Three Phase Delta Connection: Line, Phase Current, Voltages & Power in Δ Configuration
What is Delta Connection (Δ)?
Delta or Mesh Connection (Δ) System is also known as Three Phase Three Wire System (3-Phase 3 Wire) and it is the most preferred system for AC power transmission while for distribution, Star connection is generally used.
In Delta (also denoted by Δ) system of interconnection, the starting ends of the three phases or coils are connected to the finishing ends of the coil. Or the starting end of the first coil is connected to the finishing end of the second coil and so on (for all three coils) and it looks like a closed mesh or circuit as shown in fig (1).
In more clear words, all three coils are connected in series to form a close mesh or circuit. Three wires are taken out from three junctions and the all outgoing currents from junction assumed to be positive.
In Delta connection, the three windings interconnection looks like a short circuit, but this is not true, if the system is balanced, then the value of the algebraic sum of all voltages around the mesh is zero in Delta connection.
When a terminal is open in Δ, then there is no chance of flowing currents with basic frequency around the closed mesh.
Also Read:
- Star Connection (Y): Three Phase Power, Voltage & Current Values
- Difference between Star (Y) and Delta (Δ) Connections
Good to Remember: In Delta configuration, at any instant, the EMF value of one phase is equal to the resultant of the other two phases EMF values but in the opposite direction.

Voltage, Current and Power Values in Delta Connection (Δ)
Now we will find the values of Line current, Line Voltage, Phase Current, Phase Voltages and Power in three phase Delta AC system.
Line Voltages (VL) and Phase Voltages (VPh) in Delta Connection
It is seen in fig 2 that there is only one phase winding between two terminals (i.e. there is one phase winding between two wires). Therefore, in Delta Connection, the voltage between (any pair of) two lines is equal to the phase voltage of the phase winding which is connected between two lines.
Since the phase sequence is R → Y → B, therefore, the direction of voltage from R phase towards Y phase is positive (+), and the voltage of R phase is leading by 120°from Y phase voltage. Likewise, the voltage of Y phase is leading by 120° from the phase voltage of B and its direction is positive from Y towards B.
If the line voltage between;
- Line 1 and Line 2 = VRY
- Line 2 and Line 3 = VYB
- Line 3 and Line 1 = VBR
Then, we see that VRY leads VYB by 120° and VYB leads VBR by 120°.
Let’s suppose,
VRY = VYB = VBR = VL …………… (Line Voltage)
Then
VL = VPH
I.e. in Delta connection, the Line Voltage is equal to the Phase Voltage.
- Also read : Three Phase Current Values in a 3-Phase System
Line Currents (IL) and Phase Currents (IPh) in Delta Connection
It will be noted from the below (fig-2) that the total current of each Line is equal to the vector difference between two phase currents in Delta connection flowing through that line. i.e.;
- Current in Line 1= I1 = IR – IB
- Current in Line 2 =I2 = IY – IR
- Current in Line 3 =I3 = IB – IY
{Vector Difference}
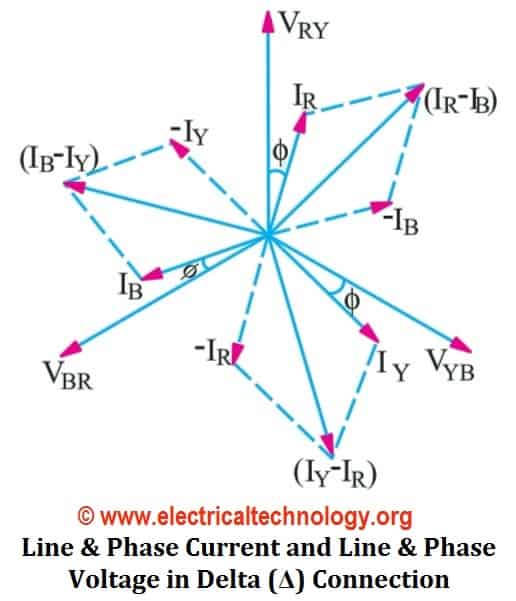
The current of Line 1 can be found by determining the vector difference between IR and IB and we can do that by increasing the IB Vector in reverse, so that, IR and IB makes a parallelogram. The diagonal of that parallelogram shows the vector difference of IR and IB which is equal to current in Line 1= I1. Moreover, by reversing the vector of IB, it may indicate as (-IB), therefore, the angle between IR and -IB (IB, when reversed = -IB) is 60°. If,
IR = IY = IB = IPH …. The phase currents
Then;
The current flowing in Line 1 would be;
IL or I1 = 2 x IPH x Cos (60°/2)
= 2 x IPH x Cos 30°
= 2 x IPH x (√3/2) …… Since Cos 30° = √3/2
IL= √3 IPH
i.e. In Delta Connection, The Line current is √3 times of Phase Current.
Similarly, we can find the reaming two Line currents as same as above. i.e.,
I2 = IY – IR … Vector Difference = √3 IPH
I3 = IB – IY … Vector difference = √3 IPH
As, all the Line current are equal in magnitude i.e.
I1 = I2 = I3 = IL
Hence
IL = √3 IPH
It is seen from the fig above that;
- The Line Currents are 120° apart from each other
- Line currents are lagging by 30° from their corresponding Phase Currents
- The angle Ф between line currents and respective line voltages is (30°+Ф), i.e. each Line current is lagging by (30°+Ф) from the corresponding line voltage.
Related Post: Star and Delta Connected Lighting Loads
Power in Delta Connection
We know that the power of each phase;
Power / Phase = VPH x IPH x CosФ
And the total power of three phases;
Total Power = P = 3 x VPH x IPH x CosФ ….. (1)
We know that the values of Phase Current and Phase Voltage in Delta Connection;
IPH = IL /√3 ….. (From IL = √3 IPH)
VPH = VL
Putting these values in power eq……. (1)
P = 3 x VL x ( IL/√3) x CosФ …… (IPH = IL / /√3)
P = √3 x√3 x VL x ( IL/√3) x CosФ …{ 3 = √3x√3 }
P = √3 x VLx IL x CosФ …
Hence proved;
Power in Delta Connection,
P = 3 x VPH x IPH x CosФ …. or
P = √3 x VL x IL x CosФ
Where Cos Φ = Power factor = the phase angle between Phase Voltage and Phase Current (not between Line current and line voltage).
The same is explained in 3-Phase Circuit MCQs with explanatory Answer (MCQs No.1)
Good to Remember:
In both Star and Delta Connections, The total power on balanced load is same.
I.e. total power in a Three Phase System = P = √3 x VL x IL x CosФ
Good to know:
Balanced System is a system where:
- All three phase voltages are equal in magnitude
- All phase voltages are in phase by each other i.e. 360°/3 = 120°
- All three phase Currents are equal in magnitude
- All phase Currents are in phase by each other i.e. 360°/3 = 120°
- A three phase balanced load is a system in which the load connected across three phases are identical.
Also Read :
- Introduction to Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Connections
- Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Connection of Batteries
- Three Phase Motor Connection STAR/DELTA Without Timer. Power & Control Diagrams
- Star Delta 3-phase Motor Automatic starter with Timer
 Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Brighter in a Parallel Circuit?
Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Brighter in a Parallel Circuit? Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Dimmer in a Series Circuit?
Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Dimmer in a Series Circuit? 3-Phase Automatic Changeover (ATS) using Contactors and Timer
3-Phase Automatic Changeover (ATS) using Contactors and Timer How to Run a Three-Phase Motor on Single-Phase Supply Using VFD?
How to Run a Three-Phase Motor on Single-Phase Supply Using VFD? Losses in a Induction Motor – Power Stages in Asynchronous Motor
Losses in a Induction Motor – Power Stages in Asynchronous Motor Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer
Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer