental removal
- Distinctive, easily recognizable and clearly visible
- Standardized on color, shape, size, type or format
- Able to indicate which are the worker(s) authorizing or applying them
Warning tags must be made of non-conducting material.
As referred, above if will be performed for more than one employee each of them must have his own device, and the equipment will multiple LOTO devices.
In those situations each key must be placed into a group lock device, such as a box, locked and tagged by the Maintenance Manager or similar responsible, so only after worker has finished his job the equipment can be unlocked and untagged.
- Related Post: Power Transformers Maintenance, Diagnostic & Monitoring
Permit to Work (PTW) & Work Assignment
Definition of PTW
Permit to Work is a document procedure issued by the company that authorizes employees to perform a specific work under certain conditions and within a preset period of time.
In most countries, regulations and laws of Work Health and Safety and their respective authorities impose this procedure for works in areas with specific hazardous. Without this document no work can be carried out.
We refer as examples HSE (Health and Safety Executive) in the UK and OSHA in the USA.
The PTW must identify the work, the location, the risks, the safety measures, the working methods, the personnel who is able to perform the work and the PPE that should be used.
PTW requires written declarations from the person in charge, authorizing the work and from the originator that the work is ready and the equipment or installation is ready for normal use.
PTW must be completed, signed and posted at the work site by the person in charge or the supervisor.
Objectives of PTW
PTW must be understood not only as a written document that allows work to be carried out, but as a system that is an important part of the quality policy of the company.
PTW must identify clearly who can authorize a work to be performed, who as the responsibility to define the safety measures, the instructions for the use of the document and the monitoring of the system.
The main objectives of PTW are:
- To ensure that the responsible for the installation where works will be done is aware of that fact
- To ensure that the work was properly authorized
- To ensure that workers are aware of the exact work to be performed, as well as its nature and extension
- To identify the possible hazardous
- To define the safety measures to be put in place
- To provide continuous control of the safety measures implemented and to ensure that the control was done by appropriate personnel
- To provide that interactions with other activities were foreseen and procedures for that situations has been implemented
- To provide feedback that can ensure that any part of the installation affected by the work is suitable for reuse
Principles OF PTW
When a PTW system is implemented management and other persons in charge must ensure that:
- Monitoring and revising of PTW is established and maintained
- Personnel as attended to training courses and that a training program is maintained
- Personnel are competent to use the PTW and the work
- Planning of PTW as well as the issue and feedback is coordinated
- If shifts are required to perform the work the information will be properly transmitted to one shift to the other
When a PTW system is produced there are some facts that must be considered:
- Human factors (stress, personal problems, fatigue, demotivation, etc.)
- Quality of personnel
- Management of PTW system
- Types of PTW required
- Contents of PTW
- Lack on identifying a hazard before and during work
- Failure to comply with PTW within hazardous environments
- Communication failure
It is therefore possible to summarize a PTW with the following principles:
- Detailed description of the work to be performed
- Justification for the work
- Choice of the personnel
- PPE to be used
- Results of shock and flash hazard analysis
- Definition of safety measures
- Guarantee that safety measures have been implemented
- Signature of approval by management
- Evidence of completion of job briefing
Related Post: Overhead Lines Protection – Faults & Protection Devices
Although a PTW exists failures can occur when:
- Wrong type PTW used
- Wrong information about work required on the PTW
- Failure to recognize the hazards where work is carried out
- Introduction of ignition source in controlled flameproof area and not foreseen or allowed at PTW
- Unauthorized personnel performing work
- Insufficient monitoring of PTW
Work Assignment
Associated to PTW it must be considered the work assignment.
This designation covers a set of procedures and operations to isolate, block, verify the lack of voltage, connect to the earth and delimit the equipment or part of the installation where the work will be done.
These procedures have the objective to ensure that the equipment or the part of the installation was disconnect from power, that the safety measures were implemented, the working area was delimited and that reenergizing only will be done after the completion of works and that the area is totally clear. For that purpose specific forms must be used.
Working Area
Areas were a PTW is required must be delimited and warning signs shall be placed.
Grounds & Personal Protective Grounds
All metallic structures, like towers, cable trays and enclosures of switchboards, including fences, gates and other metal doors, must be earthed & grounded and connected to the earth grid of the installation.
During the job a temporary ground of installation may be required and portable cables must be used for that purpose.
- Related Post: Overhead Lines Protection – Faults & Protection Devices


 Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits?
Why Does an Electric Tester Not Work in DC Circuits? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature?
What are the Cuts on the Rotor of Motor’s Armature? Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5?
Why Do Wind Turbines Have 3 Blades Instead of 2 or 5? Difference between Voltage Source Inverter & Current Source Inverter
Difference between Voltage Source Inverter & Current Source Inverter Difference Between Voltage Stabilizer and Voltage Regulator (AVR)
Difference Between Voltage Stabilizer and Voltage Regulator (AVR)